| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1961

Emile Zuckerkandl |
Emile Zuckerkandl (biology) Emile Zuckerkandl and Linus Pauling publish a paper introducing what will become known as the molecular clock concept. |
|
30 Nov 1961
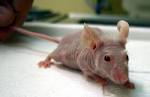
nude mouse |
nude mouse (biology) The first nude mouse strain is discovered by Dr. N. R. Grist at Ruchill Hospital's Brownlee virology laboratory in Glasgow. |
|
30 Nov 1961

Neuroscience Research Program |
Neuroscience Research Program (biology) The Neuroscience Research Program (NRP) was established by Francis O. Shmitt et al. |
|
30 Nov 1961

MIT |
MIT (computer science) At MIT, Ivan Sutherland uses the TX-2 computer to write Sketchpad, the origin of graphical programs used for computer-aided design. |
|
30 Nov 1961

Roger Tomlinson |
Roger Tomlinson (computer science) Roger Tomlinson leads development of the Canada Geographic Information System, the world's first geographic information system (GIS). |
|
30 Nov 1961

Thomas Kuhn |
Thomas Kuhn (history of science) Thomas Kuhn's The Structure of Scientific Revolutions is published in the United States. |
|
30 Nov 1961

James W. Black |
James W. Black (medicine) James W. Black synthesises propranolol, the first beta blocker (used for regulation of angina pectoris), which becomes the world's best-selling drug. |
|
30 Nov 1961

Joseph Murray |
Joseph Murray (medicine) Joseph Murray performs the first permanent cadaveric kidney transplantation. |
|
30 Nov 1961

Nodding disease |
Nodding disease (medicine) Nodding disease is first documented, in southern Tanzania. |
|
30 Nov 1961

New Austrian Tunnelling method |
New Austrian Tunnelling method (technology) The New Austrian Tunnelling method is so named. |
|
30 Nov 1961

Fields Prize in Mathematics |
Fields Prize in Mathematics (awards) Fields Prize in Mathematics: Lars Hörmander and John Milnor |
|
30 Nov 1961

Maxwell Medal and Prize |
Maxwell Medal and Prize (awards) Maxwell Medal and Prize of the Institute of Physics (first award): Abdus Salam |
|
26 Jan 1962

Ranger 3 |
Ranger 3 (astronomy and space ) Ranger 3 is launched to study the Moon. The space probe later misses the Moon by 22,000 miles. |
|
02 Feb 1962

Vaccination gun |
Vaccination gun In 1962, the USS Diamond Head set sail for Africa from Newport News, Va. Its passengers were medical workers equipped with the newly invented vaccination gun pistola de la paz ("pistol of peace"). Their mission was to conduct the first field trials of this invention of Robert Hingson. The "jet" injector, which enabled more efficient mass innoculation without need of needles and syringes and subsequently improved the health of millions of people. Hingson thought the most important benefit of the hypospray was that it did not frighten children undergoing vaccination nearly as much as did needles. Hingson was not only a pioneer in anaesthesiology, but also recognized for his humanitarian contributions to public health |
|
02 Feb 1962

Planets align |
Planets align In 1962, eight of the nine planets lined up for the first time in 400 years. |
|
04 Feb 1962

new moon |
new moon (astronomy and space ) During a new moon and total solar eclipse, an extremely rare grand conjunction of the classical planets occurs, including all five of the naked-eye planets plus the Sun and Moon, all within 16° of each another on the ecliptic. |
|
05 Feb 1962

Conjunction of the planets |
Conjunction of the planets In 1962, the Sun, the Moon, and the five naked-eye visible planets - Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn - were in conjunction. Though not in a straight line along their orbital paths, as viewed in the sky, they were within 16 degrees of each other (meaning all appeared within a circle just 16 º across). This conjunction coincided with a total solar eclipse, which made viewing Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn possible for a brief period of time from a small stretch of Earth where the eclipse's shadow hit. The five naked-eye visible planets cluster together in the sky within a circle 25 degrees or less in diameter once every 57 years, on average. The next time in the 21st century that this will happen is 8 Sep 2040. |
|
19 Feb 1962

Penumbral lunar eclipse |
Penumbral lunar eclipse (astronomy and space ) Penumbral lunar eclipse. |
|
19 Feb 1962

Georgios Papanikolaou |
death Georgios Papanikolaou Georgios Papanikolaou (born 1883), Greek American inventor of the Pap smear. |
|
20 Feb 1962

Mercury program |
Mercury program (astronomy and space ) Mercury program: While aboard Friendship 7, John Glenn orbits the Earth three times in 4 hours, 55 minutes, becoming the first American to do so. |
|
19 Mar 1962

Samuel Cate Prescott |
death Samuel Cate Prescott Samuel Cate Prescott (born 1872), American food scientist and microbiologist. |
|
24 Mar 1962

Auguste Piccard |
death Auguste Piccard Auguste Piccard (born 1884), Swiss physicist and explorer. |
|
26 Apr 1962

Ranger 4 |
Ranger 4 (astronomy and space ) The Ranger 4 spacecraft crashes into the Moon. |
|
27 Apr 1962

Edvard Moser |
birth Edvard Moser Edvard Moser, Norwegian neuroscientist, winner of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. |
|
01 May 1962

