| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1957

John Gurdon |
John Gurdon (biology) John Gurdon clones a frog using somatic-cell nuclear transfer from a Xenopus tadpole. |
|
30 Nov 1957

Anne McLaren |
Anne McLaren (biology) Anne McLaren, with John D. Biggers, reports the first mammals, a litter of mice, grown from embryos developed in vitro and transferred to a surrogate mother. |
|
30 Nov 1957
Denatonium |
Denatonium (chemistry) Denatonium, the bitterest chemical compound known (used as an aversive agent), is discovered during research on local anesthetics by Macfarlan Smith of Edinburgh, Scotland, and registered under the trademark Bitrex. |
|
30 Nov 1957

Friedrich L. Bauer |
Friedrich L. Bauer (computer science) Friedrich L. Bauer and other members of the ZMMD-Group build a working ALGOL 58 compiler. |
|
30 Nov 1957

John McCarthy |
John McCarthy (computer science) John McCarthy specifies the Lisp programming language. |
|
30 Nov 1957

Society for the History of Technology |
Society for the History of Technology (history of science) Society for the History of Technology established. |
|
30 Nov 1957

School Mathematics Study Group |
School Mathematics Study Group (mathematics) School Mathematics Study Group, directed by Edward G. Begle, established to develop a new school mathematics curriculum for the United States; it is influential in the promotion of New Math. |
|
30 Nov 1957

Earl Bakken |
Earl Bakken (medicine) Engineer Earl Bakken (U.S.) produces the first wearable external artificial pacemaker, for a patient of Dr. C. Walton Lillehei. |
|
30 Nov 1957

Karolinska Institute |
Karolinska Institute (medicine) The first clinical implantations into a human of fully implantable artificial pacemakers takes place at the Karolinska Institute in Solna, Sweden, using a pacemaker designed by Rune Elmqvist and surgeon Åke Senning. The patient, Arne Larsson (1915–2001), survives until age 86, having been fitted with 22 pacemakers throughout his life. |
|
30 Nov 1957
fecal microbiota transplantation |
fecal microbiota transplantation (medicine) B. Eiseman and colleagues from Colorado first describe fecal microbiota transplantation. |
|
30 Nov 1957

Denis Parsons Burkitt |
Denis Parsons Burkitt (medicine) Denis Parsons Burkitt first describes Burkitt's lymphoma. |
|
30 Nov 1957

Dutch |
Dutch (technology) Dutch rally driver Maus Gatsonides introduces his first roadside automobile speed measurement device. |
|
30 Nov 1957

Fields Prize in Mathematics |
Fields Prize in Mathematics (awards) Fields Prize in Mathematics: Klaus Roth and René Thom |
|
04 Jan 1958

Sputnik 1 |
Sputnik 1 (astronomy and space ) Sputnik 1 falls to Earth from its orbit and burns up (launched on October 4, 1957). |
|
31 Jan 1958

satellite |
satellite (astronomy and space ) The first successful American satellite, Explorer I, is launched into orbit. |
|
05 Feb 1958

Vanguard TV3 |
Vanguard TV3 (astronomy and space ) A backup for Vanguard TV3 fails to reach orbit. |
|
11 Feb 1958
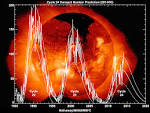
solar maximum |
solar maximum (astronomy and space ) The strongest ever known solar maximum is recorded. |
|
11 Feb 1958

Ernest Jones |
death Ernest Jones Ernest Jones (born 1879), Welsh psychoanalyst |
|
26 Feb 1958

Susan J. Helms |
birth Susan J. Helms Susan J. Helms, American astronaut |
|
05 Mar 1958

Explorer 2 |
Explorer 2 (astronomy and space ) Explorer 2 fails to reach orbit. |
|
17 Mar 1958

Vanguard 1 |
Vanguard 1 (astronomy and space ) Vanguard 1 becomes the first of its program to enter space, after three failed attempts. |
|
26 Mar 1958

Explorer 3 |
Explorer 3 (astronomy and space ) Explorer 3 is launched into orbit. |
|
31 Mar 1958

Atomic submarine division |
Atomic submarine division In 1958, the U.S. Navy established the world’s first Atomic Submarine Division. It had been announced to the press earlier in the month (17 Mar 1958), and reported in the New York Times the next day. Three atomic submarines, Nautilus, Sea Wolf, and Skate, joined three diesel powered submarines, Hardhead, Bang and Halfbreak. The latter were to be replaced as more atomic submarines were commissioned, beginning with the launch of the Skipjack (26 May 1958). For the first three months, Atomic Submarine Division 102 was under the command of Comdr. Roger G. Black, a WW II submarine veteran. Command was to be passed in July to Capt. Eugene P. Wilkinson, (first skipper of the Nautilus, the world's first atomic submarine) after he completed studies at the Naval War College. |
|
01 Apr 1958

BBC Radiophonic Workshop |
BBC Radiophonic Workshop (technology) The BBC Radiophonic Workshop is established. |
|
14 Apr 1958

Sputnik 2 |
Sputnik 2 (astronomy and space ) Sputnik 2 re-enters Earth's atmosphere. |
|
16 Apr 1958

Rosalind Franklin |
death Rosalind Franklin Rosalind Franklin (born 1920), English crystallographer |
|
17 Apr 1958

