| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1954

Jan Oort |
Jan Oort (astronomy) Jan Oort confirms that polarized light from the Crab Nebula is produced by synchrotron radiation. |
|
30 Nov 1954

ENIAC |
ENIAC (computer science) The ENIAC computer is deactivated at Aberdeen Proving Ground, Maryland, having been in continuous operation since 1947. |
|
30 Nov 1954

Luftwaffe |
Luftwaffe (computer science) Former Luftwaffe flying ace Ulrich Steinhilper, a German IBM typewriter salesman, coins and popularizes the term "Textverarbeitung" ("word processing"). |
|
30 Nov 1954

Maurice Wilkes |
Maurice Wilkes (computer science) Maurice Wilkes publishes a description of microprogramming. |
|
30 Nov 1954

RAND |
RAND (computer science) RAND publishes A Million Random Digits with 100,000 Normal Deviates. |
|
30 Nov 1954

American |
American (earth sciences) American geophysicist Clair Cameron Patterson presents his result for the age of the earth using lead isotopic data from the Canyon Diablo meteorite – 4.55 billion years (± 70 million). |
|
30 Nov 1954

Industrial archaeology |
Industrial archaeology (history of science a) The term "Industrial archaeology" first appears in print. |
|
30 Nov 1954

classification of finite simple groups |
classification of finite simple groups (mathematics) In the classification of finite simple groups, the Brauer–Fowler theorem is published and Claude Chevalley introduces Chevalley groups. |
|
04 Jul 2015
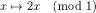
Gilbert–Shannon–Reeds model |
Gilbert–Shannon–Reeds model (mathematics) Gilbert–Shannon–Reeds model for probability distribution of riffle shuffle permutations in shuffling playing cards reported. |
|
30 Nov 1954
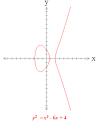
Taniyama–Shimura conjecture |
Taniyama–Shimura conjecture (mathematics) The Taniyama–Shimura conjecture is first stated by Yutaka Taniyama at an international symposium in Japan. |
|
30 Nov 1954
chronic fatigue syndrome |
chronic fatigue syndrome (medicine) Outbreak of "Royal Free disease" or "benign myalgic encephalomyelitis", strongly resembling what will later be known as chronic fatigue syndrome, among staff at the Royal Free Hospital in London. |
|
30 Nov 1954

antiproton |
antiproton (physics) Existence of the antiproton is experimentally confirmed by University of California, Berkeley, physicists Emilio Segrè and Owen Chamberlain. |
|
30 Nov 1954

University of Liverpool |
University of Liverpool (physics) University of Liverpool cyclotron begins operation. |
|
30 Nov 1954

Strömsund Bridge |
Strömsund Bridge (technology) Strömsund Bridge in Sweden completed, the first significant cable-stayed bridge of the modern era. |
|
30 Nov 1954

Swiss |
Swiss (technology) Swiss electrical engineer George de Mestral is granted a patent for the Velcro fabric hook-and-loop fastener. |
|
30 Nov 1954

Bernard Heuvelmans |
Bernard Heuvelmans (zoology) French zoologist Bernard Heuvelmans publishes Sur la piste des bêtes ignorées ("On the Track of Unknown Animals"), pioneering the pseudoscientific field of cryptozoology. |
|
30 Nov 1954

Eugene Garfield |
Eugene Garfield (publications) Eugene Garfield proposes the concept of citation indexing for scientific literature. |
|
30 Nov 1954

Huda Zoghbi |
birth Huda Zoghbi Huda Zoghbi, Lebanese-born geneticist. |
|
08 Jan 1955

Penumbral lunar eclipse |
Penumbral lunar eclipse (astronomy) Penumbral lunar eclipse. |
|
24 Jan 1955

Alan Sokal |
birth Alan Sokal Alan Sokal, American mathematical physicist and proponent of scientific objectivity. |
|
01 Feb 1955

Harold Hopkins |
Harold Hopkins (physics) Harold Hopkins and Narinder Singh Kapany publish a key paper in the development of optical fiber technology. |
|
02 Feb 1955

