| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1970
thermophile |
thermophile (biology) Francis G. Howarth discovers communities of specialized thermophile cave animals living in lava tubes at Hawaii Volcanoes National Park. |
|
30 Nov 1970

C. A. W. Jeekel |
C. A. W. Jeekel (biology) C. A. W. Jeekel publishes Nomenclator Generum et Familiarum Diplopodorum. |
|
30 Nov 1970

John O'Keefe |
John O'Keefe (biology) John O'Keefe discovers place cells in the mammalian brain. |
|
30 Nov 1970

Ray Tomlinson |
Ray Tomlinson (computer science) Ray Tomlinson sends the first ARPAnet e-mail between host computers, at BBN, Cambridge, Massachusetts, with the first use of the @ sign in an address. |
|
30 Nov 1970

Daniel Quillen |
Daniel Quillen (mathematics) Daniel Quillen publishes a proof of the Adams conjecture. |
|
30 Nov 1970

Steven Takiff |
Steven Takiff (mathematics) Steven Takiff introduces Takiff algebras. |
|
30 Nov 1970
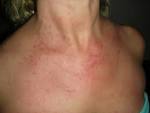
adult-onset Still's disease |
adult-onset Still's disease (medicine) E. G. L. Bywaters characterises adult-onset Still's disease, a rare form of inflammatory arthritis. |
|
30 Nov 1970
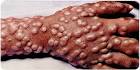
Smallpox |
Smallpox (medicine) Smallpox is eradicated from the Americas. |
|
30 Nov 1970

Konrad Lorenz |
Konrad Lorenz (psychology) Studies in Animal and Human Behavior, Volume II is published by Konrad Lorenz. |
|
30 Nov 1970

Turing Award |
Turing Award (awards) Turing Award – John McCarthy |
|
30 Nov 1970

Howard Gobioff |
birth Howard Gobioff Howard Gobioff (d. 2008), American computer scientist. |
|
31 Jan 1971

Apollo program |
Apollo program (astronomy and space ) Apollo program: Astronauts aboard Apollo 14 lift off for a mission to the moon. |
|
02 Feb 1971

Ramsar Convention |
Ramsar Convention (conservation) The international Ramsar Convention for the conservation and sustainable utilization of wetlands is signed in Ramsar, Mazandaran, Iran. |
|
05 Feb 1971

Third U.S. manned moon landing |
Third U.S. manned moon landing In 1971, Apollo 14, the third US manned Moon expedition, landed with two astronauts in the lunar highlands near the crater Fra Mauro. Commander Alan B. Shepard and Lunar Module pilot Edgar D. Mitchell became the fifth and sixth men to walk on the Moon. During this four-hour activity, they deployed the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) containing scientific experiments to be left on the lunar surface and other scientific and sample collection apparatus. Before lifting off on the next day (6 Feb 1971), the astronauts went on another moonwalk almost to the rim of nearby Cone crater, collecting 42.9-kg of samples along the traverse. At the end of this 3.45-km walk, Shepard used a contingency sampler with a 6-iron connected to the end to hit two golf balls. |
|
05 Feb 1971

Apollo 14 |
Apollo 14 (astronomy and space ) Apollo 14 lands on the Moon. |
|
09 Feb 1971

San Fernando (Sylmar) earthquake |
San Fernando (Sylmar) earthquake (earth sciences) The San Fernando (Sylmar) earthquake occurred in southern California with a magnitude of 6.6 and a perceived intensity of XI (extreme) on the Modified Mercalli Intensity scale. |
|
11 Mar 1971

Philo T. Farnsworth |
death Philo T. Farnsworth Philo T. Farnsworth (b. 1906), American television pioneer. |
|
01 Apr 1971

Kathleen Lonsdale |
death Kathleen Lonsdale Dame Kathleen Lonsdale (b. 1903), Irish-born crystallographer. |
|
06 Apr 1971

Margaret Newton |
death Margaret Newton Margaret Newton (b. 1887), Canadian plant pathologist. |
|
12 Apr 1971

Igor Yevgenyevich Tamm |
death Igor Yevgenyevich Tamm Died 12 Apr 1971 at age 75 (born 8 Jul 1895). Soviet physicist who shared the 1958 Nobel Prize for Physics with Pavel A. Cherenkov and Ilya M. Frank for his efforts in explaining Cherenkov radiation. Tamm was an outstanding theoretical physicist, after early researches in crystallo-optics, he evolved a method for interpreting the interaction of nuclear particles. Together with I. M. Frank, he developed the theoretical interpretation of the radiation of electrons moving through matter faster than the speed of light (the Cerenkov effect), and the theory of showers in cosmic rays. He has also contributed towards methods for the control of thermonuclear reactions. |
|
19 May 1971

Mars probe program |
Mars probe program (astronomy and space ) Mars probe program: Mars 2 is launched by the Soviet Union. |
|
30 May 1971

Mariner program |
Mariner program (astronomy and space ) Mariner program: Mariner 9 is launched toward Mars. |
|
06 Jun 1971

Edward Andrade |
death Edward Andrade Edward Andrade (b. 1887), English physicist. |
|
10 Jun 1971

Otto Heinrich Schindewolf |
death Otto Heinrich Schindewolf Died 10 Jun 1971 at age 75 (born 7 Jun 1896). German paleontologist, known for his research on corals and cephalopods. He was an anti-Darwinist, who advocated a cataclysmic theory of evolution to explain the origin of the higher taxonomic categories. Studying different fossil species of coral and ammonites obtained from sequential geological strata, he concluded that the most recent taxonomic categories could not have arisen by slow, intermediate steps, generally thought to characterize evolution, but rather by large, single transformations. Though his views are not accepted by many biologists, particularly the population geneticists, who consider them too controversial, he has drawn attention to fundamental problems in evolution. |
|
25 Jun 1971

