| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1961

Emile Zuckerkandl |
Emile Zuckerkandl (biology) Emile Zuckerkandl and Linus Pauling publish a paper introducing what will become known as the molecular clock concept. |
|
30 Nov 1961
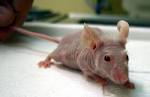
nude mouse |
nude mouse (biology) The first nude mouse strain is discovered by Dr. N. R. Grist at Ruchill Hospital's Brownlee virology laboratory in Glasgow. |
|
30 Nov 1961

Neuroscience Research Program |
Neuroscience Research Program (biology) The Neuroscience Research Program (NRP) was established by Francis O. Shmitt et al. |
|
30 Nov 1961

MIT |
MIT (computer science) At MIT, Ivan Sutherland uses the TX-2 computer to write Sketchpad, the origin of graphical programs used for computer-aided design. |
|
30 Nov 1961

Roger Tomlinson |
Roger Tomlinson (computer science) Roger Tomlinson leads development of the Canada Geographic Information System, the world's first geographic information system (GIS). |
|
30 Nov 1961

Thomas Kuhn |
Thomas Kuhn (history of science) Thomas Kuhn's The Structure of Scientific Revolutions is published in the United States. |
|
30 Nov 1961

James W. Black |
James W. Black (medicine) James W. Black synthesises propranolol, the first beta blocker (used for regulation of angina pectoris), which becomes the world's best-selling drug. |
|
30 Nov 1961

Joseph Murray |
Joseph Murray (medicine) Joseph Murray performs the first permanent cadaveric kidney transplantation. |
|
30 Nov 1961

Nodding disease |
Nodding disease (medicine) Nodding disease is first documented, in southern Tanzania. |
|
30 Nov 1961

New Austrian Tunnelling method |
New Austrian Tunnelling method (technology) The New Austrian Tunnelling method is so named. |
|
30 Nov 1961

Fields Prize in Mathematics |
Fields Prize in Mathematics (awards) Fields Prize in Mathematics: Lars Hörmander and John Milnor |
|
30 Nov 1961

Maxwell Medal and Prize |
Maxwell Medal and Prize (awards) Maxwell Medal and Prize of the Institute of Physics (first award): Abdus Salam |