| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
09 Apr 1626

Sir Francis Bacon |
death Sir Francis Bacon Died 9 Apr 1626 at age 65 (born 22 Jan 1561). English philosopher remembered for his influence promoting a scientific method. He held that the aim of scientific investigation is practical application of the understanding of nature to improve man's condition. He wrote that scientists should concentrate on certain important kinds of experimentally reproducible situations, (which he called "prerogative instances"). After tabulating such phenomena, the investigator should also aim to make a gradual ascent to more and more comprehensive laws, and will acquire greater and greater certainty as he or she moves up the pyramid of laws. At the same time each law that is reached should lead him to new kinds of experiment, that is, to kinds of experiment over and above those that led to the discovery of the law. |
|
09 Apr 1626

Francis Bacon |
death Francis Bacon Francis Bacon, English philosopher and a founder of modern scientific research (born 1561) |
|
09 Apr 1643

Benedetto Castelli |
death Benedetto Castelli Benedetto Castelli, Italian mathematician (born 1578) |
|
09 Apr 1709

Sir Godfrey Copley, 2nd Baronet |
Sir Godfrey Copley, 2nd Baronet (awards) Sir Godfrey Copley, 2nd Baronet dies and in his will provides funding to the Royal Society for the annual Copley Medal honoring achievement in science (first awarded in 1731). |
|
09 Apr 1754

Christian Freiherr von Wolff |
death Christian Freiherr von Wolff Died 9 Apr 1754 at age 75 (born 24 Jan 1679). (baron) German philosopher, mathematician, and scientist who worked in many subjects but who is best known as the German spokesman of the Enlightenment, the 18th-century philosophical movement characterized by Rationalism. Wolff's first interest was mathematics. Though he made no original contribution to the discipline, he was important in the teaching of mathematics and instrumental in introducing the new mathematics into German universities. Later, as a philosopher, he developed the most impressive coherent system of his century. Thoroughly eclectic, influenced by Leibniz and Descartes, yet he continued fundamental themes of Aristotle. His system was important in making the discoveries of modern science known in Germany. |
|
09 Apr 1754

Christan Wolff |
death Christan Wolff Christan Wolff, German philosopher, mathematician and scientist (born 1679) |
|
09 Apr 1770

Thomas Johann Seebeck |
birth Thomas Johann Seebeck Born 9 Apr 1770; died 10 Dec 1831 at age 61. German physicist who discovered (1821) that an electric current flows between different conductive materials that are kept at different temperatures, known as the Seebeck effect. It is the basis of the thermocouple and is considered the most accurate measurement of temperature. It is also a key component of the semi-conductor, the foundation of the modern computer business. Seebeck's work was the basis of German physicist Georg Simon Ohm (1789-1854) discoveries in electricity and of French physicist Jean Charles Athanase Peltier (1785-1845), whose Peltier effect became well known as a way to use electricity to freeze water (air conditioning, refrigeration). |
|
09 Apr 1791

George Peacock |
birth George Peacock Born 9 Apr 1791; died 8 Nov 1858 at age 67. English mathematician who, with fellow Cambridge undergraduates Charles Babbage and John Herschel brought reform to nomenclature in English mathematics. They formed the Analytical Society (1815) whose aims were to bring the advanced methods of calculus from Europe to Cambridge to replace the increasingly stagnant notation of Isaac Newton from the previous century. The Society produced a translation of a book of Lacroix in the differential and integral calculus. In 1830, he published Treatise on Algebra which attempted to give algebra a logical treatment, and which went at least partway toward the establishment of symbolic algebra. Instead of using only numbers he used objects, and showed the associativity and commutativity of these objects. |
|
09 Apr 1806

Isambard Kingdom Brunel |
birth Isambard Kingdom Brunel Born 9 Apr 1806; died 15 Sep 1859 at age 53. English civil and mechanical engineer of great originality and productivity who designed the first transatlantic steamer, the Great Western. In 1823, he began work with his father, Marc Brunel, on the Thames Tunnel, and later became the resident engineer at the site. In 1829, Brunel designed a suspension bridge to cross the River Avon at Clifton. In 1831, he was appointed chief engineer at the Bristol Docks, and Brunel later designed the Monkwearmouth Docks and others at Plymouth, Cardiff, Brentford and Milford Haven. In 1833, age 27, he was appointed chief engineer of the Great Western Railway, the line that linked London to Bristol. He further built bridges, viaducts, and three steam ships: the Great Western, Great Britain and Great Eastern. |
|
09 Apr 1812

