| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1972
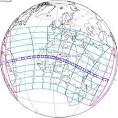
Solar eclipse of June 30, 1973 |
Solar eclipse of June 30, 1973 (astronomy and space ) Solar eclipse of June 30, 1973 – Very long total solar eclipse visible in NE South America, the Atlantic, and central Africa. During the entire Second Millennium, only seven total solar eclipses exceeded seven minutes of totality. This was the last. Observers aboard a Concorde jet were able to stretch totality to about 74 minutes by flying along the path of the moon's umbra. |
|
30 Nov 1972

http://delobueno-lomejor.com/visitas/2014/10/13/primero-pasos-mailchimp/ |
http://delobueno-lomejor.com/visitas/2014/10/13/primero-pasos-mailchimp/ (astronomy and space ) http://delobueno-lomejor.com/visitas/2014/10/13/primero-pasos-mailchimp/ |
|
30 Nov 1972

Waldo R. Tobler |
Waldo R. Tobler (cartography) Waldo R. Tobler introduces the Tobler hyperelliptical projection. |
|
30 Nov 1972
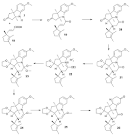
Vitamin B12 total synthesis |
Vitamin B12 total synthesis (chemistry) A successful method of Vitamin B12 total synthesis is reported by the groups of Robert Burns Woodward and Albert Eschenmoser. |
|
30 Nov 1972

Fischer Black |
Fischer Black (mathematics) Fischer Black and Myron Scholes first articulate the Black–Scholes mathematical model of a financial market containing certain derivative investment instruments. |
|
30 Nov 1972
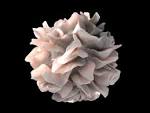
dendritic cell |
dendritic cell (physiology and medic) The term "dendritic cell" is coined by Ralph M. Steinman working with Zanvil A. Cohn. |
|
30 Nov 1972

David Rosenhan |
David Rosenhan (psychology) David Rosenhan publishes the results of his experiment into the validity of psychiatric diagnosis. |
|
30 Nov 1972

American Psychiatric Association |
American Psychiatric Association (psychology) The American Psychiatric Association officially declares that homosexuality is not a mental disorder. |
|
30 Nov 1972

humanoid robot |
humanoid robot (technology) Ichiro Kato, Waseda University, develops the world's first full-scale humanoid robot, Wabot-1. |
|
30 Nov 1972

Turing Award |
Turing Award (awards) Turing Award – Charles W. Bachman |
|
05 Feb 1973

John H. Gibbon |
death John H. Gibbon Died 5 Feb 1973 at age 69 (born 29 Sep 1903). John Heyburn Gibbon was an American surgeon who invented the heart-lung machine. He was prompted when in 1930, as a Harvard research fellow in surgery, he saw a patient undergoing heart-lung surgery suffocate on his own blood. On 10 May 1935, he had built his first external pump, and was able to maintain the cardiac and respiratory functions of a cat. In the late 1940's, Gibbon received financial and technical assistance from the IBM Corporation to develop an oxygenator with sufficient capacity for a human. By 6 May 1953, with his improved machine he was able to perform the first successful open-heart operation - the repair of an atrial septal defect on 18-yr-old Cecelia Bavolek - maintaining the patient's heart and lung functions on the machine for 26 minutes. |
|
11 Feb 1973

J. Hans D. Jensen |
death J. Hans D. Jensen J. Hans D. Jensen (b. 1907), German nuclear physicist |
|
23 Feb 1973

Dickinson W. Richards |
death Dickinson W. Richards Died 23 Feb 1973 at age 77 (born 30 Oct 1895). American physiologist who was one of three who shared the 1956 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning heart catheterization and pathological changes in the circulatory system". Richards helped develop the technique by which a catheter (a flexible tube) could be threaded through a vein into the heart to withdraw blood samples to determine cardiac abnormalities. In addition, it permits the measurement of blood pressure, blood flow or gas concentrations in various parts of the cardiac circulatory system (atrium, ventricles, or artery). This gives valuable information in the treatment of heart disease, defect or injury. Richards worked with André F. Cournand building on the original work of Werner Forssmann. |
|
06 Mar 1973

Montenegrin Academy of Sciences and Arts |
Montenegrin Academy of Sciences and Arts (institutions) The Montenegrin Academy of Sciences and Arts, founded as the Montenegrin Society for Science and Arts (Crnogorsko društvo za nauku i umjetnost), elects its first members. |
|
07 Mar 1973

Comet Kohoutek |
Comet Kohoutek (astronomy and space ) Comet Kohoutek is discovered |
|
12 Mar 1973

David Lack |
death David Lack David Lack (b. 1910), English ornithologist |
|
14 Mar 1973

