| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1966

NRAO |
NRAO (astronomy and space ) NRAO builds the 36-foot Radio Telescope, later to become the ARO 12m Radio Telescope. |
|
30 Nov 1966

Chimpanzee |
Chimpanzee (biology) Chimpanzee Washoe begins to learn American Sign Language. |
|
30 Nov 1966

Arno Peters |
Arno Peters (cartography) Arno Peters reinvents the Gall orthographic equal-area projection. |
|
30 Nov 1966

Errett Bishop |
Errett Bishop (mathematics) Errett Bishop publishes Foundations of Constructive Analysis, proving theorems in real analysis using constructive analysis. |
|
30 Nov 1966
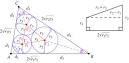
Malfatti circles |
Malfatti circles (mathematics) Michael Goldberg demonstrates that none of the original Malfatti circles are ever optimal. |
|
30 Nov 1966
Thomas Starzl |
Thomas Starzl (medicine) Thomas Starzl performs the first successful human liver transplantation, at the University of Colorado Health Sciences Center. |
|
30 Nov 1966
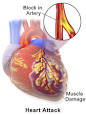
myocardial infarction |
myocardial infarction (medicine) First use, in a case of myocardial infarction, of the intra-aortic balloon pump invented by Dr Adrian Kantrowitz and his brother Arthur. |
|
30 Nov 1966

Neurosurgeons |
Neurosurgeons (medicine) Neurosurgeons Jean Talairach and Gabor Szikla create the Talairach coordinates for brain mapping. |
|
30 Nov 1966

St Christopher's Hospice |
St Christopher's Hospice (medicine) St Christopher's Hospice, the world's first purpose-built secular hospice specialising in palliative care of the terminally ill, is established in South London by Cicely Saunders. |
|
30 Nov 1966

electroweak interaction |
electroweak interaction (physics) The electroweak interaction theory is introduced by Steven Weinberg. |
|
30 Nov 1966
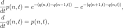
Toda lattice |
Toda lattice (physics) The Toda lattice is introduced by Morikazu Toda as a simple model for a one-dimensional crystal in solid state physics. |
|
30 Nov 1966

Turing Award |
Turing Award (awards) Turing Award – Maurice Vincent Wilkes |
|
03 Jan 1967

Reginald Punnett |
death Reginald Punnett Reginald Punnett (born 1875), English geneticist. |
|
16 Jan 1967

Robert J. Van de Graaff |
death Robert J. Van de Graaff Robert J. Van de Graaff (born 1901), American physicist. |
|
19 Jan 1967

Casimir Funk |
death Casimir Funk Casimir Funk (born 1884), Polish biochemist, coined the term vitamin. |
|
27 Jan 1967

Apollo 1 |
Apollo 1 (astronomy and space ) Apollo 1 destroyed in a fire on the launch pad. |
|
27 Jan 1967

USA |
USA (astronomy and space ) The USA, Soviet Union and UK sign the Outer Space Treaty. |
|
18 Feb 1967

J. Robert Oppenheimer |
death J. Robert Oppenheimer J. Robert Oppenheimer (born 1904), American physicist. |
|
24 Feb 1967

Brian Schmidt |
birth Brian Schmidt Brian Schmidt, Australian winner of the Nobel Prize in Physics (2011). |
|
14 Mar 1967

Therkel Mathiassen |
death Therkel Mathiassen Died 14 Mar 1967 at age 74 (born 5 Sep 1892). Danish archaeologist and ethnographer laid the groundwork for the scientific study of arctic archaeology. His excavations (1921-23) of the Thule prehistoric Eskimo culture were the first scientific archaeological investigations in the Canadian Arctic. Mathiassen, as a member of the Danish Fifth Thule Expedition (1922), excavated ruins at Naujan (called Nauyat by local people), one of the most important sites of its time period. He uncovered and mapped a dozen sod house ruins, tent rings, graves, meat caches, kayak stands, and a refuse heap almost larger than the houses. His work defined the culture of the people who had lived in there. The Thule (pronounced Too-lee) people are ancestors of the modern Inuit. |
|
27 Mar 1967

Jaroslav Heyrovský |
death Jaroslav Heyrovský Jaroslav Heyrovský (born 1890), Czech chemist. |
|
05 Apr 1967

Hermann Joseph Muller |
death Hermann Joseph Muller Hermann Joseph Muller (born 1890), American geneticist. |
|
20 Apr 1967

