| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
01 Feb 1528

Diego García de Moguer |
Diego García de Moguer (exploration) Diego García de Moguer explores the Sierra de la Plata along the Río de la Plata and begins to travel up the Paraná River. |
|
01 Feb 1556
Great Comet of 1556 |
Great Comet of 1556 (astronomy and earth ) Great Comet of 1556 becomes visible in Europe. |
|
01 Feb 1655

Giovanni Baptista Ferrari |
death Giovanni Baptista Ferrari Giovanni Baptista Ferrari, Italian Jesuit botanist and linguist (born 1584) |
|
01 Feb 1698

Colin Maclaurin |
birth Colin Maclaurin Colin Maclaurin, Scottish mathematician (died 1746) |
|
01 Feb 1734

John Floyer |
death John Floyer John Floyer, English physician (born 1649) |
|
01 Feb 1738

Great Plague of 1738 |
Great Plague of 1738 (medicine) Great Plague of 1738, an outbreak of bubonic plague, begins to spread from Banat across central Europe. |
|
01 Feb 1761

Christiaan Hendrik Persoon |
birth Christiaan Hendrik Persoon Christiaan Hendrik Persoon (died 1836), South African-born Pomeranian/Dutch mycologist. |
|
01 Feb 1788

Isaac Briggs |
Isaac Briggs (technology) Isaac Briggs and William Longstreet patent a steamboat in the United States. |
|
01 Feb 1792

Johann Friedrich Dieffenbach |
birth Johann Friedrich Dieffenbach Johann Friedrich Dieffenbach, German plastic surgeon (died 1847) |
|
01 Feb 1826

Nikolai Lobachevsky |
Nikolai Lobachevsky (mathematics) Nikolai Lobachevsky first presents his system of non-Euclidean hyperbolic geometry. |
|
01 Feb 1837

Edward Donovan |
death Edward Donovan Edward Donovan (born 1768), Anglo-Irish naturalist. |
|
01 Feb 1841

H. Fox Talbot |
H. Fox Talbot (technology) H. Fox Talbot obtains a patent in the United Kingdom for the calotype process in photography. |
|
01 Feb 1844

G. Stanley Hall |
birth G. Stanley Hall G. Stanley Hall (died 1924), American psychologist. |
|
01 Feb 1851

Foucault pendulum |
Foucault pendulum (astronomy) First public exhibition of a Foucault pendulum, at the Meridian of the Paris Observatory, demonstrating the Earth's rotation. A few weeks later Foucault installs one at the Panthéon. |
|
01 Feb 1865

Henry Luke Bolley |
birth Henry Luke Bolley Henry Luke Bolley (died 1956), American plant pathologist. |
|
01 Feb 1873

Matthew Fontaine Maury |
death Matthew Fontaine Maury Matthew Fontaine Maury (born 1806), oceanographer |
|
01 Feb 1874

Challenger expedition |
Challenger expedition (exploration) the Challenger expedition provides geological evidence for the existence of the continent of Antarctica |
|
01 Feb 1880

Thomas Edison |
Thomas Edison (publications) The journal Science is first published in the United States with financial backing from Thomas Edison. |
|
01 Feb 1903

George Gabriel Stokes |
death George Gabriel Stokes George Gabriel Stokes (born 1819), mathematician and physicist. |
|
01 Feb 1905

Emilio G. Segrè |
birth Emilio G. Segrè Emilio G. Segrè (died 1989), physicist, Nobel laureate |
|
01 Feb 1913
United States |
United States (chemistry) Daniel J. O'Conor and Herbert A. Faber file for a United States patent on the composite plastic laminate Formica. |
|
01 Feb 1923

Maudsley Hospital |
Maudsley Hospital (medicine) The Maudsley Hospital, established jointly by the London County Council and Henry Maudsley, admits its first psychiatric patients. |
|
01 Feb 1924

John Logie Baird |
John Logie Baird (technology) John Logie Baird sends rudimentary television pictures over a short distance. |
|
01 Feb 1926

Hidetsugu Yagi |
Hidetsugu Yagi (technology) Hidetsugu Yagi and Shintaro Uda publish the first description of the Yagi-Uda antenna. |
|
01 Feb 1926

David Medved |
birth David Medved David Medved (died 2009), American physicist. |
|
01 Feb 1944

Oswald T. Avery |
Oswald T. Avery (biology) Oswald T. Avery and colleagues publish the Avery–MacLeod–McCarty experiment showing that a DNA molecule can carry an inheritable trait to a living organism. This is important because many biologists thought that proteins were the hereditary material and nucleic acids too simple chemically to serve as genetic storage molecules. |
|
01 Feb 1944

Lars Onsager |
Lars Onsager (chemistry) Lars Onsager publishes the exact solution to the two-dimensional Ising model. |
|
01 Feb 1951

Ferranti |
Ferranti (computer science) Ferranti deliver their first Mark 1 computer to the University of Manchester (UK). It is the world's first commercially available general-purpose electronic computer. |
|
01 Feb 1955

Harold Hopkins |
Harold Hopkins (physics) Harold Hopkins and Narinder Singh Kapany publish a key paper in the development of optical fiber technology. |
|
01 Feb 1972

calculator |
calculator (technology) The first scientific hand-held calculator (labeled Hewlett-Packard, later designated the HP-35) is introduced, at a price of $795.00. |
|
01 Feb 1990

Adobe Photoshop |
Adobe Photoshop (computer science) Adobe Photoshop 1.0 graphics software, devised by Thomas Knoll, is released. |
|
01 Feb 1993
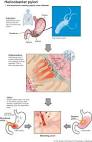
discovery that peptic ulcer disease is caused by H. pylori |
discovery that peptic ulcer disease is caused by H. pylori (medicine) The New England Journal of Medicine publishes findings demonstrating that patients with peptic ulcers can be successfully treated with antibiotics, lending strong support to the discovery that peptic ulcer disease is caused by H. pylori. |
|
01 Feb 1995

Project Phoenix |
Project Phoenix (astronomy and space ) Project Phoenix begins looking for extraterrestrial transmissions using the Parkes Observatory radio telescope in New South Wales, Australia, the largest telescope in the Southern Hemisphere. |
|
01 Feb 2001

Human Genome Project |
Human Genome Project (biology) The publicly funded Human Genome Project, led by Francis Collins and the privately funded Celera effort, led by Craig Venter simultaneously publish their decoding of the human genome (in Nature and Science, respectively). |
|
01 Feb 2003

Space Shuttle Columbia |
Space Shuttle Columbia (space exploration) Space Shuttle Columbia disintegrates over Texas upon reentry killing all seven astronauts on board. |