| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
03 May 1375

Oldest eclipse record |
Oldest eclipse record In 1375 BC, the oldest recorded eclipse occurred, according to one plausible interpretation of a date inscribed on a clay tablet retrieved from the ancient city of Ugarit, Syria (as it is now). This date is one of two plausible dates usually cited from the record, though 5 Mar 1223 BC is the more favoured date by most recent authors on the subject. Certainly by the 8th century BC, the Babylonians were keeping a systematic record of solar eclipses, and possibly by this time they may have been able to apply numerological rules to make fairly accurate predictions of the occurrence of solar eclipses. The first total solar eclipse reliably recorded by the Chinese occurred on 4 Jun 180 BC. |
|
03 May 1580

Thomas Tusser |
death Thomas Tusser Thomas Tusser, English chorister and agriculturalist (born c. 1524) |
|
03 May 1657

Johann Cysat |
death Johann Cysat Died 3 May 1657 (born 1586). Johann Baptist Cysat, Jean-Baptiste Cysat in French or Latinized as Cysatus was a Swiss astronomer who entered the Jesuit order (1604), and by 1611 was studying at the Jesuit college in Ingolstadt, Bavaria, under Christoph Scheiner, whom he assisted in the observation of sunspots. From 1618, he taught mathematics there. As an early user of a telescope, he was the first to make substantial telescopic observation of a comet (1 Dec 1618 to 22 Jan 1619), Although he discovered the Orion Nebula independently (1619), it had been first noted by Peiresc in 1610. Cysat wrote to Kepler describing a lunar eclipse (1620) and observed the transit of Mercury (1631). It is the comet study for which Cysat is noted. His measurements of its position were made using a 6-foot radius wooden sextant. He published his data and analysis in an 80-page booklet, Mathemata astronomica de locu...cometae... (1619). |
|
03 May 1661

Antonio Vallisneri |
birth Antonio Vallisneri Antonio Vallisneri, Italian physician and natural scientist (died 1730) |
|
03 May 1695

Henri Pitot |
birth Henri Pitot Born 3 May 1695; died 27 Dec 1771 at age 76. French hydraulic engineer who invented the Pitot tube (1732), an instrument to measure flow velocity either in liquids or gases. With subsequent improvements by Henri Darcy, its modern form is used to determine the airspeed of aircraft. Although originally a trained mathematician and astronomer, he became involved with an investigation of the velocity of flowing water at different depths, for which purpose he first created the Pitot tube. He disproved the prevailing belief that the velocity of flowing water increased with depth. Pitot became an engineer in charge of maintenance and construction of canals, bridges, drainage projects, and is particularly remembered for his kilometer-long Roman-arched Saint-Clément Aqueduct (1772) at Montpellier, France. |
|
03 May 1713

Alexis Claude Clairaut |
birth Alexis Claude Clairaut Alexis Claude Clairaut, French mathematician (died 1765) |
|
03 May 1715

solar eclipse |
solar eclipse (astronomy) Total solar eclipse across southern England, Sweden and Finland (last total eclipse visible in London for almost 900 years). |
|
03 May 1764

Francesco Algarotti |
death Francesco Algarotti Died 3 May 1764 at age 51 (born 11 Dec 1712). Italian scholar of the arts and sciences, recognized for his wide knowledge and elegant presentation of advanced ideas. At age 21, he wrote Il Newtonianismo per le dame (1737; "Newtonianism for Ladies"), a popular exposition of Newtonian optics. He also wrote about architecture, opera and painting. |
|
03 May 1817

Horatio Hale |
birth Horatio Hale Born 3 May 1817; died 28 Dec 1896 at age 79. Horatio (Emmons) Hale was an American anthropologist whose contributions to the science of ethnology, included his theory of the origin of the diversities of human languages and dialectsa theory suggested by his study of childlanguages (the languages invented by little children). He emphasized the importance of languages as tests of mental capacity and as criteria for the classification of human groups. Hale was the first to discover that the Tutelos of Virginia belonged to the Siouan family, and to identify the Cherokee as a member of the Iroquoian family of speech. He sailed with the scientific corps of the Wilkes Exploring Expedition (1838-42) collecting linguistic materials. He used the drift of the Polynesian tongue as a clue to the migration of this race. |
|
03 May 1833

Entomological Society of London |
Entomological Society of London (biology) The Entomological Society of London is inaugurated. |
|
03 May 1844

