| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1960

Drake equation |
Drake equation (astronomy and space ) The Drake equation is written by Frank Drake. |
|
30 Nov 1960
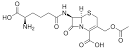
Cephalosporin C |
Cephalosporin C (biochemistry) Cephalosporin C is first characterized, by Guy Newton and Edward Abraham of the Sir William Dunn School of Pathology in the University of Oxford. |
|
30 Nov 1960
disc electrophoresis |
disc electrophoresis (chemistry) Leonard Ornstein first describes disc electrophoresis. |
|
30 Nov 1960

Francis Birch |
Francis Birch (geophysics) Francis Birch establishes Birch's law on compressional wave velocities. |
|
30 Nov 1960

Stephen Smale |
Stephen Smale (mathematics) Stephen Smale proves the Poincaré conjecture in dimensions greater than 4. |
|
30 Nov 1960
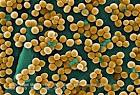
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) |
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) (medicine) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is first discovered, in the United Kingdom. |
|
30 Nov 1960

J.C.P. Williams |
J.C.P. Williams (medicine) New Zealand cardiologist J.C.P. Williams identifies Williams syndrome. |
|
30 Nov 1960

non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug |
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (pharmacology) The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug Ibuprofen, derived from propanoic acid by the research arm of Boots UK (Andrew R. M. Dunlop with Stewart Adams, John Nicholson, Vonleigh Simmons, Jeff Wilson and Colin Burrows), is patented. |
|
30 Nov 1960
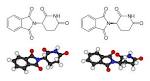
Thalidomide |
Thalidomide (pharmacology) Thalidomide is withdrawn from sale. |
|
30 Nov 1960

Spain |
Spain (physics) Spain joins CERN; Yugoslavia leaves. |
|
04 Jan 1961

Erwin Schrödinger |
death Erwin Schrödinger Erwin Schrödinger (born 1887), Austrian physicist. |
|
23 Jan 1961

Wilhelm Koppers |
death Wilhelm Koppers Died 23 Jan 1961 at age 74 (born 8 Feb 1886). Roman Catholic priest and cultural anthropologist who advocated a comparative, historical approach to understanding cultural phenomena and whose investigations of hunting and food-gathering tribes produced theories on the origin and development of society. |
|
24 Jan 1961

Albert C. Gilbert |
death Albert C. Gilbert Died 24 Jan 1961 at age 76 (born 15 Feb 1884). Albert Carlton Gilbert was an American inventor who patented the Erector set after he founded the A.C. Gilbert Co. New Haven, Connecticut (1908) to manufacture boxed magic sets. In 1913, he introduced Erector Sets. Similar construction toys then existed, such as Hornby's Meccano set made in England. Meccano sets included pulleys, gears, and several 1/2" wide strips of varying length with holes evenly spaced on them. Gilbert needed something unique for his Erector sets, so he created the square girder, made using several 1" wide strips with triangles cut in them. These had their edges bent over so 4 strips could be screwed together to form a very sturdy square girder. Over the next 40 years, some 30 million Erector Sets were sold. |
|
31 Jan 1961

Ham |
Ham (astronomy and space ) Ham, a 37-pound male chimpanzee, is rocketed into space in a test of the Project Mercury capsule designed to carry U.S. astronauts into space. |
|
14 Feb 1961

Discovery of the chemical elements |
Discovery of the chemical elements (physics) Discovery of the chemical elements: Element 103, Lawrencium, is first synthesized at Berkeley, California. |
|
10 Mar 1961

Laurel Clark |
birth Laurel Clark Laurel Clark (died 2003), American astronaut. |
|
31 Mar 1961

African-American astronaut |
African-American astronaut In 1961, the first African-American chosen for the Manned Orbiting Laboratory program was E. J. Dwight, Jr. However, he was not selected for MOL training. |
|
03 Apr 1961

Leadbeater's possum |
Leadbeater's possum (zoology) A Leadbeater's possum, a marsupial species thought to have been extinct for over 50 years, is discovered in New South Wales (Australia). |
|
12 Apr 1961

First Earth orbit by man |
First Earth orbit by man In 1961, Yuri Gagarin became the first man to orbit the Earth. His spacecraft, Vostok 1, had radio, television and life-support equipment to relay information on his condition. The flight was automated. Gagarin's controls were locked to prevent him from taking control of the ship, although a key in a sealed envelope was provided in case of an emergency. After e-entry, Gagarin ejected and made a planned descent with his own parachute. However for many years the Soviet Union denied this, because the flight would not have been recognized for various FAI world records unless the pilot had accompanied his craft to a landing. Gagarin died in a plane crash 7 years later. |
|
12 Apr 1961

Yuri Gagarin |
Yuri Gagarin (astronomy and space ) Yuri Gagarin is the first human in space. |
|
15 Apr 1961

Charles Hard Townes |
Charles Hard Townes (astronomy and space ) R. N. Schwartz and Charles Hard Townes publish "Interstellar and Interplanetary Communication by Optical Masers" in Nature, providing a basis for Optical SETI. |
|
25 Apr 1961

Integrated circuit |
Integrated circuit In 1961, the integrated circuit was patented by Robert Noyce (No. 2,981,877). |
|
29 Apr 1961

World Wildlife Fund |
World Wildlife Fund (zoology) World Wildlife Fund established. |
|
15 May 1961

