| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1947

Fairfield Osborne |
Fairfield Osborne (biology) Publication of Fairfield Osborne's Our Plundered Planet, a Malthusian critique of human environmental destruction. |
|
30 Nov 1947

psychology |
psychology (medicine and human s) In psychology, Bertram Forer demonstrates the Forer effect (that people tend to accept generalised descriptions of personality as uniquely applicable to themselves). |
|
30 Nov 1947

Kinsey Report |
Kinsey Report (medicine and human s) Kinsey Report, Sexual Behavior in the Human Male, is published in the United States. |
|
30 Nov 1947

Julius Axelrod |
Julius Axelrod (medicine and human s) Julius Axelrod and Bernard Brodie identify the analgesic properties of acetaminophen. |
|
30 Nov 1947

Herbert Fröhlich |
Herbert Fröhlich (physics) Herbert Fröhlich makes a key breakthrough in understanding superconductivity, at the University of Liverpool. |
|
30 Nov 1947

Norbert Wiener |
Norbert Wiener (publications) First publication of Norbert Wiener's Cybernetics: Or Control and Communication in the Animal and the Machine. |
|
30 Nov 1947

aeronautical engineer |
aeronautical engineer (publications) Publication in Britain of the novel No Highway by former aeronautical engineer Nevil Shute, dealing with the effects of metal fatigue on aircraft. |
|
30 Nov 1947

Margaret Allen |
birth Margaret Allen Margaret Allen, American cardiothoracic surgeon. |
|
24 Jan 1948

Early computer |
Early computer In 1948, IBM dedicated its "SSEC" in New York City. The Selective Sequence Electronic Calculator handled both data and instructions using electronic circuits made with 13,500 vacuum tubes and 21,000 relays. It occupied three sides of a 30-ft x 60-ft room. On the back wall, three punches and thirty readers provided paper-tape storage. Banks of vacuum tube circuits for card reading and sequence control and 36 paper tape readers comprising the table-lookup section occupied the left wall. Most of the right wall was filled by the electronic arithmetic unit and storage. In the center of the room were card readers, card punches, printers, and the operator's console. It was visible to pedestrians on the sidewalk outside. |
|
30 Jan 1948

Orville Wright |
death Orville Wright Orville Wright (born 1871), American pioneer aviator. |
|
28 Feb 1948

Steven Chu |
birth Steven Chu Born 28 Feb 1948. American physicist who (with Claude Cohen-Tannoudji and William D. Phillips) was awarded the 1997 Nobel Prize for Physics for their independent, pioneering research in cooling and trapping atoms using laser light. In their normal state the constant random thermal motion of atoms limits precise measurements of atomic states. Thus, physicists sought to cool and slow atoms down as much as possible. Chu used six laser beams and worked with a hot gas of sodium atoms. He managed to cool and trap atoms in what he called “optical molasses.” By 1985, he had cooled sodium atoms to a temperature of about 240 millionth of a degree above absolute zero. The atoms could be trapped in the laser beams for a period of about half a second. He was chosen by President Obama to become the 12th U.S. Secretary of Energy (2009-2013). |
|
09 Mar 1948

László Lovász |
birth László Lovász László Lovász, Hungarian computer scientist. |
|
25 Mar 1948

Tinker Air Force Base |
Tinker Air Force Base (meteorology) Meteorologists at Tinker Air Force Base in Oklahoma City issue the world's first tornado forecast, for the second of the 1948 Tinker Air Force Base tornadoes. |
|
01 Apr 1948

Ralph Asher Alpher |
Ralph Asher Alpher (physics) Physicists Ralph Asher Alpher and George Gamow publish the Alpher–Bethe–Gamow paper about the Big Bang. |
|
07 Apr 1948

World Health Organization |
World Health Organization (medicine and human s) The World Health Organization is established by the United Nations. |
|
18 Apr 1948

Yasumasa Kanada |
birth Yasumasa Kanada Yasumasa Kanada, Japanese mathematician. |
|
26 May 1948

George Newman |
death George Newman Sir George Newman (born 1870), English public health physician. |
|
10 Jun 1948