J. C. R. Licklider |
J. C. R. Licklider (computer science) J. C. R. Licklider of BBN co-presents a paper on "On-Line Man-Computer Communication". |
|
13 May 1962

Henry Trendley Dean |
death Henry Trendley Dean Henry Trendley Dean (born 1893), American dental researcher. |
|
24 May 1962

Scott Carpenter |
Scott Carpenter (astronomy and space ) Mercury program: Scott Carpenter becomes the second American to orbit the Earth aboard Aurora 7. |
|
01 Jun 1962

Rachel Carson |
Rachel Carson (ecology) Rachel Carson's Silent Spring begins serialization in The New Yorker. |
|
18 Jun 1962

Lisa Randall |
birth Lisa Randall Lisa Randall, American theoretical physicist. |
|
29 Jun 1962

George D. Zamka |
birth George D. Zamka George D. Zamka, American astronaut. |
|
11 Jul 1962

Telstar satellite |
Telstar satellite (astronomy and space ) First live transatlantic television broadcast from the United States to Britain, via AT&T's Telstar satellite (launched the previous day) and Goonhilly Satellite Earth Station. |
|
22 Jul 1962

Mariner program |
Mariner program (astronomy and space ) Mariner program: The Mariner 1 spacecraft flies erratically several minutes after launch and has to be destroyed. |
|
29 Jul 1962

Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher |
death Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher Died 29 Jul 1962 at age 72 (born 17 Feb 1890). British statistician, geneticist and evolutionary biologist whose contributions to statistical theory have become mainstays of modern statistical practice. In genetics, he established biometric genetics and studied dominance through breeding experiments with various animals). He developed methods of multivariate analysis to track the linkage of genes for different traits. To avoid introducing bias in the design of experiments that could produce inaccurate or misleading data, he applied his principle of randomization. While continuing his interest in statistics during his university coursework, he began his career as a high school teacher of mathematics (1914-19). During this time he published a paper (1918) applying statistics to yield a fundamental theorem of natural selection. He furthered his study of genetics at Rothamsted Experimental Station as a statistician in 1919. |
|
31 Jul 1962

Annular solar eclipse |
Annular solar eclipse (astronomy and space ) Annular solar eclipse. |
|
24 Aug 1962

Cosmonauts on Time cover |
Cosmonauts on Time cover In 1962, Russian cosmonauts Andian Nikolayev and Pavel Popvich (who flew the first 2-man mission in space) appeared on the cover of Time Magazine. |
|
19 Sep 1962

ICT 1301 |
ICT 1301 (computer science) The first ICT 1301 business mainframe sold, "Flossie", is installed at Senate House (University of London). It will still be operable 50 years later. |
|
20 Sep 1962

Jim Al-Khalili |
birth Jim Al-Khalili Jim Al-Khalili, Iraqi-born British theoretical physicist and science communicator. |
|
29 Sep 1962

Vandenberg Air Force Base |
Vandenberg Air Force Base (astronomy and space ) The Canadian Alouette 1, the first satellite built outside the United States or the Soviet Union, is launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. |
|
01 Oct 1962
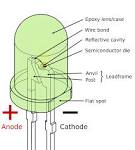
light-emitting diode |
light-emitting diode (technology) The first practical visible-spectrum (red) light-emitting diode is developed by Nick Holonyak, Jr., while working at the General Electric Company in Syracuse, New York. |
|
11 Oct 1962

Erich Tschermak von Seysenegg |
death Erich Tschermak von Seysenegg Died 11 Oct 1962 at age 90 (born 12 Nov 1871). Austrian agronomist who was one of three scientists who independently (as did Hugo de Vries and Carl Correns) rediscovered Gregor Mendel's work on the laws of genetics of the 1860's. Von Tschermak published his findings in June 1900. |
|
01 Nov 1962

John Charnley |
John Charnley (medicine) English orthopedic surgeon John Charnley makes the first successful whole hip replacement operation using a high molecular weight polyethylene (HMWP) socket, at Wrightington Hospital, Wigan. |
|
03 Nov 1962

personal computer |
personal computer (computer science) The earliest recorded use of the term "personal computer" features in The New York Times in a story about John Mauchly's speech the day before to the American Institute of Industrial Engineers. Mauchly, "inventor of some of the original room-size computers", says that "in a decade or so" everyone would have their own computer with "exchangeable wafer-thin data storage files to provide inexhaustible memories and answer most problems". He is quoted as saying, "There is no reason to suppose the average boy or girl cannot be master of a personal computer." |
|
18 Nov 1962

Niels Bohr |
death Niels Bohr Niels Bohr (born 1885), Danish physicist. |
|
07 Dec 1962
Atlas |
Atlas (computer science) The Atlas supercomputer, the most powerful in the world at this date, is dedicated at the University of Manchester in England. It is the first system designed for multiprogramming, and will be in use for the next decade. |
|
20 Dec 1962

Emil Artin |
death Emil Artin Emil Artin (born 1898), Austrian-born mathematician. |
|
24 Dec 1962

Wilhelm Ackermann |
death Wilhelm Ackermann Wilhelm Ackermann (born 1896), German mathematician. |