| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1990

Asteroid 6859 Datemasamune |
Asteroid 6859 Datemasamune (astronomy and space ) Asteroid 6859 Datemasamune is discovered by Masahiro Koishikawa. |
|
30 Nov 1990

11514 Tsunenaga |
11514 Tsunenaga (astronomy and space ) 11514 Tsunenaga is discovered. |
|
30 Nov 1990

lunar eclipses |
lunar eclipses (astronomy and space ) There are four lunar eclipses: three penumbral on January 30, July 26, and June 27, and one minor partial lunar eclipse on December 21. |
|
30 Nov 1990

solar eclipses |
solar eclipses (astronomy and space ) There are two solar eclipses, one annular eclipse on January 15, and a very long total eclipse on July 11, lasting 6 minutes and 53 seconds. |
|
30 Nov 1990

Finland |
Finland (atomic physics) Finland and Poland join CERN. |
|
30 Nov 1990
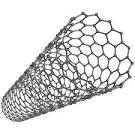
Carbon nanotubes |
Carbon nanotubes (chemistry) Carbon nanotubes discovered in the insoluble material of arc-burned graphite rods by Sumio Iijima of NEC. |
|
30 Nov 1990

Pei-Yuan Wei |
Pei-Yuan Wei (computer science) Pei-Yuan Wei releases the Web browser ViolaWWW 0.8. |
|
30 Nov 1990

Alvarez hypothesis |
Alvarez hypothesis (geophysics) Alan Hildebrand and others provide support for the Alvarez hypothesis for the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event by proposing the Chicxulub crater in the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico as the impact site for a large asteroid 66 million years ago. |
|
30 Nov 1990

Qiudong Wang |
Qiudong Wang (mathematics) Qiudong Wang produces a global solution to the n-body problem. |
|
30 Nov 1990

arXiv |
arXiv (publications) The first open-access scientific online archive, arXiv, is begun as a preprint service for physicists, initiated by Paul Ginsparg. |
|
30 Nov 1990

Turing Award |
Turing Award (awards) Turing Award – Robin Milner |
|
30 Jan 1991

John Bardeen |
death John Bardeen John Bardeen (b. 1908), American physicist, co-inventor of the transistor and twice winner of the Nobel Prize in Physics. |
|
06 Feb 1991

Salvador Luria |
death Salvador Luria Salvador Luria (b. 1912), Italian-born biologist, co-winner of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. |
|
23 Feb 1991

Charles Illingworth |
death Charles Illingworth Sir Charles Illingworth (b. 1899), British surgeon. |
|
26 Feb 1991

Tim Berners-Lee |
Tim Berners-Lee (computer science) Tim Berners-Lee introduces WorldWideWeb, the first web browser, and a WYSIWYG HTML editor. |
|
01 Mar 1991

Edwin H. Land |
death Edwin H. Land Edwin H. Land (b. 1909), American inventor of the Land Camera. |
|
18 May 1991

Helen Sharman |
Helen Sharman (astronomy and space ) Helen Sharman becomes the first British person in space, flying with the Soyuz TM-12 mission. As of 2011 she is the only British astronaut. |
|
02 Jun 1991

Mary Loveless |
death Mary Loveless Mary Loveless (b. 1899), American immunologist. |
|
05 Jun 1991

Phil Zimmermann |
Phil Zimmermann (computer science) Phil Zimmermann posts the first Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) data encryption program. |
|
05 Jun 1991

Min Chueh Chang |
death Min Chueh Chang Min Chueh Chang (b. 1908), Chinese American embryologist. |
|
23 Jun 1991

video game |
video game (computer science) The video game Sonic the Hedgehog is first released, propelling the Sega Genesis 16-bit console into mass popularity. |
|
01 Jul 1991

Philip Candelas |
Philip Candelas (mathematics) English physicist Philip Candelas and colleagues show that mirror symmetry could be used to solve problems in enumerative geometry. |
|
15 Jul 1991

Roger Revelle |
death Roger Revelle Died 15 Jul 1991 at age 82 (born 7 Mar 1909). Roger Randall Dougan Revelle was an American oceanographer whose research interests integrated study of the sea with geography, geology, geophysics, and meteorology. After WW II, as a commander in the Naval Reserve, he supervised oceanographic measurements during the Operation Crossroads (1946) atom bomb tests off Bikini. He did pioneering work in deep-sea drilling and measuring of the upward flow of heat through ocean floors. His tectonic studies in the Pacific Ocean helped to advance the theory of ocean floor spreading. Although in 1955, he was not alarmed about using the oceans as a depository for radiactive wastes, Revelle expressed an early concern about global warming (1957) due to increasing carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. |
|
06 Aug 1991

website |
website (computer science) The first website goes online at CERN. |
|
23 Aug 1991

Florence Seibert |
death Florence Seibert Died 23 Aug 1991 at age 93 (born 6 Oct 1897). American scientist who developed the protein substance used for the tuberculosis skin test, and contributed to safety measures for intravenous drug therapy. In the early 1920s, she discovered that the sudden fevers that sometimes occurred during intravenous injections were caused by bacteria in the distilled water used to make the protein solutions. She invented a distillation apparatus designed to prevent such contamination. In 1941, her improved TB skin test became the standard test in the U.S. and a year later was adopted by the World Health Organization. It is still in use today. Her later research involved the study of bacteria associated with certain cancers. |
|
01 Oct 1991

New Zealand |
New Zealand (conservation) The New Zealand Resource Management Act 1991 comes into effect. |
|
14 Oct 1991

Walter M. Elsasser |
death Walter M. Elsasser Died 14 Oct 1991 at age 87 (born 20 Mar 1904). Walter Maurice Elsasser was a German-American physicist who contributed to science in several disciplines. In atomic physics, he interpreted electron scattering. In geophysics, during the 1940's, he provided insight into radiative heat transfer in the Earth's atmosphere, and presented the currently accepted dynamo theory to explanation the origin and properties of the Earth's magnetic field. He proposed that this magnetic field resulted from electric currents induced in the fluid outer core of the Earth. He pioneered study of the magnetic orientation of minerals in rocks to reveal the Earth's history of its magnetic field. The last fifty years of his life were to a large part given to studies relevant to biology: a theory of organisms. He wished to establish the distinction between living and inanimate matter. |
|
29 Oct 1991

Gaspra asteroid |
Gaspra asteroid In 1991, space probe Galileo become the first human object to fly past an asteroid, Gaspra, making its closest approach at a distance of 1,604 km, passing at a speed of 8 km/sec (5 mi/sec). The encounter provided much data, including 150 images, which showed Gaspra has numerous craters indicating it has suffered numerous collisions since its formation. Gaspra is about 20-km long and orbits the Sun in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Gaspra, asteroid 951, was discovered by Ukrainian astronomer Grigoriy N. Neujamin (1916) who named it after a Black Sea retreat. In the photograph (left), subtle color variations have been exaggerated by NASA to highlight changes in reflectivity, surface structure and composition. |
|
29 Oct 1991

Galileo probe |
Galileo probe (astronomy and space ) The Galileo probe becomes the first spacecraft to visit an asteroid (951 Gaspra). |