| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1958

Coma Berenicids |
Coma Berenicids (astronomy and space ) Coma Berenicids discovered. |
|
30 Nov 1958
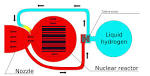
nuclear thermal rocket |
nuclear thermal rocket (astronomy and space ) First successful test of a nuclear thermal rocket engine, as part of Project Rover at Los Alamos National Laboratory in the United States under Raemer Schreiber. |
|
30 Nov 1958
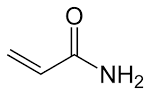
acrylamide |
acrylamide (chemistry) B. J. Davis and Leonard Ornstein first describe the use of acrylamide in gel electrophoresis at a scientific meeting. |
|
30 Nov 1958

IBM |
IBM (computer science) IBM ship the transistor-based IBM 1401 mainframe. |
|
30 Nov 1958

Edsger W. Dijkstra |
Edsger W. Dijkstra (computer science) Edsger W. Dijkstra rediscovers 'Prim's algorithm'. |
|
30 Nov 1958

Society for the History of Technology |
Society for the History of Technology (history of science) Society for the History of Technology begins publication of the journal Technology and Culture. |
|
30 Nov 1958

Kenkichi Iwasawa |
Kenkichi Iwasawa (mathematics) Kenkichi Iwasawa initiates Iwasawa theory. |
|
30 Nov 1958

Joseph Murray |
Joseph Murray (medicine) Joseph Murray performs the world's first successful allotransplantation. |
|
30 Nov 1958

Georges Mathé |
Georges Mathé (medicine) Georges Mathé, a French oncologist, performs the first bone marrow transplant on five Yugoslavian nuclear workers whose own marrow has been damaged by intense irradiation caused by a criticality accident at the Vinča Nuclear Institute, but all of these transplants are rejected. |
|
30 Nov 1958

HIV |
HIV (medicine) First known case of human HIV, in the Belgian Congo. |
|
30 Nov 1958

Yakir Aharonov |
Yakir Aharonov (physics) Yakir Aharonov and David Bohm predict the Aharonov–Bohm effect. |
|
30 Nov 1958

Agfa |
Agfa (technology) Agfa introduces the first fully automatic camera, the Optima. |
|
30 Nov 1958

Eveready Battery |
Eveready Battery (technology) Eveready Battery engineer Lewis Urry invents the long-lasting alkaline battery. |
|
30 Nov 1958

Gordon Gould |
Gordon Gould (technology) Gordon Gould publishes the term Laser. |
|
30 Nov 1958

Pilkington Brothers |
Pilkington Brothers (technology) Pilkington Brothers patent the float glass process invented by Alastair Pilkington. |
|
30 Nov 1958

CERN |
CERN (organisations) Austria joins CERN. |
|
01 Jan 1959

Cultivars |
Cultivars (biology) Cultivars of plants named after this date must be named in a modern language, not in Latin. |
|
15 Feb 1959

Sir Owen Richardson |
death Sir Owen Richardson Sir Owen Richardson (born 1879), English physicist (Nobel Prize in Physics 1928) |
|
26 Mar 1959
Jersey |
Jersey (biology) Jersey Zoo (now Durrell Wildlife Park) established by Gerald Durrell. |
|
09 Apr 1959

First astronauts selected |
First astronauts selected In 1959, NASA announced the selection of America's first seven astronauts for project Mercury. Scott Carpenter, Gordon Cooper, John Glenn, Gus Grissom, Wally Schirra, Alan Shepard and Donald Slayton were chosen from 110 applicants. Their training program at Langley, which ranged from a graduate-level course in introductory space science to simulator training and scuba-diving. Project Mercury, NASA's first high profile program, was an effort to learn if humans could survive in space. NASA required astronaut candidates to be male, not over 40 years old, not more than 5' 11" height and in excellent physical condition. On 5 May 1961, Shepard became the first American in space. |
|
25 Apr 1959

First AIDS patient |
First AIDS patient In 1959, a 25-year-old patient, David Carr, an apprentice printer, entered the Royal Manchester Infirmary in England, with unusual symptoms, including purplish skin lesions, fatigue and weight loss. He died 4½ months later for reasons not then understood. His preserved tissue samples were examined in 1990. In a letter to the journal The Lancet, (7 Jul 1990) Gerald Corbitt, director of clinical virology at the hospital, suggested this could be the earliest known AIDS case. In 1995, the journal Nature, reported that the results were anomolous: the putative HIV detected was of a “relatively modern strain.” In the 20 Jan 1996 Lancet, the earlier claim was retracted, accepting the sample had been contaminated. Having had doubts since 1992, Corbitt said he regarded the analysis as no more than a trial of PCR [polymerase chain reaction] on archival material. Belatedly, the report of a possible early AIDS case was clarified. |
|
07 May 1959

C. P. Snow |
C. P. Snow Scientist and novelist C. P. Snow delivers an influential Rede Lecture on The Two Cultures, concerning a perceived breakdown of communication between the sciences and humanities, in the Senate House, University of Cambridge. It is subsequently published as The Two Cultures and the Scientific Revolution. |
|
19 May 1959