Humphry Davy farewell lecture |
Humphry Davy farewell lecture In 1812, Humphry Davy delivered his farewell lecture in the Theatre of the Royal Institution. It was a busy week for Davy: the day before, he was the first to be knighted by the Prince Regent (later King George IV). Two days after his farewell lecture, Davy married Mrs. Apreece, described in The Journal of the Royal Institution as a “lady of very considerable fortune.” The young Michael Faraday had been attending Davy's lectures, and became his amenuensis after Davy injured an eye in Oct 1812, while making an explosive chemical. In Feb 1813, Faraday became Davy's research assistant and protégé. Davy resigned his RI professorship on 5 Apr 1813. After years of researching and lecturing at the RI, by Feb 1833, Faraday became the Fullerian Professor of Chemistry at the Royal Institution. |
|
09 Apr 1815

Alphonse(-Eugène) Beau de Rochas |
birth Alphonse(-Eugène) Beau de Rochas Born 9 Apr 1815; died 27 Mar 1893 at age 77. French railway engineer who originated the theoretical principle of the four-stroke internal-combustion engine and provide a theoretical pressure diagram (1862). His achievement lay partly in his emphasizing the previously unappreciated importance of compressing the fuel-air mixture before ignition. (French patent #52,593, 16 Jan 1862). However, he never built such an engine, nor defended his patent when the German Nikolaus August Otto produced a four-stroke engine in 1876. Beau de Rochas proposed other ideas: a rail tunnel beneath the English Channel, a submarine telegraph, a new kind of drive for canal boats, the use of steel for high-pressure boilers, and a method of improving the adhesion of locomotive wheel on Alpine tracks. |
|
09 Apr 1816

Charles-Eugène Delaunay |
birth Charles-Eugène Delaunay Born 9 Apr 1816; died 5 Aug 1872 at age 56. French mathematician and astronomer whose theory of lunar motion advanced the development of planetary-motion theories. After 20 years of work, he published two volumes on lunar theory, La Théorie du mouvement de la lune (1860,1867). This is an important case of the three body problem. Delaunay found the longitude, latitude and parallax of the Moon as infinite series. These gave results correct to 1 second of arc but were not too practical as the series converged slowly. However this work was important in the beginnings of functional analysis. Delaunay succeeded Le Verrier as director of the Paris Observatory in 1870 but two years later he and three companions drowned in a boating accident. |
|
09 Apr 1839

telegraph |
telegraph (technology) The world's first commercial electric telegraph line comes into operation alongside the Great Western Railway in England. |
|
09 Apr 1850

William Prout |
death William Prout Died 9 Apr 1850 at age 65 (born 15 Jan 1785). English biochemist and physiologist who is noted for his discoveries concerning digestion, metabolic chemistry, and atomic weights. He is best known for formulating Prout's hypothesis (1815) which states that the atomic weights of all elements are exact multiples of the atomic weight of hydrogen. At that time the atomic weight of hydrogen was taken to be 1.0, the hypothesis implied that all atomic weights would be whole numbers. In 1818, he isolated urea and uric acid for the first time. Six years later, he found hydrochloric acid in the digestive juices of the stomach. He was the first scientist (1827) to classify the components of food into the three main divisions of carbohydrates, fats and proteins. In 1920, Ernest Rutherford named the proton after Prout. |
|
09 Apr 1864

Sebastian Ziani de Ferranti |
birth Sebastian Ziani de Ferranti Born 9 Apr 1864; died 13 Jan 1930 at age 65. English electrical engineer who promoted the installation of large electrical generating stations and alternating current distribution networks in England. He was interested in electrical and mechanical devices as a youth, and in 1881, began such employment while in his late teens. In his 20's, he began planning an ambitious generating station about 8 miles outside London, to use transmission at an unprecedented 10,000 volts - four times greater than previously practical. For this he began designing suitable cables, transformers and generators. His idea of making high voltage flexible cables using wax-impregnated paper for insulation was a landmark development used exclusively until the advent of synthetic materials. His 176 patents cover varied inventions. |
|
09 Apr 1865

