| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Apr 1006

Supernova |
Supernova In 1006, Chinese and Arabic astronomers noted a supernova. The speed of the still-expanding shock wave was measured nearly a millenium later.* This is was history's brightest "new star" ever recorded, at first seen to be brighter than the planet Venus. It occurred in our Milky Way galaxy, appearing in the southern constellation Lupus, near the star Beta Lupi. It was also recorded by observers in Switzerland, Italy, Japan, Egypt and Iraq. From the careful descriptions of the Chinese astronomers of how the light varied, that it was of apparently yellow color and visible for over a year, it is possible that the supernova reached a magnitude of up to -9. Modern measurements of the speed of the shock wave have been used to estimate its distance. |
|
30 Apr 1665

Pepys records Great Plague |
Pepys records Great Plague In 1665, Samuel Pepys made his first diary reference to the Great Plague in London."Great fears of the sicknesses here in the City, it being said that two or three houses are already shut up. God preserve us all." The entries in his diary continue throughout the year, documenting the terrible conditions in the city as many thousands died, until Winter's freezing cold reduced the number of fleas that spread the disease. The symptoms of the plague begin like those of a bad cold. A high fever follows, with vomiting and painful black swellings, called buboes appearing in the groin and under the armpits. His diaries over the period Jan 1660 to May 1669. He also wrote about the Great Fire of London in 1666 |
|
30 Apr 1683

Boston Philosophical Society |
Boston Philosophical Society In 1683, the Boston Philosophical Society held its first meeting.* Rev. Increase Mather, stimulated by a recent comet sighting, and seeking to discuss how God intervenes in the natural order of things, had met earlier in the month with Samuel Willard and a few others to plan the group. Mather's idea was to model their meetings on the Royal Philosophical Society, established in London about 20 years earlier. Each last Monday of most of the following months, the members met and presented papers to emulate the transactions of the London society. However, the few local intellectuals didn't sustain interest in the society beyond about three years. Mather wrote Kometographia, or, A Discourse concerning Comets (1683). |
|
30 Apr 1696

Robert Plot |
death Robert Plot Robert Plot, English naturalist and chemist (born 1640) |
|
30 Apr 1723

Mathurin Jacques Brisson |
birth Mathurin Jacques Brisson Mathurin Jacques Brisson, French zoologist (died 1806) |
|
30 Apr 1777

Carl Friedrich Gauss |
birth Carl Friedrich Gauss Born 30 Apr 1777; died 23 Feb 1855 at age 77. Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss was a German mathematician who transformed nearly all areas of mathematics, for which his talent showed from a very early age. For his contributions to theory in magnetism and electricity, a unit of magnetic field has been named the gauss. He devised the method of least squares in statistics, and his Gaussian error curve remains well-known. He anticipated the SI system in his proposal that physical units should be based on a few absolute units such as length, mass and time. In astronomy, he calculated the orbits of the small planets Ceres and Pallas by a new method. He invented the heliotrope for trigonometric determination of the Earth's shape. With Wilhelm Weber, he developed an electromagnetic telegraph and two magnetometers. |
|
30 Apr 1792

John Montagu |
death John Montagu Died 30 Apr 1792 at age 73 (born 3 Nov 1718). (4th Earl of Sandwich) British politician, inventor and explorer, for whom the sandwich is named, which is said he invented in 1762. A story was offered in Grosley's Tour to London that Sandwich often spent excessive time gambling and he didn't want to get up from the gambling table, so he told his servants to bring him meat between two slices of bread. Although this story is often quoted, it seems without support. Rodger, Sandwich's biographer, describes the original form using salt beef, as more likely to have been invented to eat while working at his desk, where he spent long hours. Captain Cook named the Sandwich Islands (Hawaii) for him. As first lord of the admiralty (1771-82) during the American Revolution, he was held responsible for the navy's disastrous unpreparedness for war. |
|
30 Apr 1795

