| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1938

DDT |
DDT (biology) DDT's properties as an insecticide are discovered by Paul Müller of Geigy. |
|
30 Nov 1938
Kavrayskiy VII projection |
Kavrayskiy VII projection (cartography) Kavrayskiy VII projection devised by Vladimir V. Kavrayskiy. |
|
30 Nov 1938

Linus Pauling |
Linus Pauling (chemistry) Linus Pauling publishes The Nature of the Chemical Bond, a compilation of a decade's work on chemical bonding, explaining hybridization theory, covalent bonding and ionic bonding as explained through electronegativity, and resonance as a means to explain, among other things, the structure of benzene. |
|
30 Nov 1938

Isaac Beeckman |
Isaac Beeckman (history of science a) Cornelis de Waard begins to publish the Journaal of Isaac Beeckman. |
|
30 Nov 1938

Alexandre Koyré |
Alexandre Koyré (history of science a) Philosopher and historian Alexandre Koyré originates the term scientific revolution to describe the emergence of modern science during the early modern period, from the late Renaissance to the late 18th century. |
|
30 Nov 1938

Quarry Bank Mill |
Quarry Bank Mill (history of science a) Quarry Bank Mill, an 18th century working (at this time) cotton mill in north west England, is donated to the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty. |
|
30 Nov 1938

Richard von Mises |
Richard von Mises (mathematics) Richard von Mises poses the birthday problem in probability. |
|
30 Nov 1938

John H. Lawrence |
John H. Lawrence (physiology and medic) John H. Lawrence uses beams of energized neutrons from a particle accelerator to treat a patient with leukemia. |
|
30 Nov 1938

Philip Levine |
Philip Levine (physiology and medic) Drs Philip Levine and Rufus Stetson published a first case report on the clinical consequences of non-recognized Rh factor, hemolytic transfusion reaction and hemolytic disease of the newborn in its most severe form. |
|
30 Nov 1938
Kirlian photography |
Kirlian photography (technology) Kirlian photography is invented by Semyon Kirlian. |
|
01 Jan 1939
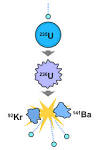
nuclear fission |
nuclear fission (physics) February – Discovery of nuclear fission is announced independently by Otto Hahn and Lise Meitner. |
|
01 Jan 1939

Hewlett-Packard |
Hewlett-Packard (technology) Hewlett-Packard is founded as an electronics company in Palo Alto, California. |
|
11 Jan 1939

Lockheed P-38 Lightning |
Lockheed P-38 Lightning (technology) First flight of the Lockheed P-38 Lightning. |
|
20 Jan 1939

Chandra Wickramasinghe |
birth Chandra Wickramasinghe Chandra Wickramasinghe, Ceylonese-born British astronomer. |
|
04 Feb 1939

Edward Sapir |
death Edward Sapir Edward Sapir (born 1884), American anthropological linguist. |
|
06 Mar 1939

Dorothea Pertz |
death Dorothea Pertz Dorothea Pertz (born 1859), English botanist. |
|
13 Mar 1939

Lucien Lévy-Bruhl |
death Lucien Lévy-Bruhl Died 13 Mar 1939 at age 81 (born 19 Apr 1857). French philosopher whose study of the psychology of primitive peoples gave anthropology a new approach to understanding irrational factors in social thought and primitive religion and mythology. |
|
30 Apr 1939

Cosmic rays generate electricity |
Cosmic rays generate electricity In 1939, cosmic rays entering a Geiger-Mueller counter produced electrical impulses used to control electrical power. This first ever such event, was used for the illumination ceremony of the 1939 New York World's Fair. The counter, at the Hayden Planetarium, New York City, switched on an electrical circuit wired to a display at the Lagoon of Nations where relays activated local battery circuits ringing bells and flashing lights to signal each capture of a cosmic ray. Albert Einstein as guest speaker explained cosmic rays. Sadly his accent and faulty amplification made his words incomprehensible to the crowd. Upon the tenth ray's signal, a huge light was to be turned on to illuminate the 600-ft Trylon triangular spire, but the power source failed. |
|
30 Apr 1939

Nylon |
Nylon (chemistry) Nylon fabric is first introduced to the general public at the New York World's Fair. |
|
19 May 1939

Dick Scobee |
birth Dick Scobee Dick Scobee (killed 1986), American astronaut. |
|
26 Jun 1939

Julia Polak |
birth Julia Polak Julia Polak (died 2014), Argentine-born British pathologist and pioneer of tissue engineering. |
|
01 Jul 1939

Edward Adelbert Doisy |
Edward Adelbert Doisy (chemistry) Edward Adelbert Doisy of Saint Louis University publishes the chemical structure of vitamin K. |
|
15 Jul 1939