Charles Proteus Steinmetz |
birth Charles Proteus Steinmetz Born 9 Apr 1865; died 26 Oct 1923 at age 58. German-American electrical engineer and inventor whose theories and mathematical analysis of alternating current systems helped establish them as the preferred form of electrical energy in the United States, and throughout the world. In 1893, Steinmetz joined the newly organized General Electric Company where he was an engineer then consultant until his death. His early research on hysteresis (loss of power due to magnetic resistance) led him to study alternating current, which could eliminate hysteresis loss in motors. He did extensive new work on the theory of a.c. for electrical engineers to use. His last research was on lightning, and its threat to the new AC power lines. He was responsible for the expansion of the electric power industry in the U.S. |
|
09 Apr 1869

American Museum of Natural History incorporated |
American Museum of Natural History incorporated In 1869, a society in the name of the American Museum of Natural history was incorporated. Its founding had been urged in a letter, dated 30 Dec 1868, and sent to Andrew H. Green, Comptroller of Central Park, New York, signed by 19 persons, including Theodore Roosevelt, A.G. Phelps Dodge and J. Piermont Morgan. They wrote: “A number of gentlemen having long desired that a great Museum of Natural History should be established in Central Park, and having now the opportunity of securing a rare and very valuable collection as a nucleus of such Museum, the undersigned wish to enquire if you are disposed to provide for its reception and development.” Their suggestion was accepted by the Park officials. Collections were purchased, and thus the great museum began. It opened 27 Apr 1871. |
|
09 Apr 1869

Élie-Joseph Cartan |
birth Élie-Joseph Cartan Born 9 Apr 1869; died 6 May 1951 at age 82. French mathematician who greatly developed the theory of Lie groups and contributed to the theory of subalgebras. By 1904 Cartan was turning to papers on differential equations and from 1916 on he published mainly on differential geometry. Cartan also published work on relativity and the theory of spinors. He is certainly one of the most important mathematicians of the first half of the 20th century. |
|
09 Apr 1872

Dried milk |
Dried milk In 1872, dried milk was patented by Samuel R. Percy. |
|
09 Apr 1889

Michel-Eugène Chevreul |
death Michel-Eugène Chevreul Died 9 Apr 1889 at age 102 (born 31 Aug 1786). French chemist who began the study of the chemistry of fats. He discovered fatty acids, which led to a great improvement in the quality of stearine candles and in the fats used to make soaps. Stearine was first described by Chevreul in 1814 and was produced by heating glycerine with stearic acid. When used in candles it gave a steadier, brighter, odourless light. He was the first to find sugar in urine. He investigated and named margarine. In physics, he introduced (1839) his attempt at producing a systematic approach to seeing colours. In his 90s he turned to the study of the psychology of the elderly. When he died at 102, in his lifespan he had experienced both the French Revolution and the building of the Eiffel Tower. |
|
09 Apr 1895

Cistern cleaners |
Cistern cleaners In 1895, cistern cleaners were patented by black American inventor, R.H. Gray, (No. 537,151). In Aug 1894, he received a patent for a baling press. |
|
09 Apr 1895

Saturn's rings |
Saturn's rings In 1895, a spectrogram made by American astronomer James Keeler proved that the rings of Saturn were indeed composed of meteoric particles, as predicted by James Maxwell. If the rings were solid, observations would show uniform rotation. However, Keeler's spectrogram of light reflected from Saturn's rings showed a Doppler shift indicating a variation in radial velocity. Thus, particles in the inner part of a ring, closer to Saturn, move at a different rotational speed from those in more distance parts of a ring, as predicted by Kepler's 3rd law. Keeler published A Spectroscopic Proof of the Meteoric Constitution of Saturn's Rings in the May 1895 issue of Astrophysical Journal, vol. 1, p.416, the journal he co-founded with George E. Hale. |
|
09 Apr 1899

James S. McDonnell |
birth James S. McDonnell Born 9 Apr 1899; died 22 Aug 1980 at age 81. American aircraft manufacturer of aircraft. McDonnell started his first company in 1928, to build the single Doodlebug, but since it found no market, he spent the next 10 years working for several aircraft companies. Then he founded the St. Louis based McDonnell Aircraft Co.on 6 Jul 1939. Among his notable achievements were the production of the U.S. Navy's first carrier based jet fighter (1946), the FM-1; Mercury, America's first manned space craft to orbit the earth (1962), and the F-4 Phantom jet. |
|
09 Apr 1901