Philippa Fawcett |
death Philippa Fawcett Philippa Fawcett (born 1868), English mathematician. |
|
13 Jun 1948

Nina L. Etkin |
birth Nina L. Etkin Nina L. Etkin (died 2009), American anthropologist and biologist. |
|
18 Jun 1948

Columbia Records |
Columbia Records (technology) Columbia Records unveil the LP records developed by Peter Goldmark of CBS Laboratories. |
|
21 Jun 1948

program |
program (computer science) World's first working program run on an electronic stored-program computer, the Manchester Small-Scale Experimental Machine ("Baby") (written by Tom Kilburn). |
|
21 Jun 1948

D'Arcy Wentworth Thompson |
death D'Arcy Wentworth Thompson D'Arcy Wentworth Thompson (born 1860), Scottish biologist. |
|
28 Jun 1948

Kenneth Alan Ribet |
birth Kenneth Alan Ribet Kenneth Alan Ribet, American mathematician. |
|
01 Jul 1948

Claude E. Shannon |
Claude E. Shannon (computer science) October – Claude E. Shannon publishes "A Mathematical Theory of Communication" in Bell System Technical Journal, regarded as a foundation of information theory, introducing the concept of Shannon entropy and adopting the term Bit. |
|
05 Jul 1948

National Health Service |
National Health Service (medicine and human s) The National Health Service begins functioning in the United Kingdom, giving the right to universal healthcare, free at point of use. |
|
07 Aug 1948
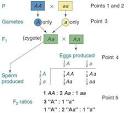
Mendelian |
Mendelian (biology) Teaching and research in Mendelian genetics is prohibited in the Soviet Union in favour of Lysenkoist theories of the inheritance of acquired characteristics. |
|
25 Aug 1948

Nicholas A. Peppas |
birth Nicholas A. Peppas Nicholas A. Peppas, Greek chemical and biomedical engineer. |
|
30 Aug 1948

Russian |
Russian (medicine and human s) Russian scientist Victor Skumin first describes "cardioprosthetic psychopathological syndrome", later known as Skumin syndrome, a form of anxiety suffered by recipients of artificial heart valves. |
|
02 Sep 1948

Christa McAuliffe |
birth Christa McAuliffe Christa McAuliffe, born Sharon Christa Corrigan (died 1986), American astronaut. |
|
05 Oct 1948

Julian Huxley |
Julian Huxley (biology) Delegates to a conference organised by Sir Julian Huxley at Fontainebleau agree to formation of the International Union for Conservation of Nature. |
|
29 Oct 1948

Frans de Waal |
birth Frans de Waal Frans de Waal, Dutch primatologist. |
|
16 Nov 1948

Frederick Gardner Cottrell |
death Frederick Gardner Cottrell Died 16 Nov 1948 at age 71 (born 10 Jan 1877). American educator and scientist who invented the industrial electrostatic precipitator (1907), which eliminates suspended particles from streams of gases. He patented the “Art of Separating Suspended Particles from Gaseous Bodies” (No. 895,729). To electrochemists, he is best known for the Cottrell equation. Electrostatic precipitators are still widely used to reduce air pollution by smoke from power plants and dust from cement kilns and other industrial sources. Cottrell contributed to the development of a process for the separation of helium from natural gas, and also was instrumental in establishing the synthetic ammonia industry in the U.S. during attempts to perfect a high temperature process for formation of nitric oxide. |
|
20 Nov 1948

Takahē |
Takahē (biology) The Takahē, a flightless bird generally thought to have been extinct for fifty years, is rediscovered by Geoffrey Orbell near Lake Te Anau in the South Island of New Zealand. |
|
12 Dec 1948

Marjory Stephenson |
death Marjory Stephenson Marjory Stephenson (born 1885), English biochemist. |
|
17 Dec 1948

Smithsonian Institution |
Smithsonian Institution (history of science) The original Wright Flyer goes on display in the Smithsonian Institution. |
|
30 Dec 1948

Randy Schekman |
birth Randy Schekman Randy Schekman, American cell biologist, winner of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. |