| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1944

Salvador Edward Luria |
Salvador Edward Luria (biology) Salvador Edward Luria and Alfred Day Hershey independently recognize that viruses undergo mutations. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Oak Ridge National Laboratory |
Oak Ridge National Laboratory (chemistry) A team at Oak Ridge National Laboratory led by Charles Coryell discovers chemical element 61, the only one still missing between 1 and 96 on the periodic table, which they will name promethium. Found by analysis of fission products of irradiated uranium fuel, its discovery is not made public until 1947. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Dorothy Hodgkin |
Dorothy Hodgkin (chemistry) Dorothy Hodgkin and C. H. (Harry) Carlisle publish the first three-dimensional molecular structure of a steroid, cholesteryl iodide. |
|
30 Nov 1944

John von Neumann |
John von Neumann (computer science) June 30 - Distribution of John von Neumann's First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC, containing the first published description of the logical design of a computer with stored-program and instruction data stored in the same address space within the memory (von Neumann architecture). |
|
30 Nov 1944

ENIAC |
ENIAC (computer science) November - Assembly of the world's first general purpose electronic computer, the Electronic Numerical Integrator Analyzer and Computer (ENIAC), is completed in the United States, covering 1,800 square feet (170 m) of floor space, and the first set of calculations is run on it. |
|
30 Nov 1944

George Stigler |
George Stigler (mathematics) George Stigler solves the Stigler diet problem heuristically. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Stamford, Connecticut |
Stamford, Connecticut (medicine) February - Raymond L. Libby of American Cyanamid's research laboratories at Stamford, Connecticut, announces a method of orally administering the antibiotic penicillin. |
|
30 Nov 1944
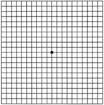
Amsler grid |
Amsler grid (medicine) The Amsler grid is introduced for monitoring of the central visual field. |
|
30 Nov 1944
Pacific |
Pacific (meteorology) High-altitude west-to-east winds across Pacific, discovered by Japanese in 1942 and by Americans in 1944, are dubbed "jet stream". |
|
30 Nov 1944

Nuclear testing |
Nuclear testing (physics) July 16 - Nuclear testing: The Trinity test, the first test of an atomic bomb, using 6 kilograms of plutonium, succeeds in detonating an explosion equivalent to that of 20 kilotons of TNT. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki |
Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki (physics) August 6 & 9 - Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki make the world aware of the power of nuclear weapons. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Smyth Report |
Smyth Report (physics) August 11 - Smyth Report released by the United States government, informing the public of the basics of nuclear fission and its military and civilian applications, and emphasizing the role played by physics in the development of the atomic bomb. |
|
30 Nov 1944

desalination |
desalination (technology) The first desalination plant becomes operational. |
|
30 Nov 1944

March 2 |
March 2 (technology) March 2 - The Bachem Ba 349 Natter is launched from Stetten am kalten Markt. The Natter is the first manned rocket, developed as an anti-aircraft weapon. The launch fails and the pilot dies. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Arthur C. Clarke |
Arthur C. Clarke (technology) October - Arthur C. Clarke puts forward the idea of a geosynchronous communications satellite. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Slinky |
Slinky (technology) November - Slinky toy first demonstrated by engineer Richard T. James in Philadelphia. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Kathleen Lonsdale |
Kathleen Lonsdale (institutions) Kathleen Lonsdale and Marjory Stephenson become the first women elected as Fellows of the Royal Society of London. |
|
30 Nov 1944
Argentine |
Argentine (publications) Argentine physicist Ernesto Sabato publishes Uno y el Universo ("One and the Universe"), a collection of essays criticizing the apparent moral neutrality of science and warning of dehumanization in technological societies. |
|
30 Nov 1944

John Krebs |
birth John Krebs April 11 - John Krebs, English zoologist. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Mike Smith |
birth Mike Smith April 30 - Mike Smith (killed 1986), American astronaut. |
|
30 Nov 1944

John McAfee |
birth John McAfee September 18 - John McAfee, Scottish American computer programmer. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Lyn Evans |
birth Lyn Evans Undated - Lyn Evans, Welsh physicist. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Napier Shaw |
death Napier Shaw March 23 - Napier Shaw (born 1854), English meteorologist. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Isis Pogson |
death Isis Pogson May 14 - Isis Pogson (born 1852), English astronomer and meteorologist. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Gerhard Gentzen |
death Gerhard Gentzen August 4 - Gerhard Gentzen (born 1909), German mathematician. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Robert Goddard |
death Robert Goddard August 10 - Robert Goddard (born 1882), American rocket scientist. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Stefan Banach |
death Stefan Banach August 31 - Stefan Banach (born 1892), Polish mathematician. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Walter Bradford Cannon |
death Walter Bradford Cannon October 1 - Walter Bradford Cannon (born 1871), American physiologist. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Hans Geiger |
death Hans Geiger September 24 - Hans Geiger (born 1882), German inventor of the Geiger counter. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Thomas Hunt Morgan |
death Thomas Hunt Morgan December 4 - Thomas Hunt Morgan (born 1866), American biologist. |
|
30 Nov 1944

Arthur Korn |
death Arthur Korn December 21/22 - Arthur Korn (born 1870), German-born inventor. |