Sir John Boyd Orr |
death Sir John Boyd Orr Died 25 Jun 1971 at age 90 (born 23 Sep 1880). Scottish physician, biologist and politician who was an authority on nutrition and winner of the Nobel Prize for Peace in 1949 for his efforts to eliminate world hunger. In 1936, he published a report, Food, Health and Income, a dietary survey by income groups made during 1935. It showed that the cost of a diet fulfilling basic nutritional requirements was beyond the means of half the British population and that 10 percent of the population was undernourished. This and other reports conducted by the Rowett Research Institute formed the basis of the British food-rationing system during WW II. He was director general of the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (1945-48). |
|
30 Jun 1971

Soyuz 11 |
Soyuz 11 (astronomy and space ) The crew of the Soyuz 11 spacecraft are killed when their air supply leaks out through a faulty valve during re-entry preparations, the only human deaths to occur outside Earth's atmosphere. |
|
04 Jul 1971

Michael S. Hart |
Michael S. Hart (computer science) Michael S. Hart posts the first e-book, a copy of the United States Declaration of Independence, on the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign's mainframe computer, the origin of Project Gutenberg. |
|
04 Jul 1971

Sivakumar Veerasamy |
birth Sivakumar Veerasamy Sivakumar Veerasamy, Indian plant geneticist. |
|
02 Aug 1971

Ruth Lawrence |
birth Ruth Lawrence Ruth Lawrence, English-born mathematician. |
|
14 Aug 1971

Stanford prison experiment |
Stanford prison experiment (psychology) Stanford prison experiment. |
|
24 Aug 1971

Carl Blegen |
death Carl Blegen Died 24 Aug 1971 at age 84 (born 27 Jan 1887). Carl William Blegen was an American archaeologist who unearthed evidence that supported and dated the sack of Troy recorded in Homer's Iliad. Storage jars, skeletons and ash piles (which he interpreted as evidence of the city's fiery destruction) reinforced his conviction. He also discovered, in 1939, clay tablets dating from about 1250 BC. At the fabled palace of King Nestor, a major figure in the Trojan War, nearly 1,100 clay tablet records of palace transactions were found there over 15 years. These were inscribed with the earliest known examples of European writing, enabling cryptographers to find the key by which the ancient tablets could be decoded, proving the existence of a Greek civilization where none was formerly thought to exist. |
|
23 Sep 1971

James W. Alexander |
death James W. Alexander Died 23 Sep 1971 at age 83 (born 19 Sep 1888). James Waddell Alexander was an American mathematician who founded the branch of mathematics originally known as analysis situs, now called topology. In 1912, he joined the faculty of the mathematics department at Princeton. Soon after, Alexander generalised the Jordan curve theorem and, in 1928, he discovered the Alexander polynomial which is much used in knot theory. |
|
01 Oct 1971

Godfrey Hounsfield |
Godfrey Hounsfield (medicine) Godfrey Hounsfield's invention, X-ray computed tomography, is first used on a patient with a cerebral cyst at Atkinson Morley Hospital in Wimbledon, London. |
|
29 Oct 1971
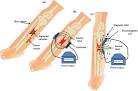
Bone repair by electricity |
Bone repair by electricity In 1971, the first successful use of electricity to repair a bone fracture is reported by surgeons at the University of Pennsylvania. Electrical currents have been used to heal bone since the mid-1800s, and the effect of electrical stimulation on bone has been long studied and well documented.When human bone is bent or broken, it generates an electrical charge ("On the Piezoelectric Effect of Bone", Fukada and Yasuda, 1957). This low level electrical charge stimulates the body's internal repair mechanism. |
|
29 Oct 1971

Arne Tiselius |
death Arne Tiselius Died 29 Oct 1971 at age 69 (born 10 Aug 1902). Arne Wilhelm Kaurin Tiselius was a Swedish biochemist who won the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1948 for his work on electrophoresis and other new methods of separating and detecting colloids and serum proteins. In electrophoresis - a method of separating chemically similar charged colloids - an electrical field is applied to the sample, and particles with different sizes migrate at different rates to the pole of opposite charge, enabling them to be detected and identified. Using the technique on blood serum Tiselius confirmed the existence of four different groups of proteins - albumins and alpha, beta, and gamma globulins. Tiselius also conducted work on chromatography (from 1940) and partition and gel filtration (from the late 1950s). |
|
13 Nov 1971

Mars satellite |
Mars satellite In 1971, Mariner-9, the first man-made object to orbit another planet, entered Martian orbit. The mission of the unmanned craft was to return photographs mapping 70% of the surface, and to study the planet's thin atmosphere, clouds, and hazes, together with its surface chemistry and seasonal changes. |
|
15 Nov 1971

Intel |
Intel (computer science) Intel release the world's first microprocessor, the 4004. |
|
12 Dec 1971

David Sarnoff |
death David Sarnoff Died 12 Dec 1971 at age 80 (born 27 Feb 1891). American inventor who was a pioneer in the development of both radio and television broadcasting. He was the first general manager of RCA and founded the television network NBC (1926). His first job was that of delivery boy, and his life continued to display a rags-to-riches element. He became a wireless operator and met Marconi in 1906. Foreseeing the multiple possibilities of radio, he became commercial manager of American Marconi in 1917, having already predicted that radio would become “a household utility in the same sense as the piano or phonograph”. RCA succeded the Marconi group (1919), and Sarnoff became its general manager (1921) then its president (1930-50). He steering it into the world of television, first black and white, then colour with NBC. |