| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1982

Derek Freeman |
Derek Freeman (anthropology) New Zealand anthropologist Derek Freeman publishes Margaret Mead and Samoa: The Making and Unmaking of an Anthropological Myth, critical of Coming of Age in Samoa (1928) by Margaret Mead (d. 1978). |
|
30 Nov 1982

US Federal Government |
US Federal Government (computer science) The US Federal Government standardizes Ada (programming language), a strongly typed, comb-structured computer language, with exception handlers, for general-purpose programming. |
|
30 Nov 1982
Word processor |
Word processor (computer science) Word processor software Multi-Tool Word, soon to become Microsoft Word, is released. Free demonstration copies on disk are distributed with the November issue of PC World magazine. |
|
30 Nov 1982

Keith Thomas |
Keith Thomas (history of science) Keith Thomas publishes Man and the Natural World: changing attitudes in England, 1500–1800. |
|
30 Nov 1982

Daniel Gorenstein |
Daniel Gorenstein (mathematics) Daniel Gorenstein (with Richard Lyons) proves the trichotomy theorem for finite simple groups of characteristic 2 type and rank at least 4, and announces that proof of the classification of finite simple groups is complete (although that for quasithin groups has not been demonstrated at this time). |
|
30 Nov 1982

Spain |
Spain (organizations) Spain re-joins CERN after having left in 1969 (originally joined for the first time in 1961). |
|
30 Nov 1982

Turing Award |
Turing Award (awards) Turing Award – Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie |
|
30 Nov 1982

Bruce Irons |
death Bruce Irons December 6 - Bruce Irons, engineer |
|
01 Jan 1983

ARPANET |
ARPANET (computer science) The ARPANET officially changes to use the Internet Protocol, creating the Internet. |
|
05 Feb 1983

Harry G. Armstrong |
death Harry G. Armstrong Died 5 Feb 1983 at age 83 (born 17 Feb 1899). American physician who, on 18 May 1935, was appointed Chief of the Physiological Research Laboratory, Wright Field, Ohio, and during a distinguished career there made great contributions to aviation medicine giving last benefits to flying safety and mission effectiveness of pilots. |
|
27 Feb 1983

Nikolai Aleksandrovich Kozyrev |
death Nikolai Aleksandrovich Kozyrev Nikolai Aleksandrovich Kozyrev, Russian astronomer and astrophysicist (b. 1908) |
|
18 Mar 1983

Ivan Vinogradov |
death Ivan Vinogradov Ivan Vinogradov, Russian mathematician (b. 1891) |
|
01 Apr 1983

Kary Mullis |
Kary Mullis (biology) Kary Mullis discovers polymerase chain reaction. |
|
25 Apr 1983

Pioneer 10 beyond Pluto orbit |
Pioneer 10 beyond Pluto orbit In 1983, Pioneer 10 crossed the orbit of Pluto, the outermost planet, to continue its voyage into the universe beyond our solar system |
|
30 Apr 1983

Joel H. Hildebrand |
death Joel H. Hildebrand Died 30 Apr 1983 at age 101 (born 16 Nov 1881). U.S. educator and chemist whose monograph Solubility (1924; later editions, Solubility of Non-Electrolytes) was the classic reference for almost a half century. The Hildebrand solubility parameter carries his name. Through his research on the chemistry of solutions, he helped to protect deep-sea divers from “bends.” He led the fight against a faculty “loyalty oath,” a non-Communist declaration, at University of California (1950). He had no sympathy with Communists, but he and other prominent members of the faculty felt that the oath, by being required of teachers alone, was discriminatory with regard to all university employees. Two years later, the California State Supreme Court decided unanimously in favour of the faculty. |
|
20 May 1983

HIV |
HIV (biology) First reports of HIV as a possible cause of AIDS, by independent virology teams led by Luc Montagnier and Robert Gallo. |
|
22 May 1983

Albert Claude |
death Albert Claude Albert Claude, Belgian biologist, co-recipient of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1974 (b. 1898) |
|
01 Jun 1983
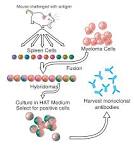
monoclonal antibody |
monoclonal antibody (biology) First report of using a monoclonal antibody as a medical test. |
|
13 Jun 1983

Neptune |
Neptune (astronomy and space ) Pioneer 10 passes the orbit of Neptune, becoming the first man-made object to travel beyond the major planets of the solar system. |
|
22 Jun 1983

