| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1904

Dominion Observatory |
Dominion Observatory (astronomy) The Dominion Observatory opens in Ottawa. |
|
30 Nov 1904

minor planets |
minor planets (astronomy) Various astronomers discover the minor planets 554 Peraga through 583 Klotilde (see List of minor planets/501–600). |
|
30 Nov 1904

nova |
nova (astronomy) The nova V604 Aquilae appears in the constellation Aquila. |
|
30 Nov 1904
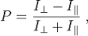
Umov effect |
Umov effect (astronomy) The Umov effect is noted by Nikolay Umov. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Reginald Punnett |
Reginald Punnett (biology) Reginald Punnett's Mendelism is published in Cambridge (U.K.), probably the first popular science book on genetics. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Frederick Blackman |
Frederick Blackman (biology) Frederick Blackman proposes his law of limiting factors in relation to photosynthesis. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Nettie Stevens |
Nettie Stevens (biology) Nettie Stevens and Edmund Beecher Wilson independently describe the XY sex-determination system. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Stamen Grigorov |
Stamen Grigorov (biology) Stamen Grigorov identifies the bacterium Lactobacillus bulgaricus, a major agent in the creation of yogurt. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Maltese |
Maltese (biology) Maltese doctor and archaeologist Themistocles Zammit identifies unpasteurized milk as the major source of the pathogen causing Brucellosis. |
|
30 Nov 1904

National Association of Audubon Societies for the Protection of Wild Birds and Animals |
National Association of Audubon Societies for the Protection of Wild Birds and Animals (biology) National Association of Audubon Societies for the Protection of Wild Birds and Animals established in the United States. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Carl von Linde |
Carl von Linde (chemistry) Carl von Linde obtains pure liquid oxygen and nitrogen by cooling air. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Alfred Einhorn |
Alfred Einhorn (chemistry) Alfred Einhorn synthesises the local anesthetic novocaine. |
|
30 Nov 1904
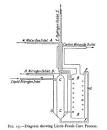
Frank–Caro process |
Frank–Caro process (chemistry) The first commercial use of the Frank–Caro process for the nitrogen fixation reaction of calcium carbide and atmospheric nitrogen to produce calcium nitrate as a fertilizer. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Fritz Haber |
Fritz Haber (chemistry) Fritz Haber and Carl Bosch develop the Haber process for making ammonia from its elements, a milestone in industrial chemistry with deep consequences in agriculture. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Pierre Fatou |
Pierre Fatou (mathematics) Pierre Fatou defines the Mandelbrot set. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Oswald Veblen |
Oswald Veblen (mathematics) Oswald Veblen proves the Jordan curve theorem. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Martin Kutta |
Martin Kutta (mathematics) Martin Kutta describes the popular fourth-order Runge-Kutta method. |
|
30 Nov 1904

James Cullen |
James Cullen (mathematics) James Cullen, S.J., begins the study of Cullen numbers. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Emanuel Lasker |
Emanuel Lasker (mathematics) Emanuel Lasker proves the Lasker–Noether theorem for the special case of polynomial rings. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Saurian Expedition |
Saurian Expedition (paleontology) The Saurian Expedition led by John C. Merriam recovers many specimens of ichthyosaur. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Henry Fairfield Osborn |
Henry Fairfield Osborn (paleontology) Tyrannosaurus rex is described and named by Henry Fairfield Osborn. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Albert Einstein |
Albert Einstein (physics) Albert Einstein publishes his four Annus Mirabilis papers. In particular, he formulates the theory of special relativity and states the law of mass-energy conservation: E = mc². He also explains the photoelectric effect by quantization and mathematically analyzes Brownian motion. Because of this, 1905 is said to be the miraculous year for physics, and its 100th anniversary (2005) will be declared the World Year of Physics. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Nikolai Korotkov |
Nikolai Korotkov (physiology and medic) Nikolai Korotkov first describes auscultatory blood pressure measurement. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Karl Landsteiner |
Karl Landsteiner (physiology and medic) Karl Landsteiner first describes Meconium ileus. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Sigmund Freud |
Sigmund Freud (psychology) Sigmund Freud publishes Drei Abhandlungen zur Sexualtheorie (Three Essays on the Theory of Sexuality) and Der Witz und seine Beziehung zum Unbewußten (Jokes and their Relation to the Unconscious). |
|
30 Nov 1904

Pathé Frères |
Pathé Frères (technology) Pathé Frères colorise black-and-white films by machine. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Alfred Buchi |
Alfred Buchi (technology) Alfred Buchi files a patent for the turbocharger. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Paul de Vivie |
Paul de Vivie (technology) Paul de Vivie invents a two-speed rear-wheel derailleur gear for bicycles. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Pipe |
Pipe (technology) Pipe manufactures the first automobile with a hemi engine. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Walter Griffiths |
Walter Griffiths (technology) Walter Griffiths invents a manually powered domestic vacuum cleaner. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Reginald Fessenden |
Reginald Fessenden (technology) Reginald Fessenden invents the superheterodyne receiver. |
|
30 Nov 1904

bascule bridge |
bascule bridge (technology) First bascule bridge to the design of Joseph Strauss built. |
|
30 Nov 1904

Ivan Sechenov |
death Ivan Sechenov November 15 (O.S. November 2) – Ivan Sechenov (born 1829), "the father of Russian physiology" |