| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1984
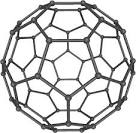
fullerene |
fullerene (chemistry) The fullerene Buckminsterfullerene (C60) is first intentionally prepared by Harold Kroto, James R. Heath, Sean O'Brien, Robert Curl and Richard Smalley at Rice University in the United States. |
|
30 Nov 1984

Jean-Pierre Serre |
Jean-Pierre Serre (mathematics) Jean-Pierre Serre provides partial proof that a Frey curve cannot be modular, showing that a proof of the semistable case of the Taniyama-Shimura conjecture would imply Fermat's Last Theorem. |
|
30 Nov 1984

Leonard Adleman |
Leonard Adleman (mathematics) Leonard Adleman, Roger Heath-Brown and Étienne Fouvry prove that the first case of Fermat's Last Theorem holds for infinitely many odd primes p. |
|
30 Nov 1984
controlled trials |
controlled trials (medicine) Publication of a classified bibliography of 3500 reports on controlled trials in perinatal medicine published since 1940. |
|
30 Nov 1984

neurologist |
neurologist (medicine) New York-based neurologist Oliver Sacks publishes The Man Who Mistook His Wife for a Hat and Other Clinical Tales. |
|
30 Nov 1984

Portugal |
Portugal (physics) Portugal joins CERN. |
|
30 Nov 1984
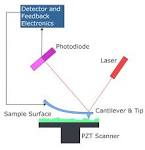
Atomic force microscope |
Atomic force microscope (technology) Atomic force microscope invented by Gerd Binnig, Calvin Quate and Christopher Berger. |
|
30 Nov 1984

Turing Award |
Turing Award (awards) Turing Award – Richard Karp – for his work on computational complexity theory |