| Date | Text | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 years anniversary | ||||
30 Nov 1923

ectogenesis |
ectogenesis (biology) The term "ectogenesis" is coined by British scientist J.B.S. Haldane to describe the growth of mammalian embryos in artificial environments. |
|||
30 Nov 1923

tetanus toxoid |
tetanus toxoid (biochemistry) The first inactive tetanus toxoid is discovered and produced. |
|||
30 Nov 1923

David Hilbert |
David Hilbert (mathematics) David Hilbert proposes Hilbert's paradox of the Grand Hotel. |
|||
30 Nov 1923

S. N. Bose |
S. N. Bose (physics) S. N. Bose and Albert Einstein publish papers in Zeitschrift für Physik applying Bose–Einstein statistics to light quanta and to atomic models and predicting existence of the Bose–Einstein condensate. |
|||
30 Nov 1923

E. C. Stoner |
E. C. Stoner (physics) E. C. Stoner publishes a paper pointing out that for a given value of the principal quantum number (n), the number of energy levels of a single electron in the alkali metal spectra in an external magnetic field, where all degenerate energy levels are separated, is equal to the number of electrons in the closed shell of the rare gases for the same value of n. This leads to discovery of the Pauli exclusion principle. |
|||
30 Nov 1923

Louis de Broglie |
Louis de Broglie (physics) Louis de Broglie introduces the wave-model of atomic structure, based on the ideas of wave-particle duality. |
|||
30 Nov 1923

Václav Holek |
Václav Holek (technology) Václav Holek designs the ZB vz. 26 light machine gun for Zbrojovka Brno. |
|||
| 75 years anniversary | ||||
30 Nov 1948
Radiocarbon dating |
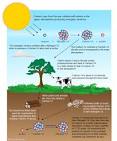
Radiocarbon dating (chemistry) Radiocarbon dating technique discovered by Willard Libby and his colleagues at the University of Chicago—work for which Libby will receive the Nobel prize in 1960. |
|||
30 Nov 1948

Dorothy Hodgkin |
Dorothy Hodgkin (chemistry) A group including Dorothy Hodgkin publish the three-dimensional molecular structure of penicillin, demonstrating that it contains a β-lactam ring. |
|||
30 Nov 1948

Herbert Butterfield |
Herbert Butterfield (history of science) Herbert Butterfield publishes The Origins of Modern Science, 1300-1800. |
|||
30 Nov 1948

lithium |
lithium (medicine) The use of lithium salts to control mania is rediscovered by Australian psychiatrist John Cade, the first mood stabilizer. |
|||
30 Nov 1948

intraocular lens |
intraocular lens (medicine) First implant of intraocular lens, by Sir Harold Ridley |
|||
30 Nov 1948

Gilbert Ryle |
Gilbert Ryle (philosophy) Gilbert Ryle's book The Concept of Mind, a founding document in the philosophy of mind, is published. |
|||
30 Nov 1948

Freeman Dyson |
Freeman Dyson (physics) Freeman Dyson demonstrates the equivalence of the formulations of quantum electrodynamics existing at this time, incidentally inventing the Dyson series. |
|||
30 Nov 1948
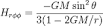
Lanczos tensor |
Lanczos tensor (physics) The Lanczos tensor is introduced in general relativity by Cornelius Lanczos. |
|||
30 Nov 1948

Konrad Lorenz |
Konrad Lorenz (zoology) Konrad Lorenz publishes King Solomon's Ring (Er redete mit dem Vieh, den Vögeln und den Fischen). |
|||
| 50 years anniversary | ||||
30 Nov 1973
Hawking radiation |
Hawking radiation (astronomy and space ) Hawking radiation is predicted by Stephen Hawking. |
|||
30 Nov 1973

F. W. Winterbotham |
F. W. Winterbotham (history of science) F. W. Winterbotham publishes The Ultra secret: the inside story of Operation Ultra, Bletchley Park and Enigma, the first popular account of cryptography carried out at Bletchley Park during World War II. |
|||
30 Nov 1973
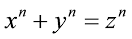
Fermat's Last Theorem |
Fermat's Last Theorem (mathematics) Yves Hellegouarch proposes a connection between Fermat's Last Theorem and the Frey curve. |
|||
30 Nov 1973
controlled trials |
controlled trials (medicine) Identification of controlled trials in perinatal medicine, as advocated by Archie Cochrane, begins in Cardiff, Wales. |
|||
30 Nov 1973