Howard A. Rusk |
birth Howard A. Rusk Born 9 Apr 1901; died 4 Nov 1989 at age 88. American physician who founded the science of rehabilitation medicine (also known as physiatry or physical therapy), which he established through efforts to rehabilitate wounded soldiers during and after WW II. He established the Rehabilitation Services in the Air Force for the casualties returning from combat. The program operated in 215 hospitals and 12 rehabilitation centers.Now this specialized medical service is aimed at rehabilitating persons disabled by such diverse problems as fractures, burns, tuberculosis, painful backs, strokes, nerve and spinal cord injuries, diabetes, birth defects, arthritis, and vision and speech impairments. He wrote a weekly column for the New York Times (1945-70). |
|
09 Apr 1903

Gregory Pincus |
birth Gregory Pincus Born 9 Apr 1903; died 22 Aug 1967 at age 64. Gregory (Goodwin) Pincus was an American endocrinologist whose work on the antifertility properties of steroids led to the development of the first effective oral contraceptive: the birth-control pill. In 1934, Pincus made national headlines by achieving in-vitro fertilization of rabbits. The public was not ready for the vision of test-tube babies; instead of fame, he received notoriety. Consequently, he moved a small independent laboratory. There he did applied research, especially on steroids. In 1953, he was approached about developing a new form of contraception. He focussed on using progesterone as an effective anti-ovulent, and showed it could be a good contraceptive drug. In 1960, a synthetic progesterone drug was approved for contraceptive use. |
|
09 Apr 1903

Gregory Goodwin Pincus |
birth Gregory Goodwin Pincus Gregory Goodwin Pincus (died 1967), American biologist who co-invented the combined oral contraceptive pill. |
|
09 Apr 1915

Friedrich August Johannes Löffler |
death Friedrich August Johannes Löffler Died 9 Apr 1915 at age 62 (born 24 Jun 1852). German bacteriologist who discovered the organism that causes diphtheria, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, (1884) which had first been observed by the German physiologist Theodor Klebs in the throats of diphtheria patients (the organism became known as the Klebs-Löffler bacillus). The isolation and cultivation of pure cultures involved a number of formidable technical problems; Löffler found it necessary to develop a new medium, thickened serum, as the conventional gelatin used by Robert Koch required temperatures far too low for the diphtheria pathogen. In 1898, with Paul Frosch, he showed that viruses could cause diseases in animals by passing foot-and-mouth disease in cows by inoculation with cell-free filtrates taken from lesions. |
|
09 Apr 1919

J. Presper Eckert Jr. |
birth J. Presper Eckert Jr. Born 9 Apr 1919; died 3 Jun 1995 at age 76. American engineer and inventor of the first general-purpose electronic computer, a digital machine that was the prototype for most computers in use today. In 1946, Eckert with John W. Mauchly fulfilled a government contract to build a digital computer to be used by the U.S. Army for military calculations. They named it ENIAC for Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer. By 1949, they had started a manufacturing company for their BINAC computer. This was followed by a business oriented computer, UNIVAC (1951), which was put to many uses and spurred the growth of the computer industry. By 1966 Eckert held 85 patents, mostly for electronic inventions. |
|
09 Apr 1920

Alex Moulton |
birth Alex Moulton Alex Moulton, English mechanical engineer and inventor (died 2012) |
|
09 Apr 1920

Moritz Cantor |
death Moritz Cantor Moritz Cantor, German historian of mathematics (born 1829). |
|
09 Apr 1922

Sir Patrick Manson |
death Sir Patrick Manson Died 9 Apr 1922 at age 77 (born 3 Oct 1844). Scottish physician and parasitologist who has been called the “father of tropical medicine.” He was the first to identify an insect for the spread of infection (1877-79). While working at Amoy, China, he found the development phase of filaria worms in the tissues of blood-sucking mosquitoes. This parasite worm causes the filariasis disease when transferred to human body tissues. In 1894, he proposed a mosquito-malaria hypothesis. Manson moved to Hong Kong (1883-89), where he set up a medical school. In 1886 he co-founded Dairy Farm to produce contamination-free cows' milk. He also researched sleeping sickness and beri-beri, and helped introduce vaccination to the Chinese. He inspired Alphonse Laveran's discovery of the malarial parasite, and Sir Ronald Ross's proof of transmission of malaria by Anopheles mosquitoes. |
|
09 Apr 1922