Jean-Jacques Barthélemy |
death Jean-Jacques Barthélemy Died 30 Apr 1795 at age 79 (born 20 Jan 1716). French archaeologist and author. During three years spent in Italy from 1755, he gained a background assisting in archaeological research. Later in his life he wrote Voyage du jeune Anacharsis en Grèce dans le milieu du IVe siècle (Voyage of Young Anacharsis in Greece in the mid-14th century; 1789). The central character in this four-volume novel was a young Scythian in the age of Plato travelling through ancient Greece, meeting famous people, with descriptions of its cities, buildings, institutions, and manners. It was one of the most widely read books in 19th-century France. As an author, his intention was to convey some knowledge of Greek civilization in an interesting form, rather than a work of strict scholarship. |
|
30 Apr 1796
Patent pills |
Patent pills In 1796, the first U.S. patent for a pill of any kind was issued to Samuel Lee, Jr., of Connecticut, for a "Composition of bilious pills" which he renewed on 24 May 1810 and marketed as "Lee's Windham Pills." These pills were the subject of patents and renewals by both him and his son Samuel H.P. Lee (1772-1863), and were highly popular for a long period.* "Lee's New-London Bilious Pills" (named after New-London, Connecticut) were patented by his son on 26 Jun 1799 and 8 Feb 1814. An advertisement of 1803 for "Doctor Lee's Patent New-London Bilious Pills" described them as "Interesting to all sea-faring People" and promised to cure a variety of ills, including "foul stomachs, where pukes are indicated." |
|
30 Apr 1829

Ferdinand von Hochstetter |
birth Ferdinand von Hochstetter Ferdinand von Hochstetter (died 1884), geologist. |
|
30 Apr 1834

John Lubbock (Lord Avebury) |
birth John Lubbock (Lord Avebury) Born 30 Apr 1834; died 28 May 1913 at age 79. English banker, politician, naturalist and archaeologist who coined the terms Neolithic and Paleolithic. Like his father, astronomer Sir John William Lubbock, his scientific work was an avocation. Lubbock was a friend and advocate of Charles Darwin. He discovered the first fossil remains of musk-ox in England (1855), and undertook archaeological work identifying prehistoric cultures. As a naturalist, he studied insect vision and colour sense. He published a number of books on natural history and primitive man. In 1870, he became a member of Parliament. The legislation he initiated included the Bank Holidays Act (1871) and the Ancient Monuments Act (1882) and the Shop Hours Act (1886). He became 1st Baron Avebury when he was made a peer in 1900. |
|
30 Apr 1834

John Lubbock |
birth John Lubbock John Lubbock (died 1913), naturalist and archaeologist. |
|
30 Apr 1857

Eugen Bleuler |
birth Eugen Bleuler Born 30 Apr 1857; died 15 Jul 1939 at age 82. Swiss psychiatrist who made notable contributions to the understanding of mental illness, and coined the term “schizophrenia” (1908) for the disorder previously named as dementia praecox by Emil Kraepelin. Bleuler realised the condition was neither a dementia, nor did it always occur in young people (praecox meaning early) and so gave the condition the name from the Greek for split (schizo) and mind (phrene). Contrary to the belief of the time, he held that schizophrenia was neither invariably incurable, nor would always progress to full dementia. He was one of the first psychiatrists to apply psychoanalytical methods in his research, and was an early proponent of the theories of Sigmund Freud. |
|
30 Apr 1865

Robert Fitzroy |
death Robert Fitzroy Died 30 Apr 1865 at age 59 (born 5 Jul 1805). English naval officer, hydrographer and meteorologist who commanded the voyage of HMS Beagle, aboard which Charles Darwin sailed around the world as the ship's naturalist. That voyage provided Darwin with much of the material on which he based his theory of evolution. Fitzroy retired from active duty in 1850 and from 1854 devoted himself to meteorology. He devised a storm warning system that was the prototype of the daily weather forecast, invented a barometer, and published The Weather Book (1863). His death was by suicide, during a bout of depression. |
|
30 Apr 1873

William Starling Sullivant |
death William Starling Sullivant Died 30 Apr 1873 at age 70 (born 15 Jan 1803). American botanist who was the foremost U.S. bryologist in his time. Sullivant graduated in the same year his father died, and took over his surveying business. He began studying and the plant life of central Ohio and published A Catalogue of Plants, Native and Naturalized, in the Vicinity of Columbus, Ohio (1840). When he expanded his interest to the bryophytes (mosses and liverworts), he cataloged not only specimens from the U.S., but also Central America, South America, and various Pacific Ocean islands. He was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 1872. The moss Sullivantia Ohioensis was named in his honour. |
|
30 Apr 1878

