| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1904

Dominion Observatory |
Dominion Observatory (astronomy) The Dominion Observatory opens in Ottawa. |
|
30 Nov 1904

minor planets |
minor planets (astronomy) Various astronomers discover the minor planets 554 Peraga through 583 Klotilde (see List of minor planets/501–600). |
|
30 Nov 1904

nova |
nova (astronomy) The nova V604 Aquilae appears in the constellation Aquila. |
|
30 Nov 1904
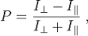
Umov effect |
Umov effect (astronomy) The Umov effect is noted by Nikolay Umov. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Reginald Punnett |
Reginald Punnett (biology) Reginald Punnett's Mendelism is published in Cambridge (U.K.), probably the first popular science book on genetics. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Frederick Blackman |
Frederick Blackman (biology) Frederick Blackman proposes his law of limiting factors in relation to photosynthesis. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Nettie Stevens |
Nettie Stevens (biology) Nettie Stevens and Edmund Beecher Wilson independently describe the XY sex-determination system. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Stamen Grigorov |
Stamen Grigorov (biology) Stamen Grigorov identifies the bacterium Lactobacillus bulgaricus, a major agent in the creation of yogurt. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Maltese |
Maltese (biology) Maltese doctor and archaeologist Themistocles Zammit identifies unpasteurized milk as the major source of the pathogen causing Brucellosis. |
|
30 Nov 1904

National Association of Audubon Societies for the Protection of Wild Birds and Animals |
National Association of Audubon Societies for the Protection of Wild Birds and Animals (biology) National Association of Audubon Societies for the Protection of Wild Birds and Animals established in the United States. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Carl von Linde |
Carl von Linde (chemistry) Carl von Linde obtains pure liquid oxygen and nitrogen by cooling air. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Alfred Einhorn |
Alfred Einhorn (chemistry) Alfred Einhorn synthesises the local anesthetic novocaine. |
|
30 Nov 1904
Frank–Caro process |
Frank–Caro process (chemistry) The first commercial use of the Frank–Caro process for the nitrogen fixation reaction of calcium carbide and atmospheric nitrogen to produce calcium nitrate as a fertilizer. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Fritz Haber |
Fritz Haber (chemistry) Fritz Haber and Carl Bosch develop the Haber process for making ammonia from its elements, a milestone in industrial chemistry with deep consequences in agriculture. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Pierre Fatou |
Pierre Fatou (mathematics) Pierre Fatou defines the Mandelbrot set. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Oswald Veblen |
Oswald Veblen (mathematics) Oswald Veblen proves the Jordan curve theorem. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Martin Kutta |
Martin Kutta (mathematics) Martin Kutta describes the popular fourth-order Runge-Kutta method. |
|
30 Nov 1904

James Cullen |
James Cullen (mathematics) James Cullen, S.J., begins the study of Cullen numbers. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Emanuel Lasker |
Emanuel Lasker (mathematics) Emanuel Lasker proves the Lasker–Noether theorem for the special case of polynomial rings. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Saurian Expedition |
Saurian Expedition (paleontology) The Saurian Expedition led by John C. Merriam recovers many specimens of ichthyosaur. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Henry Fairfield Osborn |
Henry Fairfield Osborn (paleontology) Tyrannosaurus rex is described and named by Henry Fairfield Osborn. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Albert Einstein |
Albert Einstein (physics) Albert Einstein publishes his four Annus Mirabilis papers. In particular, he formulates the theory of special relativity and states the law of mass-energy conservation: E = mc². He also explains the photoelectric effect by quantization and mathematically analyzes Brownian motion. Because of this, 1905 is said to be the miraculous year for physics, and its 100th anniversary (2005) will be declared the World Year of Physics. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Nikolai Korotkov |
Nikolai Korotkov (physiology and medic) Nikolai Korotkov first describes auscultatory blood pressure measurement. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Karl Landsteiner |
Karl Landsteiner (physiology and medic) Karl Landsteiner first describes Meconium ileus. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Sigmund Freud |
Sigmund Freud (psychology) Sigmund Freud publishes Drei Abhandlungen zur Sexualtheorie (Three Essays on the Theory of Sexuality) and Der Witz und seine Beziehung zum Unbewußten (Jokes and their Relation to the Unconscious). |
|
30 Nov 1904

