| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
10 Jun 1706

John Dollond |
birth John Dollond Born 10 Jun 1706; died 30 Nov 1761 at age 55. English optical instrument maker of optical and astronomical instruments who developed (1758) and patented an achromatic (non- colour- distorting) refracting telescope and a practical heliometer, a telescope used to measure the Sun's diameter and the angles between celestial bodies. In the 1730's, Chester More Hall, an attorney with an interest in telescopes, first discovered that flint glass appeared to have a greater color dispersion than crown glass did at the same magnifications. Hall reasoned that if he cemented the concave face of a flint glass lens to the convex face of a crown glass lens, he could remove the dispersion properties (and thus, chromatic aberration) from both lenses simultaneously. Dollond learned of the technique in the 1750's and developed it. |
|
10 Jun 1710

James Short |
birth James Short Born 10 Jun 1710; died 14 Jun 1768 at age 58. British optician and astronomer who produced the first truly parabolic and elliptic (hence nearly distortionless) mirrors for reflecting telescopes. During his working life of over 35 years, Short made about 1,360 instruments - not only for customers in Britain but also for export: one is still preserved in Leningrad, another at Uppsala and several in America. Short was principal British collator and computer of the Transit of Venus observations made throughout the world on 6th June 1761. His instruments travelled on Endeavour with Captain Cook to observe the next Transit of Venus on 3rd June 1769, but Short died before this event took place. |
|
10 Jun 1735

John Morgan |
birth John Morgan Born 10 Jun 1735; died 15 Oct 1789 at age 54. American pioneer of U.S. medical education, surgeon general of the Continental armies during the U.S. War of Independence, and founder of the United States' first medical school - the College of Philadelphia (University of Pennsylvania) in 1765. He joined the faculty and wrote his influential Discourse upon the Institution of Medical Schools in America (1765). In 1775, after the American Revolution had started, Congress appointed him medical director of the hospitals and chief physician of the colonial army. Morgan insisted upon such high standards and reforms in the medical department that his subordinates rebelled and forced him from office. He was later exonerated by George Washington, but never completely recovered, dying in poverty ten years later. |
|
10 Jun 1793

Chauncey Jerome |
birth Chauncey Jerome Born 10 Jun 1793; died 20 Apr 1868 at age 74. American inventor and clockmaker whose products enjoyed widespread popularity in the mid-19th century. About 1838 Jerome invented the one-day brass movement, an improvement over the wood clock. Applying the mass-production techniques of American inventor Eli Whitney, Jerome flooded the United States with low-priced brass clocks. His clocks quickly spread to Europe and so astonished the English that "Yankee ingenuity" became a byword. In the 1850s Jerome became associated with unethical businessmen, and his company failed; he died in poverty. |
|
10 Jun 1793

Muséum national d'histoire naturelle |
Muséum national d'histoire naturelle (biology) Muséum national d'histoire naturelle formally established in Paris by the National Convention of the French First Republic. |
|
10 Jun 1803

Henri Darcy |
birth Henri Darcy Born 10 Jun 1803; died 3 Jan 1858 at age 54. Henri-Philibert-Gaspard Darcy was a French hydraulic engineer who first derived the equation (now known as Darcy's law) that governs the laminar (nonturbulent) flow of fluids in homogeneous, porous media. In 1856, modern studies of groundwater began when Darcy was commissioned to develop a water-purification system for the city of Dijon, France. He constructed the first experimental apparatus to study the flow characteristics of water through the earth. From his experiments, he derived the Darcy's Law equation, describing the flow of water in nature, which is fundamental to understanding groundwater systems. He performed extensive tests on filtration and pipe resistance. He initiated the open-channel studies carried out by Bazin. |
|
10 Jun 1809

Steamboat |
Steamboat In 1809, the Phoenix paddle wheel steamboat took 13 days to sail from New York City to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was the first steamboat to navigate the open seas. This was John Stevens' first commercial steamboat, 100-ft long, built at Hoboken, N.J. Because of the Fulton monopoly in Jersey-New York waters, the Phoenix went to Philadelphia. There, it began to run to Bordentown in 1809, becoming a link in the fast stage-coach and boat service connecting New York and Philadelphia. |
|
10 Jun 1822
English Channel |
English Channel (technology) The Aaron Manby crosses the English Channel, making her the first seagoing iron steamboat. |
|
10 Jun 1822

Lydia White Shattuck |
birth Lydia White Shattuck Lydia White Shattuck, botanist (died 1889) |
|
10 Jun 1832