Howard Hathaway Aiken |
death Howard Hathaway Aiken Died 14 Mar 1973 at age 73 (born 9 Mar 1900). American mathematician who invented the Harvard Mark I, forerunner of the modern electronic digital computer. While a graduate student and instructor Harvard University, Aiken's research had led to a system of differential equations which could only be solved using numerical techniques, for which he began planning large computer. His idea was to use an adaptation of Hollerith's punched card machine. When eventually built, (1943) it weighed 35 tons, had 500 miles of wire and could compute to 23 significant figures. There were 72 storage registers and central units to perform multiplication and division. It was controlled by a sequence of instructions on punched paper tapes, and used punched cards to enter data and give output from the machine. |
|
14 Mar 1973

Howard H. Aiken |
death Howard H. Aiken Howard H. Aiken (b. 1900), American computing pioneer |
|
03 Apr 1973

mobile phone |
mobile phone (technology) The first handheld mobile phone call is made by Martin Cooper of Motorola in New York City. |
|
06 Apr 1973

Pioneer 11 |
Pioneer 11 (astronomy and space ) Launch of Pioneer 11 spacecraft |
|
05 May 1973

BBC Television |
BBC Television (history of science) July 28 – BBC Television series The Ascent of Man, written and presented by Jacob Bronowski, first airs; there is also an accompanying bestselling book. |
|
14 May 1973
United States |
United States (astronomy and space ) Skylab, the United States' first space station, is launched. |
|
22 Jun 1973

First Skylab crew returns |
First Skylab crew returns In 1973, the first Skylab crew of astronauts splashed down safely after a then record 28 days in space. The Skylab was a manned, orbiting spacecraft composed of five parts: the Apollo telescope mount was a solar observatory, the multiple docking adapter, the airlock module, the instrument unit, and the orbital workshop. The Skylab itself was launched on 14 May 1973. It was first manned during the period 25 May to 22 Jun 1973, by the crew of the SL-2 mission. Next, it was manned during the period Jul 28 to 5 Sep 1973 and the final manned period was from 16 Nov 1973 - 8 Feb 1974. The crew quarters contained provisions and supplies necessary to support three-person crews for periods of up to 84 days each. |
|
03 Jul 1973

Laurens Hammond |
death Laurens Hammond Laurens Hammond (b. 1895), American inventor |
|
25 Jul 1973

Soviet |
Soviet (astronomy and space ) Soviet Mars 5 space probe launched. |
|
23 Sep 1973

Ceefax teletext |
Ceefax teletext In 1973, the world's first Ceefax teletext service began on BBC Television. |
|
01 Oct 1973
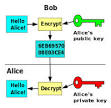
public-key cryptography |
public-key cryptography (cryptography) Asymmetric key algorithms for public-key cryptography developed by James H. Ellis, Clifford Cocks and Malcolm Williamson at the United Kingdom Government Communications Headquarters. |
|
05 Oct 1973

Cédric Villani |
birth Cédric Villani Cédric Villani, French mathematician |
|
03 Nov 1973

Mariner program |
Mariner program (astronomy and space ) Mariner program: NASA launches the Mariner 10 toward Mercury (on March 29, 1974 it became the first space probe to reach that planet). |
|
19 Nov 1973

Nim Chimpsky |
birth Nim Chimpsky Nim Chimpsky (d. 2000), chimpanzee |
|
03 Dec 1973

Pioneer program |
Pioneer program (astronomy and space ) Pioneer program: Pioneer 10 sends back the first close-up images of Jupiter. |
|
05 Dec 1973

Sir Robert Alexander Watson-Watt |
death Sir Robert Alexander Watson-Watt Died 5 Dec 1973 at age 81 (born 13 Apr 1892). Scottish physicist who is credited with the development of radar location of aircraft, in England. He studied at St Andrews University, taught at Dundee University, and in 1917 worked in the Meteorological Office, designing devices to locate thunderstorms, and investigating the ionosphere (a term he invented in 1926). He became head of the radio section of the National Physical Laboratory (1935), where he began work on locating aircraft. His work led to the development of radar (RAdio Detection And Ranging) which played a vital role in the defence of Britain against German air raids in 1940. He was knighted in 1942. |
|
05 Dec 1973

Luboš Motl |
birth Luboš Motl Luboš Motl, Czech theoretical physicist |
|
07 Dec 1973

Ohio State University Radio Observatory |
Ohio State University Radio Observatory (astronomy and space ) The "Big Ear" at the Ohio State University Radio Observatory begins a full-time SETI radio survey, running continuously until 1995. |
|
10 Dec 1973

Wolf V. Vishniac |
death Wolf V. Vishniac Wolf V. Vishniac (b. 1922), American microbiologist |
|
28 Dec 1973

Endangered Species Act |
Endangered Species Act (biology) Endangered Species Act signed into law in the United States. |