Pathé Frères |
Pathé Frères (technology) Pathé Frères colorise black-and-white films by machine. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Alfred Buchi |
Alfred Buchi (technology) Alfred Buchi files a patent for the turbocharger. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Paul de Vivie |
Paul de Vivie (technology) Paul de Vivie invents a two-speed rear-wheel derailleur gear for bicycles. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Pipe |
Pipe (technology) Pipe manufactures the first automobile with a hemi engine. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Walter Griffiths |
Walter Griffiths (technology) Walter Griffiths invents a manually powered domestic vacuum cleaner. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Reginald Fessenden |
Reginald Fessenden (technology) Reginald Fessenden invents the superheterodyne receiver. |
|
30 Nov 1904

bascule bridge |
bascule bridge (technology) First bascule bridge to the design of Joseph Strauss built. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Ivan Sechenov |
death Ivan Sechenov November 15 (O.S. November 2) – Ivan Sechenov (born 1829), "the father of Russian physiology" |
|
02 Jan 1905

Charles Dillon Perrine |
Charles Dillon Perrine (astronomy) Charles Dillon Perrine at Lick Observatory discovers Elara, one of Jupiter's natural satellites. |
|
04 Jan 1905

Paul Henry |
death Paul Henry Paul Henry (born 1848), astronomer |
|
14 Jan 1905

Ernst Abbe |
death Ernst Abbe Ernst Abbe (born 1840), physicist |
|
17 Jan 1905

Punchboards |
Punchboards In 1905, the first U.S. patent was issued for a punchboard to Charles A. Brewer and Clinton G. Scannell of Chicago, Illinois, described as “vending devices.” They were manufactured by Charles A. Brewer & Sons in the same city. (No. 780,086). Even though the equivalent of punchboards had been around for many years, they had never been available in such a neat and portable form. The invention of board stuffing machines and ticket folding and plaiting machines in the late 1910s was probably the key factor which allowed the punchboard industry to flourish. Once the boards became cheap to manufacture, they flooded the country. Noted gambling author John Scarne estimates that 30 million punchboards were sold in 1910-15. |
|
01 Feb 1905

Emilio G. Segrè |
birth Emilio G. Segrè Emilio G. Segrè (died 1989), physicist, Nobel laureate |
|
02 Feb 1905

Adolf Bastian |
death Adolf Bastian Died 2 Feb 1905 at age 78 (born 26 Jun 1826). German ethnologist and world traveller who theorized that there is a general psychic unity of humankind that is responsible for certain elementary ideas common to all peoples (Elementargedanken). Bastian proposed, on the other hand, that cultural traits, folklore, myths, and beliefs of various ethnic groups originate within each group according to laws of cultural evolution (Volkergedanken). He was the first director of the Berlin Ethnological Museum and established the Berlin Anthropology Society. |
|
23 Feb 1905

Derrick Henry Lehmer |
birth Derrick Henry Lehmer Derrick Henry Lehmer (died 1991), mathematician |
|
18 Mar 1905

Thomas Townsend Brown |
birth Thomas Townsend Brown Thomas Townsend Brown (died 1985), American inventor |
|
24 Mar 1905

Jules Verne |
death Jules Verne Jules Verne (born 1828), science fiction author |
|
27 Mar 1905

Elsie MacGill |
birth Elsie MacGill Elsie MacGill (died 1980), aeronautical engineer, "Queen of the Hurricanes" |
|
13 Apr 1905

