| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1993

Asteroid 7484 Dogo Onsesn |
Asteroid 7484 Dogo Onsesn (astronomy and space ) Asteroid 7484 Dogo Onsesn is discovered by Masahiro Koishikawa. |
|
30 Nov 1993

14032 Mego |
14032 Mego (astronomy and space ) 14032 Mego is discovered. |
|
30 Nov 1993

8C 1435+63 |
8C 1435+63 (astronomy and space ) 8C 1435+63 is discovered and at z=4.25 becomes the most distant known galaxy. |
|
30 Nov 1993

Dingiso |
Dingiso (biology and medicine) The Dingiso or tree-kangaroo of Western New Guinea is first seen by scientists. |
|
30 Nov 1993
gene |
gene (biology and medicine) The first gene linked to Alzheimer's disease is discovered. No new genes would be found until 2009. |
|
30 Nov 1993
Western Hemisphere |
Western Hemisphere (biology and medicine) The Western Hemisphere is declared free of polio. |
|
30 Nov 1993

Netscape Communications |
Netscape Communications (computer science) Netscape Communications creates HTTP Secure for its Netscape Navigator web browser. |
|
30 Nov 1993

Leonard Adleman |
Leonard Adleman (computer science) Leonard Adleman describes the experimental use of DNA as a computational system to solve a seven-node instance of the Hamiltonian path problem, the first known instance of the successful use of DNA to compute an algorithm. |
|
30 Nov 1993
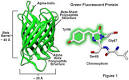
Green fluorescent protein |
Green fluorescent protein (molecular biology) Green fluorescent protein is successfully expressed in C. elegans, starting its career as a fluorescent marker. |
|
30 Nov 1993

blue LED |
blue LED (technology) The first high-brightness blue LED is achieved, an invention that earned the researchers a Nobel Prize in 2014. |
|
30 Nov 1993

Fields Prize in Mathematics |
Fields Prize in Mathematics (awards) Fields Prize in Mathematics: Efim Isakovich Zelmanov, Pierre-Louis Lions, Jean Bourgain and Jean-Christophe Yoccoz |
|
30 Nov 1993

Turing Award |
Turing Award (awards) Turing Award – Edward Feigenbaum, Raj Reddy |
|
30 Nov 1993

Wollaston Medal for Geology |
Wollaston Medal for Geology (awards) Wollaston Medal for Geology – William Jason Morgan |
|
01 Jan 1994

Jerry Yang |
Jerry Yang (computer science) Jerry Yang and David Filo create "Jerry's Guide to the World Wide Web", a hierarchically-organised website, while studying at Stanford University; in April it is renamed Yahoo! |
|
23 Jan 1994

Lee Alvin DuBridge |
death Lee Alvin DuBridge Died 23 Jan 1994 at age 92 (born 21 Sep 1901). American physicist. |
|
25 Jan 1994

Stephen Cole Kleene |
death Stephen Cole Kleene Stephen Cole Kleene (b. 1909), American mathematician. |
|
14 Mar 1994

Space Grapple |
Space Grapple In 1994, a magnetic grappling system was used in outer space for the first time. The 50-foot robot arm was operated by several Columbia astronauts taking turns. |
|
31 Mar 1994
Ethiopia |
Ethiopia (archaeology) The journal Nature reports the finding in Ethiopia of the first complete Australopithecus afarensis skull, significant in the study of human evolution. |
|
12 Apr 1994

Internet spam |
Internet spam In 1994, the first Internet spamming program was used by an attorney in Arizona. Laurence Canter created the software program, a simple Perl script, that flooded Usenet message board readers with a notice for the "Green Card Lottery" to solicit business for his law firm of Canter & Siegel (with wife, Martha Siegel.) The reaction from the online community was vigorously critical, condemning such a form of advertising. Thousands of recipients complained, but a new, burgeoning business of unsolicited mass Internet advertising had been spawned. The term "spam" was coined from a sketch in the "Monty Python's Flying Circus" BBC television show in which a waitress offered a menu full of variations of spam to an unwilling patron. |
|
17 Apr 1994

Roger Wolcott Sperry |
death Roger Wolcott Sperry Roger Wolcott Sperry (b. 1913), American neuropsychologist, neurobiologist and winner of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. |
|
06 May 1994
Channel Tunnel |
Channel Tunnel (technology) The Channel Tunnel, which took 15,000 workers over seven years to complete, opens between England and France. It is now possible to travel between the two countries in 35 minutes. |
|
25 Jun 1994