Wilbur Olin Atwater |
birth Wilbur Olin Atwater Born 3 May 1844; died 22 Sep 1907 at age 63. American agricultural chemist who developed agricultural chemistry. Atwater received his PhD from Yale in 1869 for studies on the chemical composition of corn. At Wesleyan College in Connecticut, USA, he studied the effects of fertilizers in farming and established the first agricultural experimental station in the US at Wesleyan in 1875 (which in 1877 became part of the famous Sheffield Scientific School at Yale University). From 1879 to 1882 Atwater determined the chemical composition and nutritive values of fish and animal tissues. During his life, he completed more than 500 energy-balance experiments. They confirmed that the law of conservation of energy governed transformation of matter in both the human body and inanimate world. |
|
03 May 1860

Vito Volterra |
birth Vito Volterra Born 3 May 1860; died 11 Oct 1940 at age 80. Italian mathematician who made important contributions to calculus, and mathematical theories in astronomy, elasticity and biometrics. His mathematical talent appeared as a young boy. In 1905, he began to develop the theory of dislocations in crystals that led to improved understanding of the behaviour of ductile materials. During WWI he established the Italian Office of War Inventions and designed weapons for use by airships, for which he proposed the use of helium instead of flammable hydrogen. He is remembered for achievements in function theory and differential equations. In biology, in 1925, he formulated a pair of differential equations relating populations of prey and predators (also independently proposed by Alfred J. Lotka in 1925). |
|
03 May 1860

John Scott Haldane |
birth John Scott Haldane Born 3 May 1860; died 14 Mar 1936 at age 75. Scottish physiologist and philosopher of science whose extensive work on human respiration included the effects of pulmonary diseases and the physiology of the blood. Early in his career he studied the air in sewers for microorganisms, which he found rather limited. Haldane was known for experimentation on himself to find the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood was a stimulus for the respiratory centre of the brain. He reported on investigations of the effects of carbon monoxide from mine fires and explosions (1896). For the safety of deep-sea divers, he built on Paul Bert's work on the bends and produced the first staged decompression tables (1907). He also devised a decompression apparatus. He invented a gas mask used in WW I. |
|
03 May 1874

V(agn) Walfrid Ekman |
birth V(agn) Walfrid Ekman Born 3 May 1874; died 9 Mar 1954 at age 79. Swedish physical oceanographer and mathematical physicist whose research into the dynamics of ocean currents led to his name remaining associated with terms for particular phenomena of the ocean or atmosphere, including Ekman spiral, Ekman transport and Ekman layer. Fridtjof Nansen pointed out to Ekman that he had noticed that icebergs drift at an angle of 20°-40° to the prevailing wind, rather than directly with the wind. In 1902, Ekman published an explanation, known now as the Ekman spiral, describing movement of ocean currents influenced by the Earth's rotation. He also developed experimental techniques and instruments such as the Ekman current meter and Ekman water bottle. |
|
03 May 1877

Karl Abraham |
birth Karl Abraham Born 3 May 1877; died 25 Dec 1925 at age 48. German psychoanalyst who studied who studied the role of childhood sexual trauma in relation to the symptoms of mental illness. He was initiated into psychoanalysis by Carl Gustav Jung (1904). He first met Sigmund Freud in 1907, and subsequently became one of his most reliable collaborators. Covering a wide range, Abraham's papers include work on depression, mania, auto erotism, repressed hate, as well as others on applied psychoanalysis that include papers on the Day of Atonement and a major one (1909) in which he connected myths with dreams and viewed both as wish-fulfillment fantasies. Abraham founded the Berlin Psychoanalytic Society (1910). He made pioneering efforts in the psychoanalytic treatment of manic- depressive psychosis. |
|
03 May 1878

Cruz Hernández |
birth Cruz Hernández Cruz Hernández, El Salvadorian oldest person (not fully verified) (died 2007) |
|
03 May 1880

Jonathan Homer Lane |
death Jonathan Homer Lane Died 3 May 1880 at age 60 (born 9 Aug 1819). American astrophysicist who was the first to investigate mathematically the Sun as a gaseous body. His work demonstrated the interrelationships of pressure, temperature, and density inside the Sun and was fundamental to the emergence of modern theories of stellar evolution. |
|
03 May 1888

Sir Charles Tilston Bright |
death Sir Charles Tilston Bright Died 3 May 1888 at age 55 (born 8 Jun 1832). British engineer who superintended the laying of the first Atlantic telegraph cable. He supervised the laying of hundreds of miles of underground telegraph cables, throughout the British Isles, including the first cable under the sea between Scotland and Ireland, when just 21. He joined the new Atlantic Telegraph company as chief engineer to lay the first transatlantic cable. The first attempt (1857) ended when the cable broke 280 miles off the coast. The second attempt, a year later and was initially successful but with a weak electric signal. On 16 Aug 1858, Queen Victoria sent a message to U.S. President James Buchanan. This cable failed within a few weeks. He acted as consulting engineer for the second and third transatlantic cables of 1865 and 1866. |
|
03 May 1892