Oswald Avery |
death Oswald Avery Oswald Avery (born 1877), Canadian American bacteriologist. |
|
19 Feb 1955
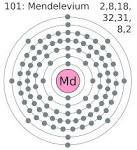
Mendelevium |
Mendelevium (chemistry) Mendelevium (atomic number 101) is first synthesized by Albert Ghiorso, Glenn T. Seaborg, Gregory R. Choppin, Bernard G. Harvey, and Stanley G. Thompson (team leader) at the University of California, Berkeley. |
|
24 Feb 1955

Steve Jobs |
birth Steve Jobs Steve Jobs (died 2011), American computing entrepreneur. |
|
26 Feb 1955

Rosalind Franklin |
Rosalind Franklin (biochemistry) Rosalind Franklin publishes her observation that tobacco mosaic virus rods are all of identical length. |
|
01 Mar 1955

Joseph Rotblat |
Joseph Rotblat (physics) Joseph Rotblat publishes his conclusions that contamination caused by nuclear fallout after the U.S. Castle Bravo hydrogen bomb test at Bikini Atoll is greater than officially stated. |
|
11 Mar 1955

Alexander Fleming |
death Alexander Fleming Sir Alexander Fleming (born 1881), British bacteriologist, winner of the 1945 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. |
|
10 Apr 1955

Pierre Teilhard de Chardin |
death Pierre Teilhard de Chardin Pierre Teilhard de Chardin, SJ (born 1881), French-born paleontologist and philosopher. |
|
12 Apr 1955

Salk vaccine field trial |
Salk vaccine field trial In 1955, the Salk vaccine against polio was announced to work, and be “safe, effective and potent,” after a year-long field trial. Dr. Thomas Francis, Jr. made the statement at a press conference in Ann Arbor, Michigan, on the tenth annniversary of the death of Franklin Roosevelt (1945), the U.S. president who was a victim of the disease. Dr. Francis was a former professor of Jonas Salk. |
|
12 Apr 1955

Salk |
Salk (medicine) The Salk polio vaccine, having passed large-scale trials earlier in the United States, receives full approval by the Food and Drug Administration. |
|
17 Apr 1955
Eduard Pernkopf |
death Eduard Pernkopf Eduard Pernkopf (born 1888), Austrian anatomist. |
|
18 Apr 1955

Albert Einstein |
death Albert Einstein Albert Einstein (born 1879), German-born winner of the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics. |
|
20 Apr 1955

Svante Pääbo |
birth Svante Pääbo Svante Pääbo, Swedish evolutionary geneticist. |
|
30 Apr 1955

Francis Muguet |
birth Francis Muguet Francis Muguet (died 2009), French chemist and advocate of open access to information. |
|
01 Jun 1955

Fred Hoyle |
Fred Hoyle (astronomy) Fred Hoyle and Martin Schwarzschild describe the mechanism for the creation of red giant stars. |
|
08 Jun 1955

Tim Berners-Lee |
birth Tim Berners-Lee Tim Berners-Lee, English-born creator of the world wide web. |
|
10 Jun 1955

Virus separation |
Virus separation In 1955, the first U.S. report was made of the separation of a virus into component parts. This work was performed on the tobacco virus, which furthermore could be reconstructed from those parts to produce a material as effective as the virus in its original form in producing disease in tabacco and other plants. They demonstrated that tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) spontaneously formed when mixtures of purified coat protein and its genomic RNA were incubated together, i.e. the structure that TMV adopts is self-ordered and corresponds to a free energy minimum. The report covered the research work of Drs. Heinz L. Fraenkel-Conrat and Robley Williams at the Virus Laboratory of the University of California at Berkeley. |
|
11 Jun 1955

Duncan Steel |
birth Duncan Steel Duncan Steel, English/Australasian space scientist. |
|
12 Jun 1955

Redcliffe N. Salaman |
death Redcliffe N. Salaman Redcliffe N. Salaman (born 1874), English botanist. |
|
20 Jun 1955

Total solar eclipse |
Total solar eclipse (astronomy) Total solar eclipse of 7 min 8 sec duration, the longest between the 11th and 22nd centuries, visible in Southeast Asia. During the entire Second Millennium, only seven such eclipses exceed seven minutes of totality. |
|
09 Jul 1955

