| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1949

Dutch |
Dutch (astronomy and space ) Dutch astronomer Jan Oort postulates the existence of an orbiting cloud of planets (the Oort cloud) at the outermost edge of the Solar System. |
|
30 Nov 1949

Melvin Calvin |
Melvin Calvin (biology) Melvin Calvin, James Bassham, and Andrew Benson at the University of California, Berkeley, discover the Calvin cycle in photosynthesis. |
|
30 Nov 1949

Entomologist |
Entomologist (biology) Entomologist Willi Hennig publishes Grundzüge einer Theorie der phylogenetischen Systematik in East Germany, pioneering the study of cladistics. |
|
30 Nov 1949

myxomatosis |
myxomatosis (biology) Full-scale release of myxomatosis for control of the Australian rabbit population. |
|
30 Nov 1949

John Forbes Nash, Jr. |
John Forbes Nash, Jr. (mathematics) John Forbes Nash, Jr. proposes the Nash equilibrium in game theory, initially in his Princeton doctoral thesis. |
|
30 Nov 1949
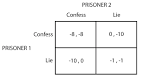
prisoner's dilemma |
prisoner's dilemma (mathematics) The prisoner's dilemma is framed by Merrill Flood and Melvin Dresher at RAND and formalized and named by Albert W. Tucker. |
|
30 Nov 1949

Antihistamine |
Antihistamine (medicine) Antihistamine discovered. |
|
30 Nov 1949
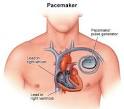
artificial pacemaker |
artificial pacemaker (medicine) An external artificial pacemaker is developed by John A. Hopps in conjunction with Wilfred Gordon Bigelow at Toronto General Hospital. |
|
30 Nov 1949

John Ward |
John Ward (physics) John Ward derives the Ward–Takahashi identity in quantum field theory. |
|
30 Nov 1949

Canadians |
Canadians (technology) Canadians Harry Wasylyk, Larry Hansen and Frank Plomp introduce the plastic bin bag for garbage collection. |
|
30 Nov 1949

pager |
pager (technology) First practical pager, developed and manufactured by the Reevesound Company, is introduced for physicians in the New York City area. |
|
30 Nov 1949

J. Z. Young |
J. Z. Young J. Z. Young delivers the BBC Reith Lectures on Doubt and Certainty in Science, introducing the radio audience to current developments in neurophysiology. |
|
30 Nov 1949

Fields Prize in Mathematics |
Fields Prize in Mathematics (awards) Fields Prize in Mathematics (first postwar award): Laurent Schwartz and Atle Selberg |