| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1907

Neanderthal |
Neanderthal (archaeology) A 40,000-year-old Neanderthal boy skeleton is found at Le Moustier in southwest France by Otto Hauser. |
|
30 Nov 1907
mean solar time |
mean solar time (astronomy) If its start and end are defined using mean solar time then due to the extreme length of day variation this is the longest year of the Julian calendar or Gregorian calendar, having a duration of 31622401.38 seconds of Terrestrial Time (or ephemeris time). |
|
30 Nov 1907

O.S. |
O.S. (astronomy) June 30 [O.S. June 17] – Tunguska event in Siberia, an explosion believed to have been caused by the air burst of a large meteoroid or comet fragment at an altitude of 5–10 kilometres (3–6 mi) above the Earth's surface. |
|
30 Nov 1907

Kikunae Ikeda |
Kikunae Ikeda (chemistry) Kikunae Ikeda discovers monosodium glutamate, the chemical behind the taste of umami. |
|
30 Nov 1907

Heike Kamerlingh Onnes |
Heike Kamerlingh Onnes (chemistry) Heike Kamerlingh Onnes liquefies helium. |
|
30 Nov 1907

G. H. Hardy |
G. H. Hardy (genetics) G. H. Hardy and Wilhelm Weinberg independently formulate the Hardy–Weinberg principle which states that both allele and genotype frequencies in a population remain in equilibrium unless disturbed. |
|
30 Nov 1907

Ulugh Beg Observatory |
Ulugh Beg Observatory (history of science) Site of Ulugh Beg Observatory located in Samarkand by Russian archaeologist V. L. Vyatkin. |
|
30 Nov 1907

National Technical Museum (Prague) |
National Technical Museum (Prague) (history of science) National Technical Museum (Prague) founded. |
|
30 Nov 1907

Ernst Zermelo |
Ernst Zermelo (mathematics) Ernst Zermelo axiomizes set theory, thus avoiding Cantor's contradictions. |
|
30 Nov 1907

Josip Plemelj |
Josip Plemelj (mathematics) Josip Plemelj solves the Riemann problem about the existence of a differential equation with a given monodromic group and uses Sokhotsky-Plemelj formulae. |
|
30 Nov 1907
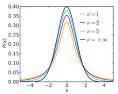
Student's t-distribution |
Student's t-distribution (mathematics) Student's t-distribution published by William Sealy Gosset (anonymously). |
|
30 Nov 1907

Swiss |
Swiss (medicine) Swiss psychiatrist Eugen Bleuler introduces the term schizophrenia. |
|
30 Nov 1907

Austrian American |
Austrian American (medicine) Austrian American pathologist Leo Buerger gives the first accurate pathological description of Thromboangiitis obliterans ("Buerger's disease") at Mount Sinai Hospital (Manhattan). |
|
30 Nov 1907

Victor Horsley |
Victor Horsley (medicine) Victor Horsley and R. Clarke invents the stereotactic method. |
|
30 Nov 1907

Hans Geiger |
Hans Geiger (physics) Hans Geiger and Ernest Rutherford invent the Geiger counter. |
|
30 Nov 1907

Gustav Mie |
Gustav Mie (physics) Gustav Mie publishes the Mie solution to Maxwell's equations on the scattering of electromagnetic radiation by a sphere. |
|
30 Nov 1907

radio |
radio (technology) A long-distance radio message is sent from the Eiffel Tower for the first time. |
|
30 Nov 1907

Henry Ford |
Henry Ford (technology) Henry Ford develops the assembly line method of automobile manufacturing and produces the first Model T automobile. |
|
03 Jan 1908

Charles Augustus Young |
death Charles Augustus Young Charles Augustus Young (born 1834), astronomer. |
|
15 Jan 1908

Edward Teller |
birth Edward Teller Edward Teller (died 2003), Hungarian-born physicist, inventor of the hydrogen bomb. |
|
18 Jan 1908

Jacob Bronowski |
birth Jacob Bronowski Jacob Bronowski (died 1974), Polish-born scientific polymath. |
|
22 Jan 1908

Lev Davidovich Landau |
birth Lev Davidovich Landau Lev Davidovich Landau (died 1968), Russian physicist. |
|
11 Feb 1908

Vivian Fuchs |
birth Vivian Fuchs Vivian Fuchs (died 1999), English geologist and explorer. |
|
23 Feb 1908