Pasteur's germ theory |
Pasteur's germ theory In 1878, Louis Pasteur lectured at the French Academy of Science in support of his germ theory of disease, in which he held that many diseases were caused by tiny organisms. Since he still met with opposition from some scientists, he called their contrary opinions “fatal to medical progress.” Pasteur also described ways to prevent infection, and provided the skeptics with an experiment with which to prove the theory to themselves. |
|
30 Apr 1883

Electric company |
Electric company In 1883, a company that would build the first U.S. three-wire central station for incandescent lighting - the Edison Electric Illuminating Co. was incorporated. The plant was a simple wooden structure erected in Sunbury, Pennsylvania. The station began service on 4 Jul 1883. An Armington & Sims steam engine drove two 110-volt direct-current generators. The electricity was delivered by overhead wires. Thomas Edison patented his three-wire system on 20 Nov 1882 to supercede the distribution system used at his first commercial central generating station in New York (4 Sep 1882) because it gave savings of over 60 per cent in copper used in conductors. This meant a smaller investment and enabled building generating plants in smaller communities. |
|
30 Apr 1891

Abram Lyle |
death Abram Lyle Died 30 Apr 1891 at age 70 (born 14 Dec 1820). Scottish shipowner and sugar refiner, known for Lyle's Golden Syrup. Lyle began in his father's cooperage business, but later extended into shipping with John Kerr. Their fleet grew from 161 tons in 1849 to 22,000 tons in 1870. As a cooper, Lyle supplied casks to ship Caribbean sugar and molasses. This led them to join with other partners to operate the Glebe Sugar Refinery (1865). Lyle moved the shipping operation in 1881 to wharves in East London where he built a refinery specialising in the production of golden syrup. When the price of raw sugar collapsed in 1882, Lyle suffered huge losses forcing reduction of his business holdings, yet his golden syrup product eventually thrived. Sugar refiner Henry Tate amalgamated with Lyle in 1921. |
|
30 Apr 1891

Joseph Leidy |
death Joseph Leidy Died 30 Apr 1891 at age 67 (born 9 Sep 1823). American zoologist who made significant contributions in a remarkably wide range of earth and natural science disciplines, including comparative anatomy, parasitology, and paleontology. As the Father of American Vertibrate Paleontology, he described not only the first relatively complete dinosaur skeleton, but the diversity of fossil finds in the American West. His knowledge of comparative anatomy enabled him to make sense of even fragmentary fossil remains. He was also a competant microscopist, scientific illustrator, and published papers in human biology and medicine. His microscopic examination of parasite cysts in cooked ham and microorganisms in housefly mouthparts enabled him to improve public heath. |
|
30 Apr 1893

Roy Chadwick |
birth Roy Chadwick Born 30 Apr 1893; died 23 Aug 1947 at age 54. British aeronautical engineer, who during WW I, designed the Avro 504 trainer. His other designs include the Baby (a truly light aircraft), Avian, and the Anson (used for RAF coastal reconnaissance). In WW II, he developed the Manchester and the famous Lancaster heavy bombers. Later, he worked jet-propelled planes, the Tudor and Ashton. He died in a test flight crash of the Tudor II prototype, near Woodford airfield, Manchester. |
|
30 Apr 1894

Iceberg |
Iceberg In 1894, an Antarctic iceberg fragment was sighted at a latitude 26.50 degrees south, comparable to Rio de Janeiro. Reported by the ship Dochra, this remains the nearest to the equator that an Antarctic iceberg has been seen. Sightings of large icebergs as far north as 42 degrees south were made from 15 vessels in 1893. The Falkland Islands Gazette warned that year of exceptional ice conditions with large icebergs in shipping lanes around Cape Horn and commented: "Ice in this latter position is absolutely unknown, and must be looked upon as a great danger." |
|
30 Apr 1897

Electron |
Electron In 1897, at the Royal Institution Friday Evening Discourse, Joseph John Thomson (1856-1940) first announced the existence of electrons (as they are now named). Thomson told his audience that earlier in the year, he had made a surprising discovery. He had found a particle of matter a thousand times smaller than the atom. He called it a corpuscle, meaning "small body." Although Thomson was director of the Cavendish Laboratory at the University of Cambridge, and one of the most respected scientists in Great Britain, the scientists present found the news hard to believe. They thought the atom was the smallest and indivisible part of matter that could exist. Nevertheless, the electron was the first elementary particle to be discovered. |
|
30 Apr 1904

