| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1975

Richard Dawkins |
Richard Dawkins (biology) Richard Dawkins publishes The Selfish Gene |
|
30 Nov 1975

Endo |
Endo (chemistry) Oberlin, Endo and Koyama publish evidence of the creation of carbon nanotubes using a vapor-growth technique. |
|
30 Nov 1975

Whitfield Diffie |
Whitfield Diffie (cryptography) An asymmetric-key cryptosystem is published by Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman who disclose the Diffie–Hellman key exchange method of public-key agreement for public-key cryptography. |
|
30 Nov 1975

Jean Gimpel |
Jean Gimpel (history of science a) Jean Gimpel's The Medieval Machine is published. |
|
30 Nov 1975

Imre Lakatos |
Imre Lakatos (mathematics) Imre Lakatos' Proofs and Refutations: the Logic of Mathematical Discovery is published posthumously. |
|
30 Nov 1975

four color theorem |
four color theorem (mathematics) The four color theorem is proved by Kenneth Appel and Wolfgang Haken, the first major theorem to be proved using a computer. |
|
30 Nov 1975
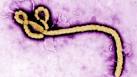
Ebola virus |
Ebola virus (physiology, medicine) The Ebola virus first emerges in outbreaks of Ebola hemorrhagic fever in Zaire and Sudan. |
|
30 Nov 1975

John Money |
John Money (physiology, medicine) The term Münchausen syndrome by proxy is first coined by John Money and June Faith Werlwas. |
|
30 Nov 1975

Norman F. Dixon |
Norman F. Dixon (physiology, medicine) Norman F. Dixon publishes On the Psychology of Military Incompetence. |
|
30 Nov 1975

Turing Award |
Turing Award (awards) Turing Award – Michael O. Rabin, Dana Scott |
|
01 Jan 1976

Cray-1 |
Cray-1 (computer science) The Cray-1, the first commercially developed supercomputer, is released by Seymour Cray's Cray Research. |
|
19 Jan 1976

Hidetsugu Yagi |
death Hidetsugu Yagi Hidetsugu Yagi (b. 1886), Japanese electrical engineer |
|
21 Jan 1976

Concorde |
Concorde (aviation) Concorde begins commercial flights. |
|
01 Mar 1976

Peter Chen |
Peter Chen (computer science) Peter Chen's key paper on the entity–relationship model is published, having first been presented at a conference in September 1975. |
|
01 Apr 1976

Apple Computer |
Apple Computer (computer science) Apple Computer Company is formed by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak and the latter begins assembling its first personal computer hobbyists kits for sale later in the year in the U.S. |
|
21 Apr 1976

Carl Benjamin Boyer |
death Carl Benjamin Boyer Carl Benjamin Boyer (b. 1906), American historian of mathematics. |
|
31 May 1976

Jacques Monod |
death Jacques Monod Jacques Monod (b. 1910), French biochemist, winner of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1965. |
|
18 Jun 1976

Gravity Probe A |
Gravity Probe A (astronomy and space ) Gravity Probe A, a satellite-based experiment to test Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity, is launched. |
|
11 Jul 1976

Keuffel and Esser |
Keuffel and Esser (mathematics) Keuffel and Esser manufacture the last slide rule in the United States. |
|
20 Jul 1976

Viking program |
Viking program (astronomy and space ) Viking program: The Viking 1 lander successfully lands on Mars. |
|
31 Jul 1976

NASA |
NASA (astronomy and space ) NASA releases the famous 'Face on Mars' photograph, taken by Viking 1 |
|
18 Aug 1976

Shintaro Uda |
death Shintaro Uda Shintaro Uda (b. 1886), Japanese electrical engineer. |
|
22 Aug 1976

Luna program |
Luna program (astronomy and space ) Luna program: Luna 24 successfully makes an unmanned landing on the Moon, the last for 37 years. |
|
17 Sep 1976

Space Shuttle Enterprise |
Space Shuttle Enterprise (astronomy and space ) Space Shuttle Enterprise rolled out. |
|
03 Oct 1976

Smithsonian Institution |
Smithsonian Institution (history of science a) Opening of the Dibner Library of the History of Science and Technology at the Smithsonian Institution's National Museum of History and Technology in Washington, D.C. |
|
05 Oct 1976

Lars Onsager |
death Lars Onsager Lars Onsager (b. 1903), Norwegian American chemist. |
|
05 Nov 1976

Willi Hennig |
death Willi Hennig Willi Hennig (b. 1913), German entomologist and pioneer of cladistics. |
|
19 Nov 1976

Jack Dorsey |
birth Jack Dorsey Jack Dorsey, American web developer |
|
20 Nov 1976

Trofim Denisovich Lysenko |
death Trofim Denisovich Lysenko Died 20 Nov 1976 at age 78 (born 29 Sep 1898). Soviet biologist and agronomist who not only believed the Mendelian theory of heredity to be wrong, but with Stalin's support for two decades actively obstructed the course of Soviet biology. He caused the imprisonment and death of many of the country's eminent biologists. He followed I. V. Michurin's fanciful idea that plants could be forced to adapt to any environmental conditions, for example converting summer wheat to winter wheat by storing the seeds in ice. As director of the Institute of Genetics of the Soviet Academy of Sciences (1940-65) his interference contributed to the disastrous decline of Soviet agriculture. After Stalin's death in 1956, he lost support and eventually in 1965 was exiled to an experimental farm. |
|
26 Nov 1976

Microsoft |
Microsoft (computer science) Little-known company Microsoft is officially registered with the Office of the Secretary of State of New Mexico. |
|
01 Dec 1976

Electric Pencil |
Electric Pencil (computer science) Release of Electric Pencil (originated by Michael Shrayer), the first word processor for home computers. |
|
08 Dec 1976

General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon |
General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon (aviation) First flight of production General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon. |