| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1894

David Bruce |
David Bruce (biology) David Bruce discovers the Trypanosoma parasite carried by the tsetse fly which causes the fatal cattle disease nagana. |
|
30 Nov 1894

Emil Fischer |
Emil Fischer (chemistry) Emil Fischer and Arthur Speier first describe Fischer–Speier esterification. |
|
30 Nov 1894

Eugen Warming |
Eugen Warming (ecology) Eugen Warming publishes Plantesamfund (translated as Oecology of Plants, 1909) and founds the scientific discipline ecology. |
|
30 Nov 1894

Sigmund Freud |
Sigmund Freud (psychiatry) Sigmund Freud and Josef Breuer publish Studien über Hysterie (Studies on Hysteria). |
|
30 Nov 1894

Ernest A. Hummel |
Ernest A. Hummel (technology) Ernest A. Hummel invents the telediagraph. |
|
30 Nov 1894

Copley Medal |
Copley Medal (awards) Copley Medal: Karl Weierstrass |
|
30 Nov 1894

Wollaston Medal |
Wollaston Medal (awards) Wollaston Medal for Geology: Archibald Geikie |
|
30 Nov 1894

Oscar H. Banker |
birth Oscar H. Banker Asatour Sarafian, later Oscar H. Banker (died 1979), Armenian American inventor. |
|
11 Jan 1895

Laurens Hammond |
birth Laurens Hammond Laurens Hammond (died 1973), American inventor. |
|
26 Jan 1895

Arthur Cayley |
death Arthur Cayley Arthur Cayley (born 1821), English mathematician. |
|
13 Feb 1895

Auguste and Louis Lumière |
Auguste and Louis Lumière (technology) Auguste and Louis Lumière patent their cinematograph motion picture film camera/projector in France. |
|
22 Mar 1895

Lumieres' first movie |
Lumieres' first movie In 1895, the first motion picture shown on a screen was presented by Auguste and Louis Lumière. An invited audience at 44 Rue de Rennes in Paris, France, viewed the film La Sortie des ouvriers de l'usine Lumière. The film they shot specially for the occasion shows workers leaving the Lumières' own factory in Lyon, which made all kinds of photographic products. The workers streamed out, most on foot and some on bicycles. Several more such screenings followed before the first public performance, at the Salon Indien of the Grand Café, 14 Boulevard des Capucines in Paris on 28th Dec 1895. The Lumières soon began opening cinemas in London, Brussels, Berlin and New York. |
|
26 Mar 1895

Scottish |
Scottish (chemistry) Scottish chemist William Ramsay isolates helium on Earth by treating the mineral cleveite. These samples are identified as helium by Norman Lockyer and William Crookes. It is independently isolated from cleveite in the same year by Per Teodor Cleve and Abraham Langlet in Uppsala, Sweden, who determine its atomic weight. |
|
09 Apr 1895

Cistern cleaners |
Cistern cleaners In 1895, cistern cleaners were patented by black American inventor, R.H. Gray, (No. 537,151). In Aug 1894, he received a patent for a baling press. |
|
09 Apr 1895

Saturn's rings |
Saturn's rings In 1895, a spectrogram made by American astronomer James Keeler proved that the rings of Saturn were indeed composed of meteoric particles, as predicted by James Maxwell. If the rings were solid, observations would show uniform rotation. However, Keeler's spectrogram of light reflected from Saturn's rings showed a Doppler shift indicating a variation in radial velocity. Thus, particles in the inner part of a ring, closer to Saturn, move at a different rotational speed from those in more distance parts of a ring, as predicted by Kepler's 3rd law. Keeler published A Spectroscopic Proof of the Meteoric Constitution of Saturn's Rings in the May 1895 issue of Astrophysical Journal, vol. 1, p.416, the journal he co-founded with George E. Hale. |
|
11 Apr 1895

Lothar Meyer |
death Lothar Meyer Lothar Meyer (born 1830), German chemist. |
|
26 Apr 1895

Wildlife Conservation Society |
Wildlife Conservation Society (biology) The New York Zoological Society, the modern-day Wildlife Conservation Society, is chartered. |
|
01 May 1895

H. G. Wells |
H. G. Wells (other s) Publication of H. G. Wells' first "scientific romance", the novella The Time Machine (serial publication completed and first book editions). |
|
05 May 1895

Karl Vogt |
death Karl Vogt Karl Vogt (born 1817), German scientist who published notable works in zoology, geology and physiology. |
|
06 May 1895
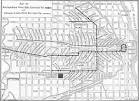
Metropolitan West Side Elevated Railroad |
Metropolitan West Side Elevated Railroad (technology) The Metropolitan West Side Elevated Railroad is opened in Chicago as the first electrically operated rapid transit system in the United States, including the first completed Scherzer rolling lift bridge. |
|
07 May 1895