George Robert Stibitz |
birth George Robert Stibitz Born 30 Apr 1904; died 31 Jan 1995 at age 90. U.S. mathematician who was regarded by many as the "father of the modern digital computer." While serving as a research mathematician at Bell Telephone Laboratories in New York City, Stibitz worked on relay switching equipment used in telephone networks. In 1937, Stibitz, a scientist at Bell Laboratories built a digital machine based on relays, flashlight bulbs, and metal strips cut from tin-cans. He called it the "Model K" because most of it was constructed on his kitchen table. It worked on the principle that if two relays were activated they caused a third relay to become active, where this third relay represented the sum of the operation. Also, in 1940, he gave a demonstration of the first remote operation of a computer. |
|
30 Apr 1916

Claude Elwood Shannon |
birth Claude Elwood Shannon Born 30 Apr 1916; died 27 Feb 2001 at age 84. American mathematician. |
|
30 Apr 1916

Claude Shannon |
birth Claude Shannon Claude Shannon (died 2001), American mathematician, "father of information theory". |
|
30 Apr 1921

Ralph A. Lewin |
birth Ralph A. Lewin Ralph A. Lewin (died 2008), Anglo-American biologist, "the father of green algae genetics". |
|
30 Apr 1934

William Henry Welch |
death William Henry Welch Died 30 Apr 1934 at age 84 (born 8 Apr 1850). American pathologist who played a major role in the introduction of modern medical practice to the U.S. As the first dean of the medical school at Johns Hopkins University (1893-98), Welch revolutionized American medicine by demanding of its students a rigorous study of physical sciences and an active involvement in clinical duties and laboratory work. His students included Walter Reed, James Carroll and Simon Flexner. As an original investigator, With Flexner, he demonstrated (1891-92) the pathological effects produced by diphtheria toxin. In 1892, he discovered Micrococcus albus and its relation to wound fever and of Clostridium welchii (Welch's bacillus), the causative agent of gas gangrene. |
|
30 Apr 1939

Cosmic rays generate electricity |
Cosmic rays generate electricity In 1939, cosmic rays entering a Geiger-Mueller counter produced electrical impulses used to control electrical power. This first ever such event, was used for the illumination ceremony of the 1939 New York World's Fair. The counter, at the Hayden Planetarium, New York City, switched on an electrical circuit wired to a display at the Lagoon of Nations where relays activated local battery circuits ringing bells and flashing lights to signal each capture of a cosmic ray. Albert Einstein as guest speaker explained cosmic rays. Sadly his accent and faulty amplification made his words incomprehensible to the crowd. Upon the tenth ray's signal, a huge light was to be turned on to illuminate the 600-ft Trylon triangular spire, but the power source failed. |
|
30 Apr 1939

Nylon |
Nylon (chemistry) Nylon fabric is first introduced to the general public at the New York World's Fair. |
|
30 Apr 1942

J.C. Arthur |
death J.C. Arthur Died 30 Apr 1942 at age 92 (born 11 Jan 1850). Joseph Charles Arthur was an American botanist who discovered basic facts about the parasitic fungi known as 'rusts.' He was the first head of the Department of Botany and Plant Pathology at Purdue University. The plant rusts form one of the largest natural groups of plant parasitic fungi. They are of great scientific interest because of their close evolutionary relationships with their host plants, their complex life cycles, and their numerous biological adaptations that permit them to thrive on all the continents (except Antarctica) under great extremes of environments. |
|
30 Apr 1945

David Randall-MacIver |
death David Randall-MacIver Died 30 Apr 1945 at age 71 (born 31 Oct 1873). English-American archaeologist and anthropologist who excaved in Egypt and Sudan. He began his career of excavation with Sir Flinders Petrie at Abydos, Egypt (1899-1901). After conducting excavations of the Great Zimbabwe ruins in Southern Rhodesia (now Zimbabwe), Randall-MacIver wrote Medieval Rhodesia (1906), in which he contended that the ruins were not built by an ancient and vanished white civilization as was currently believed but were of purely African 14th century origin (as confirmed by later archaeological study). Walls at these ruins stood as high as 32 feet over the surrounding savanna. From 1907 to 1911 Randall-MacIver led an expedition into Egypt and the Sudan. |
|
30 Apr 1947