Henry Heimlich |
Henry Heimlich (medicine) Henry Heimlich describes the "Heimlich Maneuver" as a treatment for choking. |
|||
30 Nov 1973

Arthur Lakes |
Arthur Lakes (paleoanthropology an) Teeth from what would later be documented as Tyrannosaurus rex are found by geologist Arthur Lakes near Golden, Colorado. |
|||
30 Nov 1973
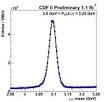
J/ψ meson |
J/ψ meson (physics) "November Revolution": J/ψ meson, the first particle found to contain a charm quark, discovered by teams at the Brookhaven National Laboratory, led by Samuel Ting, and at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, led by Burton Richter. |
|||

|
Civilized Man's Eight Deadly Sins is published by Konrad Lorenz. | |||
30 Nov 1973

Leon Kamin |
Leon Kamin (psychology) Leon Kamin demonstrates that Sir Cyril Burt's influential research into heritability of IQ using twin studies shows evidence of statistical falsification. |
|||
30 Nov 1973

Stephen Salter |
Stephen Salter (technology) Stephen Salter invents the "Salter Duck", a wave energy converter. |
|||
30 Nov 1973

Rubik's Cube |
Rubik's Cube (other s) Rubik's Cube invented by Ernő Rubik. |
|||
30 Nov 1973

Fields Prize in Mathematics |
Fields Prize in Mathematics (awards) Fields Prize in Mathematics: Enrico Bombieri and David Mumford |
|||
30 Nov 1973

Turing Award |
Turing Award (awards) Turing Award – Donald Knuth |
|||
| 25 years anniversary | ||||
30 Nov 1998

Namibia |
Namibia (biology) The bacterium Thiomargarita namibiensis is discovered off the coast of Namibia. At 0.3mm in diameter, it is largest bacteria yet discovered. |
|||
30 Nov 1998
Element 118 |
Element 118 (chemistry) Element 118 and 116 are claimed to be made for the first time. Later retracted when results could not be replicated. |
|||
30 Nov 1998

3-qubit |
3-qubit (computer science) First working 3-qubit NMR computer demonstrated at IBM's Almaden Research Center. First execution of Grover's algorithm. |
|||
30 Nov 1998

Neil Sloane |
Neil Sloane (mathematics) Eric M. Rains and Neil Sloane extend tree counting. |
|||
30 Nov 1998

CERN |
CERN (physics) CERN: Bulgaria becomes a member of CERN. |
|||
30 Nov 1998

Huda Zoghbi |
Huda Zoghbi (physiology and medic) Huda Zoghbi demonstrates that Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in the gene MECP2. |
|||
30 Nov 1998

BlackBerry |
BlackBerry (telecommunications) The first BlackBerry is released, using the same hardware as the Inter@ctive pager 950, and running on the Mobitex network. |
|||

|
Turing Award: Fred Brooks | |||
30 Nov 1998

Wollaston Medal for Geology |
Wollaston Medal for Geology (awards) Wollaston Medal for Geology: John Frederick Dewey |
|||
| 20 years anniversary | ||||
30 Nov 2003
UTC |
UTC (astronomy) 02:48 UTC) – Saturn orbit insertion of Cassini–Huygens. |
|||
30 Nov 2003

Michael Aschbacher |
Michael Aschbacher (mathematics) Michael Aschbacher and Stephen D. Smith publish their work on quasithin groups, filling the last (known) gap in the classification of finite simple groups. |
|||
30 Nov 2003

Neil Shubin |
Neil Shubin (paleontology) A team led by Neil Shubin discover fossils of the sarcopterygian Tiktaalik on Ellesmere Island in Nunavut, Canada, significant in the evolution of tetrapods. |
|||
30 Nov 2003

Abel Prize in Mathematics |
Abel Prize in Mathematics (awards) Abel Prize in Mathematics: Michael F. Atiyah and Isadore M. Singer |
|||
30 Nov 2003

Millennium Technology Prize |
Millennium Technology Prize (awards) Millennium Technology Prize (inaugural year): World Wide Web inventor Tim Berners-Lee |
|||
| 10 years anniversary | ||||
30 Nov 2013

dinosaurs |
dinosaurs (undated) Researchers proved that the dinosaurs that finally convert to birds regularly got smaller and finer boned over time. |
|||
30 Nov 2013

alcoholic beverage |
alcoholic beverage (undated) Researchers claim alcoholic beverage causes successful aging for women. |
|||