Nuclear submarine |
Nuclear submarine In 1959, the first submarine with two nuclear reactors was completed. The USS Triton had two water-cooled General Electric nuclear reactors to power electricity generators which powered the propellers. The Triton was 447-ft long, 37-ft wide, manned by 148 officers and crew and had a cruising range of 110,000 miles. After its launch on 19 Aug 1958, The first U.S. atomic powered submarine had been completed four years earlier, on 22 Apr 1955. |
|
09 Jun 1959

Adolf Windaus |
death Adolf Windaus Adolf Windaus (born 1876) German chemist (Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1928) |
|
01 Jul 1959

Minamata disease |
Minamata disease (medicine) The medical research group studying Minamata disease comes to the conclusion that mercury is the cause. |
|
03 Aug 1959

Koichi Tanaka |
birth Koichi Tanaka Koichi Tanaka, Japanese chemist (Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2002). |
|
07 Aug 1959

Explorer 6 |
Explorer 6 (astronomy and space ) The United States launches Explorer 6 from the Atlantic Missile Range in Cape Canaveral, Florida. |
|
08 Aug 1959

Min Chueh Chang |
Min Chueh Chang (biology) Min Chueh Chang reports the first mammals, a litter of rabbits, grown from ova having undergone in vitro fertilisation and transferred to a surrogate mother. |
|
29 Aug 1959

Stephen Wolfram |
birth Stephen Wolfram Stephen Wolfram, British-born mathematician. |
|
14 Sep 1959

Moon probe |
Moon probe In 1959, the first space probe to strike the moon was the Soviet Luna 2, which crashed east of the Sea of Serenity. Thirty-six hours after its launch on 12 Sep 1959, it was the first man-made object reach a celestial body. |
|
15 Sep 1959

Luna 3 |
Luna 3 (astronomy and space ) Russian probe Luna 3 sends back first photos of the far side of Earth's Moon. |
|
19 Sep 1959

Giuseppe Cocconi |
Giuseppe Cocconi (astronomy and space ) Giuseppe Cocconi and Philip Morrison establish the scientific rationale for SETI with the publishing of their seminal paper "Searching for Interstellar Communications" in Nature. |
|
22 Sep 1959

Saul Perlmutter |
birth Saul Perlmutter Saul Perlmutter, American astrophysicist (Nobel Prize in Physics 2011). |
|
30 Sep 1959

Ross Granville Harrison |
death Ross Granville Harrison Died 30 Sep 1959 at age 89 (born 13 Jan 1870). American zoologist who developed the first successful animal-tissue cultures and pioneered organ transplantation techniques. In an early experiment, using tissue grafting techniques, he joined parts of embryos from differently coloured frogs to observe the movement of cells during the subsequent development of the embryos produced in this way. In another experiment, he took tissue from an amphibian embryo that would have formed a left limb, inverted and transferred it to the embryo's right side, where it formed a right limb. He discovered the hanging-drop culture method (1907), a new method of studying cells, by which he kept fragments of living tissue alive in suitable media and watch them multiply. Using this technique, he settled a controversy about the embryonic origins of nerve fibres. The hanging-drop method has also been valuable in oncology, genetics, virology and other fields. |
|
29 Oct 1959

Samuel James Cameron |
death Samuel James Cameron Samuel James Cameron (born 1878), Scottish obstetrician. |
|
15 Nov 1959

C. T. R. Wilson |
death C. T. R. Wilson C. T. R. Wilson (born 1869), Scottish physicist (Nobel Prize in Physics 1927) |
|
19 Nov 1959

Edward C. Tolman |
death Edward C. Tolman Died 19 Nov 1959 at age 73 (born 14 Apr 1886). Edward Chace Tolman was an American psychologist who developed a system of psychology known as purposive, or molar, behaviourism, which attempts to explore the entire action of the total organism. Because of his strong affiliation with building a scientific psychology he embraced the core notion of behaviorism—that what an organism does is the source of legitimate data. Contrary to John B. Watson's atomism approach, Tolman advocated the use of intervening variables and focused on a number of very non-behaviorist processes such as purpose, expectation, belief and spatial representation. His major book was Purposive Behavior in Animals and Men (1932) in which he summarized a significant series of experiments on the white rat. |
|
24 Nov 1959

Yardymli meteorite |
Yardymli meteorite (astronomy and space ) Yardymli meteorite makes a landfall in Azerbaijan. |
|
01 Dec 1959

programming language |
programming language (computer science) The specification for the programming language COBOL is completed. |
|
04 Dec 1959

Little Joe 2 |
Little Joe 2 (astronomy and space ) Little Joe 2, a mission in the Mercury program, carries Sam the monkey into space. |
|
25 Dec 1959

Michael P. Anderson |
birth Michael P. Anderson Michael P. Anderson (died 2003), American astronaut. |