Surveyor 3 |
Surveyor 3 (astronomy and space ) Surveyor 3 probe lands on the Moon. |
|
24 Apr 1967

Soviet |
Soviet (astronomy and space ) Soviet cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov is killed during the landing of Soyuz 1. |
|
24 Apr 1967

Vladimir Komarov |
death Vladimir Komarov Vladimir Komarov (born 1927), cosmonaut on Soyuz 1. |
|
01 May 1967

René Favaloro |
René Favaloro (medicine) Dr René Favaloro performs the first saphenous vein autograft in coronary artery bypass surgery, at the Cleveland Clinic in the United States. |
|
05 May 1967

Owen Thomas Jones |
death Owen Thomas Jones Owen Thomas Jones (born 1878), Welsh geologist |
|
27 May 1967

Tilly Edinger |
death Tilly Edinger Tilly Edinger (born 1897), German American paleoneurologist. |
|
15 Aug 1967

Nicodemus Abel |
birth Nicodemus Abel Nicodemus Abel, Indian Plant geneticist. |
|
22 Aug 1967

Gregory Goodwin Pincus |
death Gregory Goodwin Pincus Gregory Goodwin Pincus (born 1903), American biologist who co-invented the combined oral contraceptive pill. |
|
29 Aug 1967

Charles Darrow |
death Charles Darrow Died 29 Aug 1967 at age 78 (born 10 Aug 1889). Charles Brace Darrow was an American inventor who designed the board game Monopoly. He had invented the game on 7 Mar 1933, though it was preceded by other real-estate board games. On 31 Dec 1935, a patent was issued for the game of Monopoly assigned to Parker Brothers, Inc., by Charles Darrow of Pennsylvania (No. 2,026,082). The patent titled it a “Board Game Apparatus” and described it as “intended primarily to provide a game of barter, thus involving trading and bargaining” in which “much of the interest in the game lies in trading and in striking shrewd bargains.” Illustrations included with the patent showed not only the playing board and pieces, cards, and the scrip money. Parker Brothers began mass marketing the game on 7 Feb 1935. |
|
03 Oct 1967

Record speed |
Record speed In 1967, the X-15 rocket plane achieved a world record speed of Mach 6.7, which is 4,520 mph or over a mile per second, with U.S. Air Force pilot Pete Knight. It reached an altitude of 192,100 feet (58,552 m). Its internal structure of titanium was covered with a skin of Inconel X, a chrome-nickel alloy. To save fuel, the X-15 was air launched from a B-52 aircraft at about 45,000 ft. Test flights between 8 Jun 1959 and 24 Oct 1968 provided data on hypersonic air flow, aerodynamic heating, control and stability at hypersonic speeds and piloting techniques for reentry used in the development of the Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo spaceflight programs. The X-15 reached 354,200 feet (67 miles) on 22 Aug 1963. |
|
12 Oct 1967

Desmond Morris |
Desmond Morris (anthropology) Desmond Morris publishes The Naked Ape. |
|
18 Oct 1967

Venera 4 |
Venera 4 (astronomy and space ) The Soviet Venera 4 probe descends through the Venusian atmosphere, which it analyzes. |
|
19 Oct 1967

Mariner 5 |
Mariner 5 (astronomy and space ) Mariner 5 probe flies by Venus. |
|
01 Nov 1967
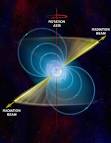
Pulsars |
Pulsars (astronomy and space ) Pulsars discovered by Jocelyn Bell working with Antony Hewish at the University of Cambridge, for which Hewish is awarded a Nobel Prize in Physics in 1974. These rapidly pulsating radio sources are explained a year later as rotating neutron stars. |
|
09 Nov 1967

Apollo program |
Apollo program (astronomy and space ) Apollo program: NASA launches a Saturn V rocket carrying the unmanned Apollo 4 test spacecraft from Cape Kennedy. |
|
03 Dec 1967

Christiaan Barnard |
Christiaan Barnard (medicine) Dr Christiaan Barnard and a team including his brother Marius perform the first successful human heart transplantation, at Groote Schuur Hospital in Cape Town, South Africa, on Louis Washkansky, who survives for eighteen days before dying of pneumonia. |
|
06 Dec 1967

Adrian Kantrowitz |
Adrian Kantrowitz (medicine) Dr Adrian Kantrowitz performs the first pediatric heart transplant, at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, United States, on a 19-day-old infant, who survives for six hours. |