| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1949

Dutch |
Dutch (astronomy and space ) Dutch astronomer Jan Oort postulates the existence of an orbiting cloud of planets (the Oort cloud) at the outermost edge of the Solar System. |
|
30 Nov 1949

Melvin Calvin |
Melvin Calvin (biology) Melvin Calvin, James Bassham, and Andrew Benson at the University of California, Berkeley, discover the Calvin cycle in photosynthesis. |
|
30 Nov 1949

Entomologist |
Entomologist (biology) Entomologist Willi Hennig publishes Grundzüge einer Theorie der phylogenetischen Systematik in East Germany, pioneering the study of cladistics. |
|
30 Nov 1949

myxomatosis |
myxomatosis (biology) Full-scale release of myxomatosis for control of the Australian rabbit population. |
|
30 Nov 1949

John Forbes Nash, Jr. |
John Forbes Nash, Jr. (mathematics) John Forbes Nash, Jr. proposes the Nash equilibrium in game theory, initially in his Princeton doctoral thesis. |
|
30 Nov 1949
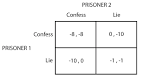
prisoner's dilemma |
prisoner's dilemma (mathematics) The prisoner's dilemma is framed by Merrill Flood and Melvin Dresher at RAND and formalized and named by Albert W. Tucker. |
|
30 Nov 1949

Antihistamine |
Antihistamine (medicine) Antihistamine discovered. |
|
30 Nov 1949
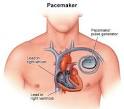
artificial pacemaker |
artificial pacemaker (medicine) An external artificial pacemaker is developed by John A. Hopps in conjunction with Wilfred Gordon Bigelow at Toronto General Hospital. |
|
30 Nov 1949

John Ward |
John Ward (physics) John Ward derives the Ward–Takahashi identity in quantum field theory. |
|
30 Nov 1949

Canadians |
Canadians (technology) Canadians Harry Wasylyk, Larry Hansen and Frank Plomp introduce the plastic bin bag for garbage collection. |
|
30 Nov 1949

pager |
pager (technology) First practical pager, developed and manufactured by the Reevesound Company, is introduced for physicians in the New York City area. |
|
30 Nov 1949

J. Z. Young |
J. Z. Young J. Z. Young delivers the BBC Reith Lectures on Doubt and Certainty in Science, introducing the radio audience to current developments in neurophysiology. |
|
30 Nov 1949

Fields Prize in Mathematics |
Fields Prize in Mathematics (awards) Fields Prize in Mathematics (first postwar award): Laurent Schwartz and Atle Selberg |
|
24 Jan 1950
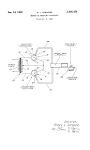
Microwave patent |
Microwave patent In 1950, the original microwave oven patent was issued to its inventor Percy LeBaron Spencer under the title "Method of Treating Foodstuffs." (U.S. No. 2,495,429.) |
|
02 Feb 1950

Constantin Carathéodory |
death Constantin Carathéodory Died 2 Feb 1950 at age 76 (born 13 Sep 1873). German mathematician of Greek origin who made important contributions to the theory of real functions and to the theory of point-set measure. He demonstrated that the calculus of variations (the theory of maxima and minima in curves) could be applied not just to smooth curves, but also those with corners. He also contributed to thermodynamics and helped develop Einstein's special theory of relativity. |
|
09 Feb 1950
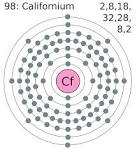
Californium |
Californium (chemistry) Californium, a radioactive actinide transuranium element, is first synthesized by Stanley G. Thompson, Kenneth Street, Jr., Albert Ghiorso and Glenn T. Seaborg at the University of California, Berkeley. |
|
25 Feb 1950

George Minot |
death George Minot George Minot (born 1885), American physician, Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1934 |
|
01 Mar 1950

Claude Shannon |
Claude Shannon (computer science) Publication of Claude Shannon's paper "Programming a Computer for Playing Chess", seminal in the development of computer chess and introducing the Shannon number. |
|
02 Mar 1950

James W. Pennebaker |
birth James W. Pennebaker James W. Pennebaker, American social psychologist. |
|
05 Mar 1950

Henry Marsh |
birth Henry Marsh Henry Marsh, English neurosurgeon. |
|
18 Mar 1950

Linda Partridge |
birth Linda Partridge Linda Partridge, English biogerontologist. |
|
30 Mar 1950

Phototransistor |
Phototransistor In 1950, the invention of the phototransistor was announced. This was a transistor operated by light rather than electric current, invented by Dr. John Northrup Shive of the Bell Telephone Laboratories at Murray Hill, N.J. It used a tiny chip of germanium, a semiconductor material, but only a single collector wire. The tip of this wire rests in a small dimple ground into one side of the germanium disk. At this point the germanium disk is only three thousandths of an inch thick. Light focussed on the opposite, un-dimpled side of the disk can control the flow of current in the wire, thus making a control device similar in function to a photo-electric cell. |
|
01 Apr 1950

Richard Hamming |
Richard Hamming (computer science) Publication of Richard Hamming's paper "Error detecting and error correcting codes", seminal in the construction of error detection and correction codesand from which Hamming code and the Hamming distance derive. |
|
28 Apr 1950

Oakes Ames |
death Oakes Ames Oakes Ames (born 1874), American botanist. |
|
16 May 1950

Georg Bednorz |
birth Georg Bednorz Georg Bednorz, German physicist, Nobel Prize in physics 1987. |
|
17 Jun 1950
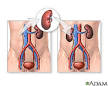
kidney transplantation |
kidney transplantation (medicine) The first cadaveric internal kidney transplantation is performed on Ruth Tucker, a 44-year-old woman with polycystic kidney disease, at Little Company of Mary Hospital (Evergreen Park), Illinois. Although the donated kidney is rejected 10 months later because no effective immunosuppressive drugs have been developed at this time, the intervening time gives Tucker's remaining kidney time to recover and she lives another 5 years. |
|
21 Sep 1950

Arthur Milne |
death Arthur Milne Arthur Milne (born 1896), British space physicist |
|
01 Oct 1950

Alan Turing |
Alan Turing (computer science) Publication of Alan Turing's paper "Computing Machinery and Intelligence", seminal in the study of artificial intelligence and presenting the Turing test. |
|
01 Oct 1950

Australian |
Australian (medicine) Australian-born British thoracic surgeon Norman Barrett describes the condition which will become known as Barrett's oesophagus. |
|
11 Oct 1950
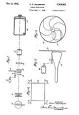
field-sequential color system |
field-sequential color system (technology) A field-sequential color system developed by Hungarian American engineer Dr. Peter Goldmark becomes the first color television system to be adopted for commercial use (by CBS in the United States), but is abandoned a year later. |
|
21 Oct 1950

Ronald McNair |
birth Ronald McNair Ronald McNair (died on mission 1986), African American physicist and astronaut. |
|
01 Nov 1950

Robert B. Laughlin |
birth Robert B. Laughlin Robert B. Laughlin, American physicist, Nobel prize in physics 1998. |
|
03 Nov 1950

James Rothman |
birth James Rothman James Rothman, American cell biologist, Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2013. |
|
11 Dec 1950

typical antipsychotic |
typical antipsychotic (medicine) The typical antipsychotic Chlorpromazine is first synthesized. |
|
11 Dec 1950

Leslie Comrie |
death Leslie Comrie Leslie Comrie (born 1893), New Zealand astronomer and computing pioneer. |
|
13 Dec 1950

Julia Slingo |
birth Julia Slingo Julia Slingo, English meteorologist. |