Nikolaus August Otto |
birth Nikolaus August Otto Born 10 Jun 1832; died 26 Jan 1891 at age 58. German engineer and inventor who developed the four-stroke internal-combustion engine, which offered the first practical alternative to the steam engine as a power source. A French engineer, Alphonse Beau de Rochas, formulated the basic design for the four-stroke internal combustion engine and patented it in 1862, but never built a working model. In 1876, Otto used principles from Beau de Rochas and others to construct the prototype of today's automobile engines, often called the Otto-cycle engine. He sold thousands of copies before Beau de Rochas sued him and invalidated Otto's patent. But light, efficient Otto-cycle engines largely enabled the creation of automobiles, powerboats, motorcycles and even airplanes. |
|
10 Jun 1836

André-Marie Ampère |
death André-Marie Ampère Died 10 Jun 1836 at age 61 (born 22 Jan 1775). French mathematician, physicist and chemist who founded and named the science of electrodynamics, now known as electromagnetism. His interests included mathematics, metaphysics, physics and chemistry. In mathematics he worked on partial differential equations. Ampère made significant contributions to chemistry. In 1811 he suggested that an anhydrous acid prepared two years earlier was a compound of hydrogen with an unknown element, analogous to chlorine, for which he suggested the name fluorine. He produced a classification of elements in 1816. Ampère also worked on the wave theory of light. By the early 1820's, Ampère was working on a combined theory of electricity and magnetism, after hearing about Hans Oersted's experiments. |
|
10 Jun 1844

Carl Hagenbeck |
birth Carl Hagenbeck Carl Hagenbeck (died 1913), German zoologist. |
|
10 Jun 1854
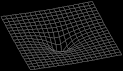
Curved space |
Curved space In 1854, G.F. Bernhard Riemann proposed that space is curved in a lecture titled Über die Hypothesen welche der Geometrie zu Grunde liegen. He described the old-fashioned Euclidean plane geometry and solid geometry, respectively, as two-, and three-dimensional examples of what we now call Riemann spaces with zero curvature. Saying that the space is curved, rather than flat or Euclidean, is another way saying that the familiar properties of Euclidean geometry - such as the Pythagorean theorem - do not hold. He went on to suggest that all physical laws become simpler when expressed in higher dimensions. Albert Einstein in 1915 used Rieman's work in his theory of General Relativity which incorporated time as the fourth dimension. |
|
10 Jun 1858

Robert Brown |
death Robert Brown Died 10 Jun 1858 at age 84 (born 21 Dec 1773). Scottish botanist who was an outsatanding authority on plant physiology in his day. He improved the natural classification of plants by establishing and defining new families and genera, but is best known for being the first to notice the natural continuous movement of minute particles in colloidal solution (1828), since known as Brownian movement. Later scientists recognized that this gives direct evidence of molecular motion in liquids, and links to the kinetic theory of gases. Brown distinquished (1826) between what became known as the conifers (gymnosperms) and the flowering plants (angiosperms). In living cells he recognized a structure for which he coined the name nucleus (Latin: "little nut"). |
|
10 Jun 1861

Pierre Duhem |
birth Pierre Duhem Born 10 Jun 1861; died 14 Sep 1916 at age 55. Pierre-Maurice-Marie Duhem was a French physicist, philosopher of science and mathematician who emphasized a history of modern science based on evolutionary metaphysical concepts. He had a wide variety of mathematical interests from mechanics and physics to philosophy and the history of mathematics. Duhem studied magnetism following the work of Gibbs and Helmholtz and also worked on thermodynamics and hydrodynamics producing over 400 papers. He maintained that the role of theory in science is to systematize relationships rather than to interpret new phenomena. |
|
10 Jun 1869

Frozen food |
Frozen food In 1869, machine-frozen food was transported a significant distance in the U.S. for the first time. A shipment of frozen Texas beef had been processed by refrigeration equipment invented by John Gorrie, and delivered by the steamship Agnes in New Orleans, La. The meat was served in meals at hospitals, and celebration banquiets at hotels and restaurants. This was an irony, for John Gorrie had unsuccessfully sought financial support to develop his invention in New Orleans and had died shortly thereafter in 1855. |
|
10 Jun 1890

Grass catcher |
Grass catcher In 1890, black American inventor Daniel Johnson received a patent for "Grass Receivers for Lawn Mowers" (U.S. No. 429,629). This was an improvement on the inventor's own earlier patent application. It consists of a means for suspending the receiver from the mower-handle and enabling the weight of the receiver to be equally distributed. The side of the receiver is covered with woven wire netting. For the purpose of dumping the contents of the receiver, a sliding bottom is provided, operated with a foot stirrup. The patent application was signed by Daniel Johnson making his X mark with two witnesses adding their signatures. |
|
10 Jun 1900

