| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
01 Mar 1547

Rudolph Goclenius |
birth Rudolph Goclenius Rudolph Goclenius, German philosopher and polymath (died 1628) |
|
01 Mar 1559

Juan Fernández Ladrillero |
Juan Fernández Ladrillero (exploration) Juan Fernández Ladrillero completes a double transit of the Straits of Magellan from the west. |
|
01 Mar 1588

Jacques Daléchamps |
death Jacques Daléchamps Jacques Daléchamps, French physician and botanist (born 1513) |
|
01 Mar 1592

Yi Sun-sin |
Yi Sun-sin (technology) Korean Admiral Yi Sun-sin perfects the armed turtle ship. |
|
01 Mar 1606

Duke of York |
Duke of York (exploration) The Duke of York's ship Duyfken, under Captain Willem Janszoon, explores the western coast of Cape York Peninsula. |
|
01 Mar 1610

John Pell |
birth John Pell John Pell, English mathematician (died 1685) |
|
01 Mar 1626

Jean-Baptiste de La Quintinie |
birth Jean-Baptiste de La Quintinie Jean-Baptiste de La Quintinie, French horticulturalist (died 1688) |
|
01 Mar 1641

Menno van Coehoorn |
birth Menno van Coehoorn Menno van Coehoorn, Dutch military engineer (died 1704) |
|
01 Mar 1672

Peter Blondeau |
death Peter Blondeau Peter Blondeau, French-born pioneer of mechanised minting of coin |
|
01 Mar 1693

James Bradley |
birth James Bradley James Bradley, Astronomer Royal (died 1762) |
|
01 Mar 1697

Francesco Redi |
death Francesco Redi Francesco Redi, Italian physician and biologist (born 1626) |
|
01 Mar 1714

Roger Cotes |
Roger Cotes (mathematics) Roger Cotes publishes Logometrica in the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society. He provides the first proof of what is now known as Euler's formula and constructs the logarithmic spiral. |
|
01 Mar 1715

William Dampier |
death William Dampier William Dampier, English explorer, hydrographic surveyor and triple circumnavigator (born 1651) |
|
01 Mar 1777
Third voyage of James Cook |
Third voyage of James Cook (exploration) Third voyage of James Cook: English explorer Captain Cook discovers Mangaia and Atiu in the Cook Islands. |
|
01 Mar 1785

James Hutton |
James Hutton (earth sciences) July – James Hutton's Theory of the Earth is first presented, at the Royal Society of Edinburgh. |
|
01 Mar 1791

National Constituent Assembly |
National Constituent Assembly (metrology) In France, the National Constituent Assembly accepts the recommendation of its Commission of Weights and Measures that the nation should adopt the metric system. |
|
01 Mar 1799

Pneumatic Institution |
Pneumatic Institution (medicine) The Pneumatic Institution for research into the medical implications of newly discovered gases is established by Thomas Beddoes in Bristol. |
|
01 Mar 1813

Humphry Davy |
Humphry Davy (institutions) Sir Humphry Davy employs Michael Faraday as "chemical assistant" at the Royal Institution of Great Britain in London. |
|
01 Mar 1817
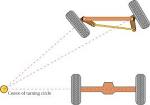
Ackermann steering geometry |
Ackermann steering geometry (technology) Ackermann steering geometry invented by Georg Lankensperger. |
|
01 Mar 1829

Thomas Earnshaw |
death Thomas Earnshaw Thomas Earnshaw (born 1749), watchmaker. |
|
01 Mar 1834

William Whewell |
William Whewell William Whewell (anonymously) first publishes the term scientist in the Quarterly Review, but notes it as "not generally palatable". |
|
01 Mar 1837

Charles Darwin |
Charles Darwin (biology) July – Charles Darwin begins privately to develop his theory of transmutation of species. |
|
01 Mar 1850

Benjamin Guy Babington |
Benjamin Guy Babington (medicine) Dr Benjamin Guy Babington founds the London Epidemiological Society. |
|
01 Mar 1851

English |
English (chemistry) English sculptor Frederick Scott Archer makes public the wet plate collodion photographic process. |
|
01 Mar 1855

Mary Seacole |
Mary Seacole (medicine) Mary Seacole opens the British Hotel at Balaklava, a nursing and convalescent establishment for Crimean War officers. |
|
01 Mar 1856

William Perkin |
William Perkin (chemistry) William Perkin first discovers an aniline dye, mauveine. |
|
01 Mar 1862

Peter Barlow |
death Peter Barlow Peter Barlow (born 1776), English mathematician |
|
01 Mar 1868

geologist |
geologist (paleontology) French geologist Louis Lartet discovers the first identified skeletons of Cro-Magnon, the first anatomically modern humans (early Homo sapiens sapiens), at Abri de Crô-Magnon, a rock shelter at Les Eyzies, Dordogne, France. |
|
01 Mar 1872

