science · 05 February 1861 · 163 years ago
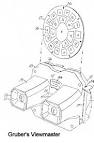 In 1861, a stereoscope design that may be regarded as the first U.S. precursor to the peep show machine was patented by Samuel D. Goodale of Cincinnati (No. 31,310). Stereoscopic pictures were fastened by one edge to an axis in such a way that they stood out like spokes. As it was turned by hand, different scenes appeared to be viewed, each one held steady against a detent projecting from the interior of the case before the lens, until flipped away as the shaft rotated to almost instantly reveal the next scene. The equipment was easily portable, and the lens holder, reflector and diffusing glass could be compactly folded within the case. The case was made in two sections that could be opened to view and replace the scenes.
In 1861, a stereoscope design that may be regarded as the first U.S. precursor to the peep show machine was patented by Samuel D. Goodale of Cincinnati (No. 31,310). Stereoscopic pictures were fastened by one edge to an axis in such a way that they stood out like spokes. As it was turned by hand, different scenes appeared to be viewed, each one held steady against a detent projecting from the interior of the case before the lens, until flipped away as the shaft rotated to almost instantly reveal the next scene. The equipment was easily portable, and the lens holder, reflector and diffusing glass could be compactly folded within the case. The case was made in two sections that could be opened to view and replace the scenes.