Wilhelm Friedrich (Willy) Kühne |
death Wilhelm Friedrich (Willy) Kühne Died 10 Jun 1900 at age 63 (born 28 Mar 1837). Wilhelm Friedrich Kühne was a German physiologist known for his researches on vision and the chemical changes occurring in the retina under the influence of light. His original work falls into two main groups—the physiology of muscle and nerve, which occupied the earlier years of his life, and the chemistry of digestion, which he began to investigate while at Berlin with Virchow. He was proposed the word enzyme meaning "in yeast" (1878), and he isolated trypsin from pancreatic juice. He demonstrated usefulness of cytophysiological investigations for solving problems of general physiology. He devised an "artificial eye," discovered the light sensitive "visual purple" in the retina and was first to perceive migrating pigments in the living retina (1877-78). |
|
10 Jun 1902
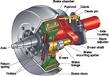
Air brake |
Air brake In 1902, An “Automatic Air Brake” patent was issued to black American inventor Granville T. Woods (U.S. No. 701,981), which was an important safety device for the railroads. |
|
10 Jun 1902

Window envelope |
Window envelope In 1902, the first U.S. patent for a window envelope was issued to Americus F. Callahan of Chicago, Ill., which he called the outlook envelope (U.S. No. 701,839). He leased the patent to the Envelope company of Springfield, Mass., which began its manufacture in Jul 1902. This style of envelope was able to save expense of printing or labour of addressing, and in addition save time in preparing the message for dispatch when the customary addresses are already on the letter paper itself. |
|
10 Jun 1903

Luigi Cremona |
death Luigi Cremona Died 10 Jun 1903 at age 72 (born 7 Dec 1830). Antonio Luigi Gaudenzio Giuseppe Cremona was an Italian mathematician who was an originator of graphical statics (the use of graphical methods to study forces in equilibrium) and work in projective geometry. Cremona's work in statics is of great importance and he gave, in a clearer form, some theorems due to Maxwell. In a paper of 1872 Cremona took an idea of Maxwell's on forces in frame structures that had appeared in an engineering journal in 1867 and interpreted Maxwell's notion of reciprocal figures as duality in projective 3-space. These reciprocal figures, for example, have three forces in equilibrium in one figure represented by a triangle while in the reciprocal figure they are represented by three concurrent lines. |
|
10 Jun 1906

Mary Putnam Jacobi |
death Mary Putnam Jacobi Died 10 Jun 1906 at age 63 (born 31 Aug 1842). (née Mary Corinna Putnam) American physician, well-respected for her medical abilities, who advocated social reform to expand educational opportunities for women by providing the same training and clinical practice as men. She was awarded Harvard University's Boylston Prize for her 1876 essay, The Question of Rest for Women during Menstruation. In this work, she refuted allegations of the physical limitations of women, such as published by Dr. Edward H. Clarke's in Sex in Education (1873). She supported her position with scientific data including sphygmographic tracings of pulse rate, force, and variations to confirm that a woman maintained vigorous health throughout her monthly cycle. Jacobi became the first female member of the Academy of Medicine. |
|
10 Jun 1913

Edward Abraham |
birth Edward Abraham Edward Abraham (died 1999), English biochemist. |
|
10 Jun 1924

Electrical stethoscope |
Electrical stethoscope In 1924, the first U.S. portable electrical stethoscope was demonstrated in Chicago, Ill. to amplify the sounds of the human body. It was designed by the Western Electric Co. with Bell System engineers and physiologist Dr. Horatio B. Williams. It was subsequently maketed in Oct 1925. |
|
10 Jun 1929

Edward O. Wilson |
birth Edward O. Wilson Born 10 Jun 1929. Edward Osborne Wilson is an American biologist recognized as the world's leading authority on ants who has conducted extensive studies of the ecology and evolution of the ant. He has travelled the world studying ant populations, and he has discovered several new ant species. These currently number practically 9,000, but Wilson predicts that count will someday total nearly 20,000. He also estimates that within these species there are over a million billion individuals. In 1967, he co-published The Theory of Island Biogeography, a study of islands, which examines the relation between island size, the number of species contained, and their evolutionary balance. He is also active in sociobiology, a genetic study of social behaviour. |
|
10 Jun 1929

E. O. Wilson |
birth E. O. Wilson E. O. Wilson, American entomologist. |
|
10 Jun 1932

Artificial lightning |
Artificial lightning In 1932, artificial lightning using 10 million volts of electricity was demonstrated in the U.S. by the General Electric Company at Pittsfield, Mass. This was twice the previous maximum voltage produced in a laboratory. |
|
10 Jun 1943