Yellowstone National Park |
Yellowstone National Park (conservation) Yellowstone National Park is established in the United States, the world's first national park |
|
01 Mar 1878
phosphoric |
phosphoric (technology) The 'basic' process, enabling the use of phosphoric iron ore in steelmaking, developed at Blaenavon Ironworks by Percy Gilchrist and Sidney Gilchrist Thomas, is first made public. |
|
01 Mar 1881

Cunard Line |
Cunard Line (technology) The Cunard Line's SS Servia, the first steel transatlantic liner, is launched at J. & G. Thomson's yard at Clydebank in Scotland. |
|
01 Mar 1896

French |
French (physics) French physicist Henri Becquerel discovers the principle of radioactive decay when he exposes photographic plates to uranium. |
|
01 Mar 1903

David Bruce |
David Bruce (medicine) April – David Bruce identifies the parasitic Trypanosoma protist as the source of African trypanosomiasis ("sleeping sickness"). |
|
01 Mar 1911

Frederick Winslow Taylor |
Frederick Winslow Taylor (other s) May – A serialized version of Frederick Winslow Taylor's monograph, The Principles of Scientific Management appears in The American Magazine, boosting the efficiency movement. |
|
01 Mar 1911

Jacobus van 't Hoff |
death Jacobus van 't Hoff Jacobus van 't Hoff (born 1852), Dutch chemist. |
|
01 Mar 1912

Boris Chertok |
birth Boris Chertok Boris Chertok (died 2011), Russian rocket designer. |
|
01 Mar 1940

Frisch–Peierls memorandum |
Frisch–Peierls memorandum (physics) Frisch–Peierls memorandum: Otto Frisch and Rudolf Peierls, at this time working at the University of Birmingham in England, calculate that an atomic bomb could be produced using very much less enriched uranium than has previously been supposed, making it a practical proposition. |
|
01 Mar 1942

Isaac Asimov |
Isaac Asimov (technology) Isaac Asimov's Three Laws of Robotics are introduced in his short story "Runaround" published in Astounding Science-Fiction. |
|
01 Mar 1943

Colossus computer |
Colossus computer (computer science) December – Construction of British prototype Mark I Colossus computer, the world's first totally electronic programmable computing device, at the Post Office Research Station, Dollis Hill, to assist in cryptanalysis at Bletchley Park. |
|
01 Mar 1944

John R.F. Jeffreys |
death John R.F. Jeffreys John R.F. Jeffreys (born 1918), British mathematician and cryptanalysist. |
|
01 Mar 1950

Claude Shannon |
Claude Shannon (computer science) Publication of Claude Shannon's paper "Programming a Computer for Playing Chess", seminal in the development of computer chess and introducing the Shannon number. |
|
01 Mar 1952

British Psychological Society |
British Psychological Society (medicine) The British Psychological Society is founded. |
|
01 Mar 1954

hydrogen bomb |
hydrogen bomb (physics) United States carries out a hydrogen bomb test on Bikini Atoll in the Pacific Ocean. |
|
01 Mar 1955

Joseph Rotblat |
Joseph Rotblat (physics) Joseph Rotblat publishes his conclusions that contamination caused by nuclear fallout after the U.S. Castle Bravo hydrogen bomb test at Bikini Atoll is greater than officially stated. |
|
01 Mar 1956

Denham Harman |
Denham Harman (biology) Denham Harman proposes the free-radical theory of aging. |
|
01 Mar 1966

Venera 3 |
Venera 3 (astronomy and space ) Venera 3 Soviet space probe crashes on Venus becoming the first spacecraft to land on another planet's surface. |
|
01 Mar 1966

Fritz Houtermans |
death Fritz Houtermans Fritz Houtermans (born 1903), Prussian-born Dutch physicist. |
|
01 Mar 1976

Peter Chen |
Peter Chen (computer science) Peter Chen's key paper on the entity–relationship model is published, having first been presented at a conference in September 1975. |
|
01 Mar 1979

Philips |
Philips (technology) Philips publicly demonstrate a prototype of an optical digital audio disc at a press conference in Eindhoven, Netherlands. |
|
01 Mar 1985

Louis de Branges de Bourcia |
Louis de Branges de Bourcia (mathematics) Louis de Branges de Bourcia publishes proof of de Branges's theorem. |
|
01 Mar 1985

Joshua Silver |
Joshua Silver (medicine) May – Joshua Silver develops an adjustable corrective lens. |
|
01 Mar 1991

Edwin H. Land |
death Edwin H. Land Edwin H. Land (b. 1909), American inventor of the Land Camera. |
|
01 Mar 1996

Cochrane Library |
Cochrane Library (medicine) The Cochrane Library launched. |
|
01 Mar 2003

digital camera |
digital camera (technology) The world's first digital camera with an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) display is released by Kodak. |