Patrick Manson |
death Patrick Manson Sir Patrick Manson (born 1844), the "father of tropical medicine". |
|
09 Apr 1929

Frederick Cossom Hollows |
birth Frederick Cossom Hollows Born 9 Apr 1929; died 10 Feb 1993 at age 63. New Zealand-born Australian physician, who was a leader in the campaign to combat eye diseases (especially trachoma) among Aboriginal peoples and cofounder of the Aboriginal Medical Service (AMS), which established a system of community clinics. |
|
09 Apr 1934

Oskar von Miller |
death Oskar von Miller Died 9 Apr 1934 at age 78 (born 7 May 1855). German electrical engineer who fostered the electric-power industry in Germany and founded the Deutsches Museum of science and technology in Munich. He made fundamental initial experiments on long-distance energy transmission such as (in 1882) over 57 km from Miesbach to Munich with 1400 volts direct current. In 1891, he organized a 20,000-volt power transmission line over 175 km from Lauffen to Frankfurt, an important advance in the transmission of alternating current. From 1918-24, he was project manager building the power station on Lake Walchen, at that time the largest hydroelectric power station in the world. With an average of 300 million kWh a year, the Lake Walchen power plant is still one of Germany's largest peak load power stations. |
|
09 Apr 1951

Vilhelm Bjerknes |
death Vilhelm Bjerknes Died 9 Apr 1951 at age 89 (born 14 Mar 1862). Vilhelm F(riman) K(oren) Bjerknes was a Norwegian meteorologist and physicist, one of the founders of the modern science of weather forecasting. As a young boy, Bjerknes assisted his father, Carl Bjerknes (a professor of mathematics) in carrying out experiments to verify the theoretical predictions that resulted from his father's hydrodynamic research. After graduating from university, Bjerknes moved on to his own work applying hydrodynamic and thermodynamic theories to atmospheric and hydrospheric conditions in order to predict future weather conditions. His work in meteorology and on electric waves was important in the early development of wireless telegraphy. He evolved a theory of cyclones known as the polar front theory with his son Jakob. |
|
09 Apr 1959

First astronauts selected |
First astronauts selected In 1959, NASA announced the selection of America's first seven astronauts for project Mercury. Scott Carpenter, Gordon Cooper, John Glenn, Gus Grissom, Wally Schirra, Alan Shepard and Donald Slayton were chosen from 110 applicants. Their training program at Langley, which ranged from a graduate-level course in introductory space science to simulator training and scuba-diving. Project Mercury, NASA's first high profile program, was an effort to learn if humans could survive in space. NASA required astronaut candidates to be male, not over 40 years old, not more than 5' 11" height and in excellent physical condition. On 5 May 1961, Shepard became the first American in space. |
|
09 Apr 1969

First flight of British Concorde prototype 002 |
First flight of British Concorde prototype 002 In 1969, the British Concorde prototype 002 left Filton airport, Bristol, on its first flight with test pilot Brian Trubshaw at the controls. The French prototype Concorde 001 had already made its first flight the previous month, on 2 Mar 1969, from Toulouse. An even earlier first flight was made on 31 Dec 1968, by the Russian Tupolev TU-144 supersonic-capable airliner (a Concorde look-alike, dubbed Concordski in the West). The first Concorde to fly at supersonic speed, over Mach 1, was prototype 001 on 1 Oct 1969. |
|
09 Apr 1974
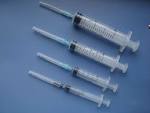
Disposable syringe |
Disposable syringe In 1974, African American, Phil Brooks was issued a U.S. patent for a disposable syringe (No. 3,802,434). |
|
09 Apr 1981

Longest scientific name |
Longest scientific name In 1981, Nature published the longest scientific name in history. With 16,569 nucleotides, the systematic name for human mitochondrial DNA is 207,000 letters long. |
|
09 Apr 1982

Robert Havemann |
death Robert Havemann Robert Havemann (b. 1910), German chemist. |