Friedrich von Esmarch |
death Friedrich von Esmarch Died 23 Feb 1908 at age 85 (born 9 Jan 1823). German surgeon who was the first to introduce a first-aid kit and triage on the battlefield. He introduced first aid training for both military and civilian personnel. His handbooks of military surgical techniques were used extensively as the best on the topic. The Esmarch bandage is a triangular piece of linen or cotton, with a long side about 4 ft. It can be used folded or open, and applied in 32 different ways. Esmarch insisted that every soldier carry one in battle for temporary dressing and field-work. Esmarch also invented an apparatus, using a narrow hard rubber tourniquet with a chain fastener to control bleeding in tying off an extremity in such a way that it is made bloodless. When used during amputation, being bloodless made it easier to operate on a limb. |
|
15 May 1908

Declaration of the Conservation Conference |
Declaration of the Conservation Conference In 1908, a declaration supporting conservation was issued at the conclusion of a three-day Conference of Governors held at the White House, called by Roosevelt to consider the problems of conservation. It recognized that the U.S. "natural resources include the land on which we live and which yields our food; the living waters which fertilize the soil, supply power, and form great avenues of commerce; the forests which yield the materials for our homes, prevent erosion of the soil, and conserve the navigation and other uses of our streams; and the minerals which form the basis of our industrial life, an supply us with heat, light, and power." It recommended that each State appoint a Commission on the Conservation of Natural Resources. |
|
23 May 1908

John Bardeen |
birth John Bardeen John Bardeen (died 1991), American physicist, co-inventor of the transistor. Only physicist to receive the Nobel Prize in Physics twice. |
|
29 May 1908

William Arnold Anthony |
death William Arnold Anthony Died 29 May 1908 at age 72 (born 17 Nov 1835). American physicist and electrical engineer who initiated and developed one of the first courses in electrical engineering in the U.S. (1883), while teaching in the Physics Department at Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y. During 1872-75, Anthony, with the aid of student George Moler, built the first American Gramme dynamo for direct current, used to power arc lamps that lighted the Cornell campus, the first American electrical outdoor-lighting system. Anthony also built a mammoth tangent galvanometer, a device which utilized the earth's magnetic field for the measurement of current. He designed the dynamo for first underground electricity distributing system. Anthony contributed to development of gas-filled electric lamps. |
|
25 Aug 1908

Henri Becquerel |
death Henri Becquerel Henri Becquerel (born 1852), physicist. |
|
02 Sep 1908

Nikolai Aleksandrovich Kozyrev |
birth Nikolai Aleksandrovich Kozyrev Nikolai Aleksandrovich Kozyrev (died 1983), Russian astronomer and astrophysicist. |
|
06 Sep 1908

Louis Essen |
birth Louis Essen Louis Essen (died 1997), English physicist, co-developer of the first practical atomic clock. |
|
10 Oct 1908

Min Chueh Chang |
birth Min Chueh Chang Min Chueh Chang (died 1991), Chinese-born embryologist. |
|
14 Oct 1908

George Harold Brown |
birth George Harold Brown Born 14 Oct 1908; died 11 Dec 1987 at age 79. American electrical engineer, a pioneer in radio-thermics, who made major contributions to the development of radio and television broadcast antennas. In 1936, Brown invented the so-called turnstyle antenna for television broadcasting. Because of this, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) adopted a TV system of 441 lines. In 1938, Brown developed the vestigial sideband filter for use in television transmission, doubling the horizontal resolution of television pictures at any given bandwith. During WW II, with RCA's researchers, George Brown's group used radio-frequency heating in the bulk dehydration of penicillin at E.R. Squibb, a "sewing machine" for thermoplastics, and more consistent riveting and welding techniques. |
|
21 Oct 1908

Elsie Widdowson |
birth Elsie Widdowson Elsie Widdowson (died 2000), English nutritionist. |
|
04 Nov 1908

Józef Rotblat |
birth Józef Rotblat Józef Rotblat (died 2005), Polish-born physicist. |
|
05 Dec 1908

Eldon W. Lyle |
birth Eldon W. Lyle Born 5 Dec 1908; died 28 Dec 1997 at age 89. American plant pathologist who was an expert on the diseases of roses. He lived in Tyler, Texas, and greatly assisted the city's rose-growing industry. His interest stretched over 50 years; his doctorate dissertation in 1937 was his first study on the control of black spot disease. He found that the chief source of black spot spores is from lesions on the canes, and not the black-spotted leaflets. When spraying for black spot, he found it was important to wet all the woody parts of the plant on a weekly basis. Affected leaflets, when left in place, in fact contributed to the food production of the rose plant. He also helped breed various rose varieties, investigated hybrids, genetic composition, cultural adaptation and the best use of fertilizers. |