J. Heinrich Matthaei |
J. Heinrich Matthaei (biology) J. Heinrich Matthaei performs the Poly-U-Experiment in the United States, opening the way to solution of the genetic code, a key event in modern genetics. |
|
19 May 1961

Venera program |
Venera program (astronomy and space ) Venera program: Venera 1 becomes the first manmade object to fly-by another planet by passing Venus (however the probe had lost contact with earth a month earlier and does not send back any data). |
|
25 May 1961

Apollo program |
Apollo program (astronomy and space ) Apollo program: President Kennedy announces before a special joint session of Congress his goal to initiate a project to put a "man on the moon" before the end of the decade. |
|
29 May 1961

Arnold Gesell |
death Arnold Gesell Died 29 May 1961 at age 80 (born 21 Jun 1880). Arnold Lucius Gesell was an American psychologist and pediatrician who pioneered the use of motion-picture cameras (1926) to study the physical and mental development of normal infants and children. His books gave norms for behavior at successive stages of development and were widely read by parents. Gesell was one of the first to attempt a quantitative study of child development, developing his own methods of observation and measurement. Gesell's initial work focused on developmentally disabled children, but he believed that it was necessary to understand normal infant and child development in order to understand nonnormality. He also studied Down's syndrome, cretinism, and cerebral palsy. |
|
04 Jun 1961

William Astbury |
death William Astbury William Astbury (born 1898), English physicist and molecular biologist. |
|
06 Jun 1961

Carl Jung |
death Carl Jung Carl Jung (born 1875), Swiss psychiatrist. |
|
01 Jul 1961
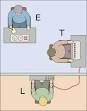
Milgram experiment |
Milgram experiment (psychology) First Milgram experiment on obedience to authority figures. |
|
01 Jul 1961

Kalpana Chawla |
birth Kalpana Chawla Kalpana Chawla (died 2003), Indian astronaut. |
|
03 Jul 1961

First fatal nuclear accident in the U.S. |
First fatal nuclear accident in the U.S. In 1961, three men were killed in the first fatal nuclear accident in the U.S. when an experimental reactor exploded. The Stationary Low-Power Plant No.1 (SL-1), was part of the National Reactor Testing Station (NRTS), near Idaho Falls, Idaho. An 80-lb control rod was lifted by hand beyond its safe position, causing a core meltdown and explosion of the reactor. Four days were spent to devise a safe method to recover one of the corpses. All three bodies were extremely radioactivity, causing problems for their burial. Clean-up took 18 months. Investigators were never able to determine why this “abnormal act” occurred. Two decades later, a documentary speculated one of the men had marital problems and sabotaged the reactor. |
|
04 Sep 1961

Emil von Dungern |
death Emil von Dungern Emil von Dungern (born 1867), German serologist. |
|
23 Sep 1961

William C. McCool |
birth William C. McCool William C. McCool (died 2003), American astronaut. |
|
09 Nov 1961

International Code of Zoological Nomenclature |
International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (zoology) First edition of new International Code of Zoological Nomenclature published. |
|
15 Nov 1961

Johanna Westerdijk |
death Johanna Westerdijk Johanna Westerdijk (born 1883), Dutch plant pathologist |
|
12 Dec 1961

First privately-built satellite |
First privately-built satellite In 1961, the first satellite built by private citizens was put in to orbit. A Thor-Agena rocket, launched to deploy a military Discoverer-36 satellite, also carried the 10-lb OSCAR I . The Orbiting Satellite Carrying Amateur Radio was deployed in low orbit, just above Earth's atmosphere, and it began transmitting "HI" in Morse code,10 times a minute. It was the 60th anniversary of Marconi's first transatlantic radio transmission, and little more than four years since Russia launched Sputnik on 4 Oct 1957. OSCAR 1 was designed and hand-built for $63 by California radio amateurs. The battery powered a 140-mW transmitter on 144.983 MHz, transmitting HI in Morse code for 22 days, for 312 orbits until 1 Jan 1962 when its non-rechargeable battery failed. It burned up in the atmosphere on 31 Jan 1962. |
|
25 Dec 1961

Otto Loewi |
death Otto Loewi Died 25 Dec 1961 at age 88 (born 3 Jun 1873). German-born American physician and pharmacologist who shared the 1936 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine (with Sir Henry Dale) “for their discoveries relating to the chemical transmission of nerve impulses.” Sadly, just two years later he was a victim of Nazi persecution, imprisoned for being Jewish. As ransom for his life, he was forced to hand over his possessions, including his Nobel Prize money, and Loewi escaped to England. From there he moved to America in 1940. His research showed that it was the release of a certain chemical (the transmitter) acetylcholine, that enabled the transmission of nerve impulses. Loewi also investigated action of drugs able to blockade or assist nerve impulse transmission.. |
|
29 Dec 1961

Anton Flettner |
death Anton Flettner Died 29 Dec 1961 at age 76 (born 1 Nov 1885). German inventor who produced a practical helicopter for the German navy (1940). He also developed a device that allowed airplane pilots to raise or lower a plane's nose for better control. It evolved into a mechanism called the Flettner trim-tab control which is still used on all airplanes. He designed a rotor ship (1924) on which he replaced sails with unique propulsion - two 50-ft cylinders, electrically rotated, mounted vertically on the deck. A transatlantic voyage was accomplished using the aerodynamic power of the Magnus Effect which builds pressure behind a rotating cylinder. After WW II, he went to the U.S., and conducted helicopter research for the U.S. Army. He also invented a windmill and the Flettner marine rudder. |