Eugen Bleuler |
death Eugen Bleuler Died 15 Jul 1939 at age 82 (born 30 Apr 1857). Swiss psychiatrist who made notable contributions to the understanding of mental illness, and coined the term “schizophrenia” (1908) for the disorder previously named as dementia praecox by Emil Kraepelin. Bleuler realised the condition was neither a dementia, nor did it always occur in young people (praecox meaning early) and so gave the condition the name from the Greek for split (schizo) and mind (phrene). Contrary to the belief of the time, he held that schizophrenia was neither invariably incurable, nor would always progress to full dementia. He was one of the first psychiatrists to apply psychoanalytical methods in his research, and was an early proponent of the theories of Sigmund Freud. |
|
02 Aug 1939

Einstein–Szilárd letter |
Einstein–Szilárd letter (physics) The Einstein–Szilárd letter is signed, advising President of the United States Franklin D. Roosevelt of the potential use of uranium to construct an atomic bomb. It is delivered on October 11. |
|
19 Aug 1939

Alan Baker |
birth Alan Baker Alan Baker, English mathematician. |
|
27 Aug 1939

Heinkel He 178 |
Heinkel He 178 (technology) Flying the Heinkel He 178, Erich Warsitz makes the first flight entirely on turbojet power (the HeS 3 jet engine). |
|
04 Sep 1939

Alan Turing |
Alan Turing (computer science) Alan Turing and Gordon Welchman report to the United Kingdom Government Code and Cypher School, Bletchley Park. |
|
23 Sep 1939

Sigmund Freud |
death Sigmund Freud Died 23 Sep 1939 at age 83 (born 6 May 1856). Austrian father of psychoanalysis, best known for such works as Interpretation of Dreams (1900) and the New Introductory Lectures on Psychoanalysis (1933). In the publication of these, and numerous other works, he revolutionized the field of psychotherapy, so much so that often later workers have failed to recognize forebearers prior to him. Throughout his work he emphasized the role of unconscious and nonrational functioning, going against much of contemporary thought by suggesting that dreams and “mistakes” may also have meaning. Freud battled cancer of the jaw from 1923 until his death in 1939 in London - after 16 operations. |
|
30 Sep 1939

Martha Wollstein |
death Martha Wollstein Died 30 Sep 1939 at age 70 (born 21 Nov 1868). American physician and pediatric pathologist. Her first experimental work involved infant diarrhea and confirmed earlier studies relating the dysentery bacillus to the disease. At the Rockefeller Institute of Medical Research, she collaborated on the first experimental work on polio in the U.S., worked on an early investigation of pneumonia and developed, with Harold Amoss, a method for preparing antimeningitis serum. She also pioneered in early research on mumps, indicating, though not proving, its viral nature. After 1921, Wollstein investigated pediatric pathology at the Babies Hospital, especially jaundice, congenital anomalies, tuberculosis, meningitis, and leukemia. In 1930, she was the first female member of the American Pediatric Society. |
|
01 Oct 1939

John V. Atanasoff |
John V. Atanasoff (computer science) John V. Atanasoff with Clifford Berry demonstrate the first prototype Atanasoff–Berry Computer at Iowa State University. |
|
07 Oct 1939

John Hopcroft |
birth John Hopcroft John Hopcroft, American theoretical computer scientist. |
|
07 Oct 1939

Harvey Cushing |
death Harvey Cushing Harvey Cushing (born 1869), American neurosurgeon. |
|
10 Oct 1939

Neil Sloane |
birth Neil Sloane Neil Sloane, Welsh-born American mathematician. |
|
21 Oct 1939

Advisory Committee on Uranium |
Advisory Committee on Uranium (physics) First meeting of the Advisory Committee on Uranium under Lyman James Briggs, authorised by President Roosevelt to oversee neutron experiments. |
|
01 Nov 1939

Physicist |
Physicist (technology) Physicist Hans Ferdinand Mayer writes the Oslo Report on German weapons systems and passes it to the British Secret Intelligence Service. |
|
06 Nov 1939

Sonderaktion Krakau |
Sonderaktion Krakau Sonderaktion Krakau: The Gestapo arrests scientists from the Jagiellonian University and other institutions in Kraków, Poland; on November 27 they are sent to Sachsenhausen concentration camp. |
|
11 Nov 1939

Alf Adams |
birth Alf Adams Alf Adams, English physicist. |
|
18 Nov 1939

John O'Keefe |
birth John O'Keefe John O'Keefe, American-born British neuroscientist, winner of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. |
|
09 Dec 1939

Liberator |
Liberator (technology) First flight of the Consolidated XB-24 "Liberator" bomber prototype. |
|
29 Dec 1939

Shockley semiconductor amplifier idea |
Shockley semiconductor amplifier idea In 1939, William Shockley wrote in his laboratory notebook: “It has today occurred to me that an amplifier using semiconductors rather than vacuum is in principle possible.&rdquo. He went on to develop the transistor, for which he shared (with John Bardeen and Walter Brattain) the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics. |