Alexander Stepanovich Popov |
Alexander Stepanovich Popov (physics) Alexander Stepanovich Popov demonstrates a radio receiver (containing a coherer) refined as a lightning detector to the Russian Physico-Chemical Society, recognized as the first practical application of electromagnetic waves. |
|
20 May 1895

R. J. Mitchell |
birth R. J. Mitchell R. J. Mitchell (died 1937), English aeronautical engineer. |
|
29 Jun 1895

Thomas Henry Huxley |
death Thomas Henry Huxley Sir Thomas Henry Huxley (born 1825), English biologist. |
|
25 Jul 1895

Maria Skłodowska |
Maria Skłodowska (other s) Maria Skłodowska marries Pierre Curie in the town hall at Sceaux. |
|
10 Aug 1895

Ernst Felix Hoppe-Seyler |
death Ernst Felix Hoppe-Seyler Died 10 Aug 1895 at age 69 (born 26 Dec 1825). Ernst Felix (Immanuel) Hoppe-Seyler was a German physician, who was a pioneer of physiological chemistry (biochemistry). He studied the chemical of blood and urine using the new technique of absorption spectroscopy, prepared hemoglobin in crystalline form and clarified its role in red blood cells. He demonstrated that the oxidation reactions between haemoglobin, oxygen and carbon monoxide took place in the tissues rather than in the blood itself. He also studied chlorophyll and was the first to prepare lecithin in a pure form. He coined the word proteid, now replaced with the word protein. He also investigated bile acids, lipid metabolism, quantification and classification of proteins and inspired research on nucleic acids. |
|
10 Aug 1895

Felix Hoppe-Seyler |
death Felix Hoppe-Seyler Felix Hoppe-Seyler (born 1825), German physiologist. |
|
26 Aug 1895

Friedrich Miescher |
death Friedrich Miescher Friedrich Miescher (born 1844), Swiss biologist. |
|
14 Sep 1895

Charles Valentine Riley |
death Charles Valentine Riley Died 14 Sep 1895 at age 51 (born 18 Sep 1843). British-born American entomologist who pioneered the scientific study of insects for their economic impact in agriculture. He was a keen observer of relationships in nature, and enhanced his written observations with drawings. He initiated biological control. After studying the parasites and predators of the cottony cushion scale, which was destroying the citrus industry in California, he introduced (1888) a natural enemy of the scale from Australia. The effectiveness of the Vedalia cardinalis beetle in reducing the populations of the cottony cushion scale promoted the study of biological control of pests. He helped establish the Division of Entomology of the U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
|
24 Sep 1895

Hermann Hellriegel |
death Hermann Hellriegel Hermann Hellriegel (born 1831), German agricultural chemist who discovered the mechanism by which leguminous plants assimilate the free nitrogen of the atmosphere. |
|
28 Sep 1895

Louis Pasteur |
death Louis Pasteur Louis Pasteur (born 1822), French biologist. |
|
19 Oct 1895

Lewis Mumford |
birth Lewis Mumford Lewis Mumford (died 1990), American historian & philosopher of science. |
|
22 Oct 1895

Rolf Nevanlinna |
birth Rolf Nevanlinna Rolf Nevanlinna (died 1980), Finnish mathematician. |
|
23 Oct 1895

Hans Ferdinand Mayer |
birth Hans Ferdinand Mayer Hans Ferdinand Mayer (died 1980), German physicist. |
|
30 Oct 1895

Gerhard Domagk |
birth Gerhard Domagk Gerhard Domagk (died 1964), German winner of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. |
|
08 Nov 1895

Wilhelm Röntgen |
Wilhelm Röntgen (physics) Wilhelm Röntgen discovers a type of electromagnetic radiation which he calls X-rays. |
|
19 Nov 1895

Paper pencil |
Paper pencil In 1895, the first U.S. patent for a paper pencil was issued to Fredrick E. Blaisdell of Philadelphia, Pa. His patent No. 549,952 was accompanied by No. 550,212 on the same date on a machine for manufacturing pencils. |
|
02 Dec 1895

W. Conway Pierce |
birth W. Conway Pierce W. Conway Pierce (died 1974), American chemist. |
|
31 Dec 1895

electric bicycle |
electric bicycle (technology) Ogden Bolton Jr. is granted U.S. Patent 552,271 for an electric bicycle. |