Sir George Paget Thomson |
birth Sir George Paget Thomson Born 3 May 1892; died 10 Sep 1975 at age 83. English physicist who shared (with Clinton J. Davisson of the U.S.) the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1937 for demonstrating that electrons undergo diffraction, a behaviour peculiar to waves that is widely exploited in determining the atomic structure of solids and liquids. He was the son of Sir J.J. Thomson who discovered the electron as a particle. |
|
03 May 1902
Alfred Kastler |
birth Alfred Kastler Born 3 May 1902; died 7 Jan 1984 at age 81. French physicist who won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1966 for his discovery and development of methods for observing Hertzian resonances within atoms. This research facilitated the greater understanding of the structure of the atom by studying the radiations that atoms emit when excited by light and radio waves. He developed a method called "optical pumping" which caused atoms in a sample substance to enter higher energy states. This idea was an important predecessor to the development of masers and the lasers which utilized the light energy that was re-emitted when excited atoms released the extra energy obtained from optical pumping. |
|
03 May 1910

Howard T. Ricketts |
death Howard T. Ricketts Died 3 May 1910 at age 39 (born 9 Feb 1871). Howard Taylor Ricketts was an American pathologist who discovered the causative organisms and mode of transmission of Rocky Mountain spotted fever and epidemic typhus. In 1906, Ricketts, a Univeristy of Chicago pathologist, demonstrated that Rocky Mountain spotted fever is spread by cattle ticks and caused by a blood-borne "bipolar bacillus." In 1910 he showed that typhus is caused by a similar organism carried by lice. Ricketts was in Mexico City investigating the disease (known in Mexico, as tabardillo) that year when he was stricken by typhus and died at age 39. The two organisms Ricketts discovered were the first of what were later shown to be an unusual genus of virus-like bacteria - now named the Rickettsiae. |
|
03 May 1910

Helen M. Duncan |
birth Helen M. Duncan Helen M. Duncan (died 1971), geologist and paleontologist |
|
03 May 1933

Steven Weinberg |
birth Steven Weinberg Born 3 May 1933. American nuclear physicist who shared the 1979 Nobel Prize for Physics (with Sheldon Lee Glashow and Abdus Salam) for work in formulating the electroweak theory, which explains the unity of electromagnetism with the weak nuclear force. |
|
03 May 1937

Esther Boise Van Deman |
death Esther Boise Van Deman Died 3 May 1937 at age 74 (born 1 Oct 1862). American archaeologist who was studying on a scholarship in Rome when she decided that Roman archaeology was to be her chosen field of work. In 1907, while attending a lecture in the Atrium Vestae, that she noticed that the bricks blocking up a doorway were different from those in the structure itself, and she speculated that those differences in building materials might provide a wealth of information for dating the choronology of Roman structures. Thus began thirty years of life in Rome. She was the first woman to specialize in Roman field archaeology. She established lasting criteria for the dating of ancient constructions, which advanced the serious study of Roman architecture. |
|
03 May 1954

Earnest A. Hooton |
death Earnest A. Hooton Died 3 May 1954 at age 66 (born 20 Nov 1887). Earnest Albert Hooton was an American physical anthropologist and primatologist who investigated human evolution and racial differentiation, classified and described human populations, and examined the relationship between personality and physical type, particularly with respect to criminal behaviour. He established Harvard University as a principal U.S. centre for physical anthropology. In the 1930s, he studied American criminals, and in his controversial books, The American Criminal (1939) and Crime and the Man (1939), he sought to to connect criminal behaviour with physical or racial factors. His books written for the layperson include: Up from the Ape; Apes, Men and Morons; and Twilight of Man, Why We Behave Like Apes and Vice Versa. |
|
03 May 1960

Jaron Lanier |
birth Jaron Lanier Jaron Lanier, American computer scientist. |
|
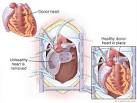
03 May 1968
Heart transplant |
Heart transplant In 1968, Dr. Denton Cooley of the Texas Heart Institute performed the first successful heart transplant in the United States on Everett Thomas, whose heart was damaged from rheumatic heart disease. The patient lived for 204 days with the heart donated from a 15-year-old girl. In 1969, Cooley became the first heart surgeon to implant an artificial heart in man. |
|
03 May 1982

Henri Tajfel |
death Henri Tajfel Henri Tajfel (b. 1919), Polish-born British social psychologist. |
|
03 May 1997

Manuel Elizalde |
death Manuel Elizalde Died 3 May 1997 (born c. 1937). Philippine official and amateur anthropologist who in 1971 announced the discovery in Mindanao of the Tasaday, a tiny, primitive tribe living in isolation in the rain forest in such harmony there was no word for "war"; he was later accused of having perpetrated a hoax, and the controversy was never completely settled |