Sir Almroth Wright |
death Sir Almroth Wright Died 30 Apr 1947 at age 85 (born 10 Aug 1861). Sir Almroth Edward Wright was an English bacteriologist who developed an immunization against typhoid fever that protected British soldiers in WW I, saving lives from infection. It was the result of his work beginning in 1892, while professor of pathology at the Army Medical School, using typhoid bacilli killed by heat. Tests on over 3,000 soldiers in India were followed by its successful use during the South African (Boer) War. He was noted for creating autogenous vaccines, prepared from the bacteria harboured by the patient. Wright also developed vaccines against enteric tuberculosis and pneumonia and contributed to the study of opsonins (blood enzymes that make bacteria more susceptible to phagocytosis by white cells.) |
|
30 Apr 1955
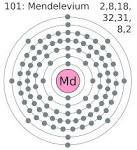
Mendelevium |
Mendelevium In 1955, the element 101, a new artificial element was announced. It was synthesized by bombardment of Es-253 with helium nuclei using the cyclotron at the Radiation Laboratory of the University of California by Albert Ghiorso, Bernard G. Harvey, G.R. Choppin and S.G. Thompson, research chemists, headed by the Nobel laureate Glenn T. Seaborg. Being radioactive, with a half-life of between a half hour to several hours, this transuranic element cannot exist in nature since it decays so rapidly into lighter elements. It was named mendelevium, named in honour of Dmitry Mendeleev, the Russian chemist who worked on the periodic classification of the elements. |
|
30 Apr 1955

Francis Muguet |
birth Francis Muguet Francis Muguet (died 2009), French chemist and advocate of open access to information. |
|
30 Apr 1960

Little brown bat |
Little brown bat In 1960, the oldest U.S. bat was identified as 24 years old, having been banded on 22 Jun 1937 in Mashpee, Massachusetts. The female little brown bat (Myotis lucifugus), the most abundant bat in the U.S., was found in a cave on Mount Aeolis, Vermont. The little brown bat has a wing span of 222-269 mm with glossy fur on its back and paler underside colours ranging from pale tan to dark brown. The species is found throughout forested areas of North America and Alaska, in tree or cliff cavities, caves, mines and the attics. They feed on a wide variety of insects. On 25 Aug 1999, a newspaper reported a 33-yr-old wild bat in Europe. On 20 Jun 2005, a journal received an article identifying a 41-yr-old bat in Siberia. |
|
30 Apr 1983

Joel H. Hildebrand |
death Joel H. Hildebrand Died 30 Apr 1983 at age 101 (born 16 Nov 1881). U.S. educator and chemist whose monograph Solubility (1924; later editions, Solubility of Non-Electrolytes) was the classic reference for almost a half century. The Hildebrand solubility parameter carries his name. Through his research on the chemistry of solutions, he helped to protect deep-sea divers from “bends.” He led the fight against a faculty “loyalty oath,” a non-Communist declaration, at University of California (1950). He had no sympathy with Communists, but he and other prominent members of the faculty felt that the oath, by being required of teachers alone, was discriminatory with regard to all university employees. Two years later, the California State Supreme Court decided unanimously in favour of the faculty. |
|
30 Apr 1993
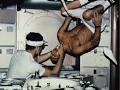
Space medicine |
Space medicine In 1993, an astronaut received a test infusion while in orbit on the space shuttle Columbia. German physicist Hans Schlegel had the saline solution at body temperature pumped into him through a needle. The experiment provided a means to address dehydration and other common space problems such as puffy face and skinny legs. |
|
30 Apr 2004

University of California at Irvine |
University of California at Irvine (technology) Scientists from the University of California at Irvine announce the first high-speed transistor made from a carbon nanotube, operating at microwave frequencies. |
|
30 Apr 2011

Daniel Gray Quillen |
death Daniel Gray Quillen Died 30 Apr 2011 at age 70 (born 27 Jun 1940). American mathematician who was awarded the Fields Medal in 1978 for contribution of geometric and topological techniques to the study of algebraic K-theory. |