Sir Christopher Hinton |
death Sir Christopher Hinton Died 22 Jun 1983 at age 82 (born 12 May 1901). (Baron of Bankside) English engineer who was a leading figure in the development of the nuclear energy industry in Britain; he supervised the construction of Calder Hall, the world's first large-scale nuclear power station (opened in 1956). He first worked for Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) where at age 29 he was appointed chief engineer of the Alkali Groups. While at ICI he was selected to start building nuclear power plants. Britain's first four such plants were completed in six years. He played a founding role in fast breeder technology. The decision to build the Dounreay Fast Reactor was made in 1954, which ran successfully for over two decades, until its planned shutdown in 1977, thus demonstrating the safe operation of the concept. |
|
01 Jul 1983
type I |
type I (biology) Determination of the first sequences of type I and type II keratins and prediction of the α-helical domain structure of intermediate filament proteins. |
|
07 Jul 1983

Herman Kahn |
death Herman Kahn Died 7 Jul 1983 at age 61 (born 15 Feb 1922). American physicist who worked on nuclear strategy as a military analyst (1948-61). Later, he became known as a futurist making controversial studies of nuclear warfare in his books, including his provocative analysis of nuclear war in On Thermonuclear War (1960) and his predictions of the probability and survivability of nuclear war in Thinking About the Unthinkable (1962). He held that since it might be possible to survive a nuclear war, it was essential to plan to do just that. Kahn founded the influential Hudson Institute in New York in 1961 to study aspects of national security related to narcotics policy, international economics and trade, population, transportation, crime, medicine. |
|
01 Aug 1983

MIDI 1.0 |
MIDI 1.0 (computer science) MIDI 1.0 specification for a Musical Instrument Digital Interface (originally devised by Dave Smith of Sequential Circuits) published. |
|
02 Aug 1983

Edmund Jaeger |
death Edmund Jaeger Edmund Jaeger, American naturalist (b. 1887) |
|
26 Sep 1983

Baikonur Cosmodrome |
Baikonur Cosmodrome (astronomy and space ) The Soyuz T-10-1 mission ends in a pad abort at the Baikonur Cosmodrome, when a pad fire occurs at the base of the Soyuz U rocket during the launch countdown. The escape tower system, attached to the top of the capsule containing the crew and Soyuz spacecraft, fires immediately pulling the crew safe from the vehicle, a few seconds before the rocket explodes, destroying the launch complex. |
|
27 Sep 1983

Richard Stallman |
Richard Stallman (computer science) Richard Stallman announces the GNU Project. |
|
11 Oct 1983

Telephone |
Telephone In 1983, the last hand-cranked (magneto) telephones in the United States went out of service as 440 telephone customers in Bryant Pond, Maine, were switched to direct-dial service. Prior to that time a resident's number could be as short as 33. Those living close enough to the telephone office might get to answer the phone, even if they were outside because the operator could just yell out the window! The last hand-cranked telphone call in Bryant pond was made the following day, on 12 Oct 1983. |
|
21 Oct 1983

General Conference on Weights and Measures |
General Conference on Weights and Measures (metrology) At the seventeenth General Conference on Weights and Measures, the length of a metre is redefined as the distance light travels in vacuum in 1/299,792,458 of a second. |
|
26 Oct 1983

Alfred Tarski |
death Alfred Tarski Alfred Tarski, Polish American logician and mathematician (b. 1901) |
|
10 Nov 1983

Fred Cohen |
Fred Cohen (computer science) Fred Cohen demonstrates a self-replicating source code which his academic adviser at the University of Southern California, Leonard Adleman, likens to a virus. |
|
19 Nov 1983

Reinout Willem van Bemmelen |
death Reinout Willem van Bemmelen Died 19 Nov 1983 at age 79 (born 14 Apr 1904). Dutch geologist whose studies of the regional geology of Indonesia led to recognition of the importance of island areas in the development of the Earth's crust. Long before others even thought about compiling an article on this archipelagos, he published his biggest contribution, the Geology of Indonesia (1949). Still often cited, this book covers broad aspects of the regional geology of Indonesia, which is prolific in terms of hydrocarbon and other mineral resources. Indonesia is part of the volcanic “ring of fire” and one of the most complex geological settings in the world because it lies at the junction of three major tectonic plates (Pacific, Indian-Australian, and Eurasian). He also researched continental drift and the winds of the equatorial stratosphere. |
|
01 Dec 1983

Yugoslav |
Yugoslav (computer science) Yugoslav popular science magazine Galaksija releases a special (January 1984) issue, Računari u vašoj kući, with complete instructions on how to build a full-featured home computer, Galaksija. |