Vu Quang ox |
Vu Quang ox In 1994, the capture of the first live specimen of the Vu Quang ox in Vietnam, a previously unknown species of mammal, was reported in the London newspaper The Times. Its existence was first discovered during May 1992 from remains in hunters' villages, including several skulls with horns. This was the first discovery of new large mammal species since the Okapi (Okapia johnstoni) in 1910. The captured calf was held in an enclosure at the Vietnam's Forest Inventory and Planning Institute. The species was named Pseudoryx nghetinhensis. It is presently thought to be restricted to an area of approximately 4,000 sq. km along the Vietnam-Laos border within the Vu Quang Nature Reserve. |
|
16 Jul 1994

Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 |
Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 (astronomy and space ) July 22 – The fragments of Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 impact the planet Jupiter |
|
18 Jul 1994

Artificial insemination birth |
Artificial insemination birth In 1994, Rosanna Della Corte, a 62-year-old Italian woman, gave birth to a healthy son, Riccardo. Her egg was artificially imseminated by the sperm of her 63-year-old husband, Mauro, at Dr. Severino Antinori's fertility clinic in Rome, Italy. Rosanna Della Corte had earlier lost her only son at 17 in a terrible car accident. She had often tried to adopt another son, but in vain. These were the reasons she turned to the procedure. In reaction, restrictions were introduced in the Italian legislature in the wake of a papal encyclical, Evangelium Vitae, condemning in vitro fertilization and many of other high-tech fertility procedures. |
|
21 Jul 1994

Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy |
Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy (astronomy and space ) R. Ibata, M. Irwin, and G. Gilmore discover the Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, considered the closest galaxy to the Milky Way until 2003. |
|
29 Jul 1994

Dorothy Crowfoot Hodgkin |
death Dorothy Crowfoot Hodgkin Died 29 Jul 1994 at age 84 (born 12 May 1910). Dorothy Mary Crowfoot Hodgkin (née Crowfoot) was an English biochemist and X-ray crystallographer, born in Cairo, Egypt to English parents, who was awarded the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1964 for her discoveries, by the use of X-ray techniques, of the structure of biologically important molecules, including penicillin (1946), vitamin B-12 (1956), and later, the protein hormone insulin (1969). Her achievements included not only these structure determinations and the scientific insight they provided but also the development of methods that made such structure determinations possible. (One of her students was Margaret Roberts, later Margaret Thatcher, the only British prime minister with a degree in science.) |
|
29 Jul 1994

Dorothy Hodgkin |
death Dorothy Hodgkin Dorothy Hodgkin (b. 1910), British biochemist and winner of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. |
|
15 Aug 1994

Lowest temperature ever |
Lowest temperature ever In 1994, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) issued a press release that physicists there recently cooled atoms to 700 nanokelvins, the coldest temperature ever recorded for matter. NIST scientists chilled a cloud of cesium atoms very close to absolute zero using lasers to catch the atoms in an optical lattice. The atoms reached 700 nanokelvins, or 700 billionths of a degree above absolute zero. Zero kelvin (-273ºC), or absolute zero, is the temperature at which atomic thermal motion would cease. Since the late 1970s, physicists have sought to use lasers to cool atoms closer to absolute zero, primarily for improving atomic timekeeping, certain experimental measurements and lithography processes for the semiconductor industry. |
|
16 Aug 1994

smartphone |
smartphone (technology) The world's first smartphone, the IBM Simon, goes on sale. |
|
19 Aug 1994

Linus Pauling |
death Linus Pauling Linus Pauling (b. 1901), American chemist. |
|
29 Aug 1994

Arthur Mourant |
death Arthur Mourant Arthur Mourant (b. 1904), Jersiais hematologist. |
|
10 Sep 1994

rainforest |
rainforest (biology and medicine) Wollemia (the 'Wollemi Pine'), previously known only from fossils, is discovered living in remote rainforest gorges in the Wollemi National Park of New South Wales by David Noble. |
|
19 Sep 1994