Bruno Rossi |
birth Bruno Rossi Born 13 Apr 1905; died 21 Nov 1993 at age 88. Bruno Benedetto Rossi was an Italian-American physicist who was a pioneer in the study of cosmic radiation. In the 1930s, his experimental investigations of cosmic rays and their interactions with matter laid the foundation for high energy particle physics. Cosmic rays are atomic particles that enter earth's atmosphere from outer space at speeds approaching that of light, bombarding atmospheric atoms to produce mesons as well as secondary particles possessing some of the original energy. He was one of the first to use rockets to study cosmic rays above the Earth's atmosphere. Finding X-rays from space he became the grandfather of high energy astrophysics, being largely responsible for starting X-ray astronomy, as well as the study of interplanetary plasma. |
|
14 Apr 1905

Otto Wilhelm von Struve |
death Otto Wilhelm von Struve Otto Wilhelm von Struve (born 1819), astronomer |
|
18 Apr 1905

William Bateson |
William Bateson (biology) William Bateson coins the term "genetics" in a letter to Adam Sedgwick. |
|
18 Apr 1905

George H. Hitchings |
birth George H. Hitchings George H. Hitchings (died 1998), scientist, Nobel laureate in Medicine |
|
20 Apr 1905

Albrecht Unsöld |
birth Albrecht Unsöld Albrecht Unsöld (died 1995), astronomer |
|
29 May 1905

Largest transporter bridge |
Largest transporter bridge In 1905, the Runcorn-Widnes Transporter Bridge was opened to replace a ferry across the River Mersey. It was the first of its kind in Britain: a high-level gantry along which a wheeled trolley travelled with a cargo-carrying platform suspended beneath it at ground level. Thus traffic could cross the river using a bridge that needed no long approach ramps required for a high-level road bridge, and yet permitted tall, ocean-going ships to pass beneath the structure. The span of the bridge was 1000-ft (305-m) with towers standing 190-ft (58-m) above high water. It was the largest of its type ever built in the world, designed by John Webster and John Wood. It closed on 22 Jul 1961 and shortly afterwards was demolished. |
|
01 Jun 1905

Alfred Binet |
Alfred Binet (psychology) Alfred Binet and Théodore Simon publish the first Binet-Simon Intelligence Test for intelligence testing of children with mental retardation. |
|
18 Jun 1905

Per Teodor Cleve |
death Per Teodor Cleve Per Teodor Cleve (born 1840), chemist |
|
25 Jun 1905

Rupert Wildt |
birth Rupert Wildt Born 25 Jun 1905; died 9 Jan 1976 at age 70. German-American astronomer who studied atmospheres of planets. He identified (1932) certain absorption bands (observed by Slipher) in the spectra of Jupiter and the outer planets as indicative of ammonia and methane as minor components of these planets which are primarily composed of hydrogen and helium. He speculated (1937) that droplets of formaldehyde formed the clouds of Venus, since water was not detected. (In fact, surface water is absent on Venus, but the clouds do contain water with sulphur and sulphuric acid.) In 1939, he realized the importance of the negative hydrogen ion for stellar opacity. By the 1940s, he proposed the greenhouse theory to explain how atmospheric gases produced unexpectedly high temperatures of Venus. |
|
07 Jul 1905

Marie-Louise Dubreil-Jacotin |
birth Marie-Louise Dubreil-Jacotin Marie-Louise Dubreil-Jacotin (died 1972), mathematician |
|
01 Aug 1905

Helen Sawyer Hogg |
birth Helen Sawyer Hogg Helen Sawyer Hogg (died 1993), astronomer |
|
11 Aug 1905

Erwin Chargaff |
birth Erwin Chargaff Erwin Chargaff (died 2002), biochemist |
|
16 Aug 1905

Marian Rejewski |
birth Marian Rejewski Marian Rejewski (died 1980), mathematician and cryptologist |
|
20 Aug 1905

Franz Reuleaux |
death Franz Reuleaux Franz Reuleaux (born 1829), mechanical engineer |
|
31 Aug 1905

