| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1968

Thomas D. Brock |
Thomas D. Brock (biology) Thomas D. Brock and Hudson Freeze of Indiana University publish their findings on hyperthermophilic bacteria, most notably Thermus aquaticus, a thermophilic bacterium species living at a temperature of 60-80°C in a hot spring at Yellowstone National Park.T. aquaticus (Taq) later becomes a standard source of enzymes able to withstand higher temperatures than those from E. Coli and is significant in the history of polymerase chain reaction. |
|
30 Nov 1968

Przewalski's Horse |
Przewalski's Horse (biology) Last Przewalski's Horse sighted in the wild, in Mongolia. |
|
30 Nov 1968

Dorothy Hodgkin |
Dorothy Hodgkin (chemistry) Dorothy Hodgkin and colleagues at the University of Oxford determine the structure of insulin. |
|
30 Nov 1968

laser printer |
laser printer (computer science) The laser printer is invented at Xerox by Gary Starkweather. |
|
30 Nov 1968
AIDS virus |
AIDS virus (medicine) Reported as being the year the first strain of the AIDS virus (HIV) migrates to the United States via Haiti. |
|
30 Nov 1968
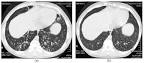
diffuse panbronchiolitis |
diffuse panbronchiolitis (medicine) The condition diffuse panbronchiolitis is named, in Japan. |
|
30 Nov 1968

Sudden infant death syndrome |
Sudden infant death syndrome (medicine) International adoption of the diagnostic term 'Sudden infant death syndrome'. |
|
30 Nov 1968

Eugene, Oregon |
Eugene, Oregon (meteorology) Eugene, Oregon, has a record snowfall of 3 feet in 3 days: a pineapple express moves into the region with a shot of cold air, followed by some snow showers. |
|
30 Nov 1968

Herbert Saffir |
Herbert Saffir (meteorology) Herbert Saffir and Bob Simpson develop the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale. |
|
30 Nov 1968

John Ostrom |
John Ostrom (paleontology) John Ostrom publishes his findings on the dinosaur Deinonychus, describing it as being a small, agile species closely related to the birds. |
|
30 Nov 1968

Yoichiro Nambu |
Yoichiro Nambu (physics) Yoichiro Nambu and Leonard Susskind make the first presentations of string theory. |
|
30 Nov 1968

Spain |
Spain (physics) Spain withdraws from CERN. |
|
30 Nov 1968

Turing Award |
Turing Award (awards) Turing Award – Marvin Minsky |
|
30 Nov 1968

Thomas Reardon |
birth Thomas Reardon Thomas Reardon, American computer programmer. |
|
03 Mar 1969

Elizabeth Laird |
death Elizabeth Laird Elizabeth Laird (born 1874), Canadian physicist. |
|
04 Apr 1969

Denton Cooley |
Denton Cooley (medicine) Surgeons Denton Cooley and Domingo Liotta implant the first temporary artificial heart. |
|
07 Apr 1969

RFC 1 |
RFC 1 (computer science) RFC 1, the first Request for Comments document from the Internet Engineering Task Force, is published. |
|
09 Apr 1969

First flight of British Concorde prototype 002 |
First flight of British Concorde prototype 002 In 1969, the British Concorde prototype 002 left Filton airport, Bristol, on its first flight with test pilot Brian Trubshaw at the controls. The French prototype Concorde 001 had already made its first flight the previous month, on 2 Mar 1969, from Toulouse. An even earlier first flight was made on 31 Dec 1968, by the Russian Tupolev TU-144 supersonic-capable airliner (a Concorde look-alike, dubbed Concordski in the West). The first Concorde to fly at supersonic speed, over Mach 1, was prototype 001 on 1 Oct 1969. |
|
14 May 1969

Walter Pitts |
death Walter Pitts Walter Pitts (born 1923), American logician and cognitive psychologist. |
|
22 Jun 1969