Russell–Einstein Manifesto |
Russell–Einstein Manifesto Russell–Einstein Manifesto issued in London by Bertrand Russell with the signatures of the late Albert Einstein, Max Born and other prominent scientists drawing the attention of world political leaders to the dangers posed by nuclear weapons. |
|
21 Jul 1955

J. B. Christopherson |
death J. B. Christopherson J. B. Christopherson (born 1868), English physician. |
|
09 Aug 1955

Gilbert Plass |
Gilbert Plass (climatology) Gilbert Plass submits his seminal article "The Carbon Dioxide Theory of Climate Change". |
|
11 Aug 1955

Robert W. Wood |
death Robert W. Wood Robert W. Wood (born 1868), American optical physicist. |
|
12 Aug 1955

James B. Sumner |
death James B. Sumner James B. Sumner (born 1887), American winner of the 1946 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. |
|
20 Aug 1955

Dorothy Hodgkin |
Dorothy Hodgkin (chemistry) Dorothy Hodgkin and colleagues publish the final structure of vitamin B12. |
|
24 Aug 1955

atomic clock |
atomic clock (technology) The first accurate atomic clock, a caesium standard based on a certain transition of the caesium-133 atom, is built by Louis Essen with J.V.L. Parry at the National Physical Laboratory (United Kingdom). |
|
01 Oct 1955
Ultra high frequency |
Ultra high frequency (physics) Ultra high frequency AN/FPS-31 early warning radar developed by Lincoln Laboratory begins operation on Jug Handle Hill at West Bath, Maine. |
|
02 Oct 1955

Nancy Rothwell |
birth Nancy Rothwell Nancy Rothwell, English physiologist. |
|
28 Oct 1955

Bill Gates |
birth Bill Gates Bill Gates, American software designer and entrepreneur. |
|
25 Nov 1955

Arthur Tansley |
death Arthur Tansley Sir Arthur Tansley (born 1871), English botanist and ecologist. |
|
29 Nov 1955

Partial lunar eclipse |
Partial lunar eclipse (astronomy) Partial lunar eclipse. |
|
08 Dec 1955

Hermann Weyl |
death Hermann Weyl Died 8 Dec 1955 at age 70 (born 9 Nov 1885). Hermann Klaus Hugo Weyl was a German-American mathematician whose widely varied contributions in mathematics linked pure mathematics and theoretical physics. He made significant contributions to quantum mechanics and the theory of relativity. He attempted to incorporate electromagnetism into the geometric formalism of general relativity. Weyl published Die Idee der Riemannschen Fläche (1913) which united analysis, geometry and topology. He produced the first guage theory in which the Maxwell electromagnetic field and the gravitational field appear as geometrical properties of space-time. He evolved (1923-38) the concept of continuous groups using matrix representations. Applying group theory to quantum mechanics he set up the modern subject. |
|
12 Dec 1955

Hovercraft |
Hovercraft In 1955, Christopher Cockerell, father of the hovercraft air-cushion vehicle, filed his first patent for the hovercraft. The following year he formed a company known as Hovercraft Ltd. to apply this new approach of reducing the problem of hydrodynamic drag on the hull of a boat by using air as lubrication. |
|
13 Dec 1955

Antonio Egas Moniz |
death Antonio Egas Moniz Antonio Egas Moniz (born 1874), Portuguese neurologist, winner of the 1949 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. |
|
14 Dec 1955

Annular solar eclipse |
Annular solar eclipse (astronomy) Annular solar eclipse. |
|
22 Dec 1955
Cytogeneticist |
Cytogeneticist (biochemistry) Cytogeneticist Joe Hin Tjio working with Albert Levan at Lund University demonstrates that there are forty-six human chromosomes. |
|
22 Dec 1955

Thomas C. Südhof |
birth Thomas C. Südhof Thomas C. Südhof, German-born biochemist, winner of the 2013 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. |
|
24 Dec 1955

Henry K. Beecher |
Henry K. Beecher (medicine) Henry K. Beecher publishes a paper indicating the powerful effect of placebos on patient outcomes. |