Robert Bacher |
birth Robert Bacher Robert Bacher (died 2004), nuclear physicist |
|
03 Sep 1905

Carl David Anderson |
birth Carl David Anderson Carl David Anderson (died 1991), physicist, Nobel laureate |
|
14 Sep 1905

RAC |
RAC In 1905, the oldest car race still run was first held on the Isle of Man, Great Britain for the Royal Automobile Club Tourist Trophy. |
|
17 Sep 1905

Hans Freudenthal |
birth Hans Freudenthal Hans Freudenthal (died 1990), mathematician |
|
19 Sep 1905

Thomas Barnardo |
death Thomas Barnardo Thomas Barnardo (born 1845), physician and philanthropist |
|
22 Sep 1905

Eugen Sänger |
birth Eugen Sänger Eugen Sänger (died 1964), aerospace engineer |
|
24 Sep 1905

Severo Ochoa |
birth Severo Ochoa Severo Ochoa (died 1993), biochemist, Nobel laureate |
|
30 Sep 1905

Sir Nevill F. Mott |
birth Sir Nevill F. Mott Born 30 Sep 1905; died 8 Aug 1996 at age 90. Nevill Francis Mott was an English physicist who shared (with PhilipW. Anderson and John H. Van Vleck of the U.S.) the 1977 Nobel Prize for Physics for his independent researches on the magnetic and electrical properties of amorphous semiconductors. Whereas the electric properties of crystals are described by the Band Theory - which compares the conductivity of metals, semiconductors, and insulators - a famous exception is provided by nickel oxide. According to band theory, nickel oxide ought to be a metallic conductor but in reality is an insulator. Mott refined the theory to include electron-electron interaction and explained so-called Mott transitions, by which some metals become insulators as the electron density decreases by separating the atoms from each other in some convenient way. |
|
30 Sep 1905

Nevill Francis Mott |
birth Nevill Francis Mott Nevill Francis Mott (died 1996), physicist, Nobel laureate |
|
06 Oct 1905

Ferdinand von Richthofen |
death Ferdinand von Richthofen Ferdinand von Richthofen (born 1833), geologist |
|
15 Oct 1905

C. P. Snow |
birth C. P. Snow C. P. Snow (died 1980), physicist and novelist |
|
22 Oct 1905

Karl Guthe Jansky |
birth Karl Guthe Jansky Karl Guthe Jansky (died 1950), physicist |
|
22 Oct 1905

Albert Whitford |
birth Albert Whitford Albert Whitford (died 2002), astronomer |
|
23 Oct 1905

Felix Bloch |
birth Felix Bloch Felix Bloch (died 1983), physicist, Nobel laureate |
|
31 Oct 1905

Harry Harlow |
birth Harry Harlow Harry Harlow (died 1981), psychologist |
|
07 Dec 1905

Gerard Kuiper |
birth Gerard Kuiper Gerard Kuiper (died 1973), astronomer |
|
16 Dec 1905

Piet Hein |
birth Piet Hein Piet Hein (died 1996), mathematician |
|
22 Dec 1905

Tommy Flowers |
birth Tommy Flowers Tommy Flowers (died 1998), computer engineer |
|
29 Dec 1905

Henri-Gaston Busignies |
birth Henri-Gaston Busignies Born 29 Dec 1905; died 20 Jun 1981 at age 75. French-American electrronics engineer whose invention (1936) of high-frequency direction finders (HF/DF, or "Huff Duff") permitted the U.S. Navy during World War II to detect enemy transmissions and quickly pinpoint the direction from which a radio transmission was coming. Busignies invented the radiocompass (1926) while still a student at Jules Ferry College in Versailles, France. In 1934, he started developing the direction finder based on his earlier radiocompass. Busignies developed the moving target indicator for wartime radar. It scrubbed off the radar screen every echo from stationary objects and left only echoes from moving objects, such as aircraft. |