Cuyahoga River fire |
Cuyahoga River fire In 1969, in America, oil-sodden floating debris on the Cuyahoga River ignited (perhaps by sparks from a passing train) and burned with flames reported up to five stories high. Although fire-fighters extinguished the blaze in a half-hour or so, it caused $50,000 in damage. For a century the Cleveland, Ohio river had been an open sewer for industrial waste, through the times when factory production seemed more important than worrying about the environment. Several fires had happened in the prior hundred years, but attitudes changed to outrage as this time, national attention was aroused. It became one of several disasters that led to the Clean Water Act and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Determined remedial action for decades since has resulted in cleaner water, and improving aquatic life. |
|
24 Jun 1969

Willy Ley |
death Willy Ley Willy Ley (born 1906), German American scientific populariser. |
|
08 Aug 1969
Otmar von Verschuer |
death Otmar von Verschuer Otmar von Verschuer (born 1896), German eugenicist. |
|
17 Aug 1969

Otto Stern |
death Otto Stern Otto Stern (born 1888), German physicist, Nobel laureate in Physics in 1943. |
|
16 Sep 1969

Henry Fairfield Osborn, Jr. |
death Henry Fairfield Osborn, Jr. Henry Fairfield Osborn, Jr. (born 1887), American conservationist. |
|
24 Sep 1969

Warren Sturgis McCulloch |
death Warren Sturgis McCulloch Warren Sturgis McCulloch (born 1898), American neurophysiologist and cybernetician. |
|
30 Sep 1969

Sir Frederic Bartlett |
death Sir Frederic Bartlett Died 30 Sep 1969 at age 82 (born 20 Oct 1886). Sir Frederic Charles Bartlett was an English psychologist who was Britain's most outstanding cognitive psychologist between the World Wars. He wrote on practical (ergonomic) problems in applied psychology, but is best-known for his pioneering cognitive approach to understanding human memory. In forming one of the earliest models of memory, Bartlett observed that in remembering stories or events there is a tendency for distortions to occur. In his most famous experiment, Bartlett had subjects read a folk tale, tested their recall several times, and studied their changing recountings of the story. People tend to remember what they regard as most important and recall what would have been expected rather than what actually occurred. |
|
07 Oct 1969

Karen L. Nyberg |
birth Karen L. Nyberg Karen L. Nyberg, American space engineer and astronaut. |
|
21 Oct 1969

Wacław Sierpiński |
death Wacław Sierpiński Wacław Sierpiński (born 1882), Polish mathematician. |
|
29 Oct 1969

ARPANET |
ARPANET (computer science) The first ARPANET message is sent, between computers at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and Stanford Research Institute. |
|
12 Nov 1969

William F. Friedman |
death William F. Friedman William F. Friedman (born 1891), Russian American cryptanalyst. |
|
21 Nov 1969

Interface Message Processors |
Interface Message Processors (computer science) The first permanent ARPANET link is established, between Interface Message Processors at UCLA and Stanford. |
|
05 Dec 1969
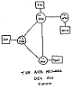
ARPANET linked four nodes |
ARPANET linked four nodes In 1969, the nacent ARPANET grew to four nodes when ARPA (the U.S. Department of Defense's Advanced Research Projects Agency) connected computer network nodes at four universities: the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), the Stanford Research Institute (SRI) in Menlo Park, Calif., U.C. Santa Barbara, and the University of Utah. Initial test login characters had been sent on 29 Oct 1969 from a ULCA computer to a computer at SRI, which were permanently connected on 21 Nov 1969 through early routers (small packet-switching computers then called Interface Message Processors). This “network of networks” eventually evolved into what became known as the Internet of the mid-1980s. |
|
16 Dec 1969

Adam Riess |
birth Adam Riess Adam Riess, American astrophysicist, Nobel laureate in Physics in 2011. |
|
28 Dec 1969

Linus Torvalds |
birth Linus Torvalds Linus Torvalds, Finnish computer programmer. |