Ball point pen |
Ball point pen In 1943, Laszlo Biro filed for a British patent (No. 564172) on a practical ball point pen with quick-drying ink. Biro was a journalist, in 1938, in Budapest (also sculptor and hypnotist) when he took out a Hungarian patent for his first design of the pen. In 1940, he escaped the Nazis by going via Paris to Buenos Aires, Argentina. There a British entrpreneur, Henry Martin, saw Biro’s pen and realized its value for air crews making high altitude navigational calculations. It could write blot-free, unaffected by low or changing atmospheric pressure. Martin bought the rights and began small scale production of ballpoint pens for the RAF. In 1945, the Eterpen Co in Buenos Aires began commercial production. |
|
10 Jun 1948

Philippa Fawcett |
death Philippa Fawcett Philippa Fawcett (born 1868), English mathematician. |
|
10 Jun 1949

Filippo Silvestri |
death Filippo Silvestri Died 10 Jun 1949 at age 75 (born 22 Jun 1873). Italian entomologist, best remembered for his pioneering work in polyembryony, the development of more than one individual from a single fertilized egg cell. During the late 1930s Silvestri discovered that this type of reproduction occurs in the insect species Litomatix truncatellus. His finding, resulting from a close analysis of the reproductive stages, cell division, and egg structure of these parasitic hymenopterans, attracted the attention of many biologists because of its implications for the nature of the egg and the causes of multiple generation. He also studied the morphology and biology of the Termitidae, the most highly evolved family of termites. He also made a comparative study of the form and structure of the millipede and the centipede. |
|
10 Jun 1952

Mylar |
Mylar In 1952, Mylar® was registered as a DuPont trademark for an extraordinarily strong polyester film that grew out of the development of Dacron® in the early 1950s. During the 1960s its superior strength steadily replaced cellophane because of its its superior strength, heat resistance, and excellent insulating properties. The unique qualities of the film made new consumer markets in magnetic audio and video tape, capacitor dielectrics, packaging and batteries possible. By the 1970s, it become DuPont's best-selling film, despite mounting competition. It is also used as food wrap, for balloons, and by instrument manufacturers to produce high-quality drumheads. |
|
10 Jun 1954

Gas turbine bus |
Gas turbine bus In 1954, General Motors announced their GM Turbocruiser, a modifed GMC coach powered by a gas turbine, had been built by their research staff and its test runs already exceeded a total of 2,000 miles. The engine consisted of a single burner with two turbine wheels. While one turbine wheel was used to drive the centrifugal compressor, the second delivered power for the transmission to the rear wheels of the vehicle |
|
10 Jun 1955

Virus separation |
Virus separation In 1955, the first U.S. report was made of the separation of a virus into component parts. This work was performed on the tobacco virus, which furthermore could be reconstructed from those parts to produce a material as effective as the virus in its original form in producing disease in tabacco and other plants. They demonstrated that tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) spontaneously formed when mixtures of purified coat protein and its genomic RNA were incubated together, i.e. the structure that TMV adopts is self-ordered and corresponds to a free energy minimum. The report covered the research work of Drs. Heinz L. Fraenkel-Conrat and Robley Williams at the Virus Laboratory of the University of California at Berkeley. |
|
10 Jun 1971

Otto Heinrich Schindewolf |
death Otto Heinrich Schindewolf Died 10 Jun 1971 at age 75 (born 7 Jun 1896). German paleontologist, known for his research on corals and cephalopods. He was an anti-Darwinist, who advocated a cataclysmic theory of evolution to explain the origin of the higher taxonomic categories. Studying different fossil species of coral and ammonites obtained from sequential geological strata, he concluded that the most recent taxonomic categories could not have arisen by slow, intermediate steps, generally thought to characterize evolution, but rather by large, single transformations. Though his views are not accepted by many biologists, particularly the population geneticists, who consider them too controversial, he has drawn attention to fundamental problems in evolution. |
|
10 Jun 2000

Millenium Bridge |
Millenium Bridge In 2000, the Millenium Bridge - a footbridge across the River Thames - was opened by Queen Elizabeth. The radical new design was the work of architect Sir Norman Foster with sculptor Sir Anthony Caro and engineering support from Arup. It was the first new crossing of the River Thames in over 100. As the first few thousand people crossed the bridge, it developed an unexpected and potentially dangerous lateral "wobble". This caused people to unwittingly walk "in step", which increased the oscillation. The design had been adapted from a computer model typical for a car bridge, but which did not take into account the lateral forces associated with human walking. After structural damping was added to stop the oscillation, the bridge re-opened in 2002. |
|
10 Jun 2002

Annular solar eclipse |
Annular solar eclipse (astronomy and space ) Annular solar eclipse. |