Wiles' proof of Fermat's Last Theorem |
Wiles' proof of Fermat's Last Theorem (mathematics) Wiles' proof of Fermat's Last Theorem: Andrew Wiles devizes a new approach to the final proof of Fermat's Last Theorem, sending his proof to colleagues on October 6 and submitting for publication on October 24. |
|
30 Sep 1994

André Michel Lwoff |
death André Michel Lwoff Died 30 Sep 1994 at age 92 (born 8 May 1902). French biologist who contributed to the understanding of lysogeny, in which a bacterial virus, or bacteriophage, infects bacteria and is transmitted to subsequent bacterial generations solely through the cell division of its host. The observation of isolated bacteria led him to the conclusion that lysogenic bacteria did not secrete bacteriophages, that the production of bacteriophages led to the death of the bacterium, and above all that this production must be induced by external factors. It was this hypothesis which, together with Louis Siminovitch and Niels Kjeldgaard, led Lwoff to discover the inductive action of ultraviolet irradiation (1950). His discoveries brought him (with François Jacob and Jacques Monod) the 1965 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine. |
|
01 Oct 1994

Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews |
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (biology and medicine) First public demonstration of the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. |
|
03 Oct 1994

Heart device |
Heart device In 1994, the Food and Drug Administration approved the Left Ventricular Assist Device, which helps failing hearts continue to function. |
|
11 Oct 1994

Magellan ends mission |
Magellan ends mission In 1994, the space probe Magellan ended its mission to explore Venus when flight controllers lowered its orbit into Venus' dense atmosphere and it plunged toward the surface. Radio contact was lost the next day. Although much of Magellan was vaporized, some sections are thought to have hit the planet's surface intact. Launched 4 May 1989 in the cargo bay with the STS-30 Space Shuttle Atlantis mission, Magellan arrived at its planned polar orbit around Venus on 10 Aug 1990. As it circled once every 3-hr 15-min, the planet rotated slowly beneath it, and Magellan had collected radar images of the surface in strips about 17-28 km (10-17 mi) wide and radioed back the information on the large shield volcanoes, vast lava plains and sparse craters. |
|
12 Oct 1994

NASA |
NASA (astronomy and space ) NASA loses contact with the Magellan spacecraft after a successful mission. The probe crashes into Venus shortly after. |
|
28 Oct 1994

Calvin Souther Fuller |
death Calvin Souther Fuller Calvin Souther Fuller, American physical chemist at AT&T Bell Laboratories. |
|
09 Nov 1994

first detected |
first detected (chemistry) Darmstadtium first detected at the Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung (GSI) in Darmstadt, Germany, by Peter Armbruster and Gottfried Münzenberg, under the direction of Prof. Sigurd Hofmann. |
|
03 Dec 1994

Sony |
Sony (computer science) Sony release the PlayStation fifth generation home video game console in Japan. |
|
03 Dec 1994

PlayStation |
PlayStation (technology) The first PlayStation gaming console is released in Japan. |
|
08 Dec 1994

Element 111 |
Element 111 In 1994, approximately one month after announcing the creation of element 110, a team of German scientists led by Peter Armbruster at the Gesellschaft für schwerionenforschung (GSI) facility at Darmstadt, Germany, claimed to have created element 111. Its atom has 111 protons and 161 neutrons in its nucleus, giving it a mass number of 272. As a new element it was named unununium, symbol Uuu, according to an internationally adopted system for naming new elements. Only three atoms of the element were made by accelerating nickel atoms to high speed and bombarding them into bismuth. When an atom of each fused to make the new nucleus, it lasted for about four-thousandths of a second before decaying into smaller nuclei. |
|
08 Dec 1994

atoms |
atoms (chemistry) The first three atoms of Roentgenium are observed by an international team led by Sigurd Hofmann at the GSI in Darmstadt. |
|
15 Dec 1994

Fukuda |
Fukuda (biology and medicine) Publication of the "Fukuda" clinical description of chronic fatigue syndrome. |
|
18 Dec 1994

Chauvet Cave |
Chauvet Cave (archaeology) Chauvet Cave discovered by Jean-Marie Chauvet and other speleologists near Vallon-Pont-d'Arc in the Ardèche department of southern France, containing some of the earliest known cave paintings of animals, as well as other evidence of Upper Paleolithic life. |
|
21 Dec 1994

Popocatépetl |
Popocatépetl (earth sciences) Mexico's Popocatépetl volcano, dormant for 47 years, resumes eruption. |