Expo 58 |
Expo 58 October 19 – Expo 58 in Brussels. The centrepiece is the Atomium; and a model of tobacco mosaic virus structure by Rosalind Franklin's research team is exhibited. |
|
25 Apr 1958

Charles Mauguin |
death Charles Mauguin Died 25 Apr 1958 at age 79 (born 19 Sep 1878). Charles-Victor Mauguin was a French mineralogist and crystallographer who was one of the first to make a systematic study of the silicate minerals. Using X-ray diffraction techniques, he determined the structure of a large number of micas. He also published the atomic structure of cinnabar, calomel and graphite and devised a system of symbols for designation of symmetry properties of crystals, adopted (1935) as international standard. |
|
22 May 1958

Jérôme Lejeune |
Jérôme Lejeune (medicine) Jérôme Lejeune, working with Marthe Gautier in Raymond Turpin's French laboratory, discovers that the genetic cause of Down syndrome is an extra copy of chromosome 21. |
|
27 May 1958

ACM |
ACM (computer science) June 2 – A joint meeting of the ACM and GAMM at ETH Zurich agrees to produce the International Algebraic Language, which will become the programming language ALGOL. |
|
07 Jun 1958

Ian Donald |
Ian Donald (medicine) Ian Donald publishes an article in The Lancet which describes the diagnostic use of ultrasound. |
|
09 Jul 1958

1958 Lituya Bay megatsunami |
1958 Lituya Bay megatsunami 1958 Lituya Bay megatsunami: A 7.5 Richter scale earthquake in Lituya Bay, Alaska, causes a landslide that produces a 520-meter high megatsunami. |
|
18 Jul 1958

Henri Farman |
death Henri Farman Died 18 Jul 1958 at age 84 (born 26 May 1874). French aviator and aircraft designer who developed ailerons (1908) to solve the enormously difficult and dangerous problems of lateral control. His an innovation subsequently came into general use on all planes. His first steps in aircraft design began in 1907 when he ordered his own aircraft incorporating his design modifications of a dihedral in the wings and the reduction of the tail to a single plane. These intuitive rather than scientific modifications were the beginning of a long career in which Farman diagnosed and solved a myriad of aircraft control and structural problems. The Farman “Goliath” was the first long-distance passenger airliner, beginning regular Paris–London flights on 8 Feb 1919. His younger brother Maurice Farman was also an aviator. They were born of English parents in Paris. |
|
29 Jul 1958

United States Congress |
United States Congress (astronomy and space ) The United States Congress formally creates the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). |
|
14 Aug 1958

Frédéric Joliot-Curie |
death Frédéric Joliot-Curie Frédéric Joliot-Curie (born 1900), French physicist (Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1935) |
|
27 Aug 1958

Ernest Lawrence |
death Ernest Lawrence Ernest Lawrence (born 1901), American physicist (Nobel Prize in Physics 1932) |
|
12 Sep 1958

Jack Kilby |
Jack Kilby (technology) Jack Kilby demonstrates the first integrated circuit. |
|
14 Sep 1958

rockets |
rockets (astronomy and space ) Two rockets designed by Ernst Mohr (the first post-war German rockets) reach the upper atmosphere. |
|
02 Oct 1958

Marie Stopes |
death Marie Stopes Marie Stopes (born 1880), Scottish-born paleobotanist and pioneer of birth control |
|
11 Oct 1958

Pioneer 1 launch |
Pioneer 1 launch In 1958, the lunar probe Pioneer 1 was launched atop a Thor-Able rocket, from the Eastern Test range (now the Kennedy Space Center). Its intended mission was to reach the moon, but it failed to go as far as planned and fell back to Earth. It transmitted 43 hours of data before burning up in the atmosphere. NASA (the National Aeronautics and Space Administration) had just been formed at the beginning of the month. |
|
14 Oct 1958

Sir Douglas Mawson |
death Sir Douglas Mawson Died 14 Oct 1958 at age 76 (born 5 May 1882). Australian geologist and explorer whose travels in the Antarctic earned him worldwide acclaim. |
|
17 Nov 1958

Yutaka Taniyama |
death Yutaka Taniyama Yutaka Taniyama (born 1927), Japanese mathematician (suicide) |
|
05 Dec 1958

Britain's first motorway |
Britain's first motorway In 1958, Britain's first stretch of motorway, the 8 mile Preston bypass was officially opened by the Prime Minister, Harold MacMillan. The path of the by-pass was designed as part of a North-South Motorway, other lengths of which were under construction. The original bypass started in Walton-le-Dale at a roundabout on the Manchester-Preston Trunk Road a short distance south of the A49 junction, travelled by viaduct over the River Darwen and ended at a roundabout on the A6 a short distance south of Broughton. As a model for all other British motorways it drew such a very large number of visits of inspection by Engineering Institutions and Associations that the County Council appointed a panel of retired engineers to act as guides. |
|
12 Dec 1958

Milutin Milanković |
death Milutin Milanković Milutin Milanković (born 1879), Serbian geophysicist |
|
15 Dec 1958

Arthur L. Schawlow |
Arthur L. Schawlow (technology) Arthur L. Schawlow and Charles H. Townes of Bell Laboratories publish a paper in Physical Review Letters setting out the principles of the optical laser. |
|
15 Dec 1958

Wolfgang Pauli |
death Wolfgang Pauli Wolfgang Pauli (born 1900), Austrian theoretical physicist |
|
18 Dec 1958
SCORE |
SCORE (astronomy and space ) The United States launches SCORE, the world's first communications satellite. |