| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1986

Asteroid 7816 Hanoi |
Asteroid 7816 Hanoi (astronomy) Asteroid 7816 Hanoi is discovered by Masahiro Koishikawa. |
|
30 Nov 1986

10500 Nishi-koen |
10500 Nishi-koen (astronomy) 10500 Nishi-koen is discovered. |
|
30 Nov 1986

Robert V. Bruce |
Robert V. Bruce (history of science) Robert V. Bruce publishes The Launching of Modern American Science, 1846–1876. |
|
30 Nov 1986

Gödel's ontological proof |
Gödel's ontological proof (mathematics) Gödel's ontological proof of the existence of God is published posthumously. |
|
30 Nov 1986

Ben Carson |
Ben Carson (medicine) September 5 - The first successful surgical separation of craniopagus twins is done by Dr. Ben Carson. |
|
30 Nov 1986

Turing Award |
Turing Award (awards) Turing Award – John Cocke |
|
30 Nov 1986

Wollaston Medal for Geology |
Wollaston Medal for Geology (awards) Wollaston Medal for Geology – Claude Jean Allègre |
|
01 Jan 1987
Mitochondrial Eve |
Mitochondrial Eve (paleoanthropology) The 'Mitochondrial Eve' hypothesis is proposed. |
|
23 Feb 1987

Supernova |
Supernova In 1987, supernova 1987A in LMC was first seen. The brightest of the twentieth century, it was the first supernova visible with the naked eye since 1604. |
|
23 Feb 1987

Supernova 1987a |
Supernova 1987a (astronomy) Supernova 1987a is observed, the first "naked-eye" supernova since 1604. |
|
18 Mar 1987

Woodstock of physics |
Woodstock of physics (physics) Woodstock of physics, the marathon session of the American Physical Society’s meeting featuring 51 presentations concerning the science of high-temperature superconductors. |
|
19 Mar 1987

Louis de Broglie |
death Louis de Broglie Louis de Broglie (b. 1892), French physicist and winner of the Nobel Prize in Physics (1929). |
|
20 Mar 1987

Food and Drug Administration |
Food and Drug Administration (medicine) The United States Food and Drug Administration approves anti-AIDS drug AZT. |
|
26 Mar 1987

Gwyn Macfarlane |
death Gwyn Macfarlane Gwyn Macfarlane (b. 1907), British hematologist. |
|
11 May 1987
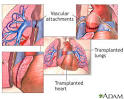
heart-lung transplant |
heart-lung transplant (medicine) The first heart-lung transplant takes place. |
|
19 May 1987

Keeping a head alive |
Keeping a head alive In 1987, a patent for "keeping a head alive" was issued to Chet Fleming (U.S. No. 4,666,425). A cabinet provides physical and biochemical support for an animal's head severed from its body. Oxygenated blood and nutrients are circulated by means of tubes connected to arteries and veins that emerge from the neck. A series of processing components removes carbon dioxide and add oxygen to the blood. If desired, waste products and other metabolites may be removed from the blood, and nutrients, therapeutic or experimental drugs, anti-coagulants, and other substances may be added to the blood. After being thoroughly tested on research animals, the patent suggests it might also be used on humans suffering from various terminal illnesses. |
|
17 Jun 1987

Dusky Seaside Sparrow |
Dusky Seaside Sparrow (zoology) The last known purebred Dusky Seaside Sparrow, "Orange Band", dies in Florida. |
|
03 Jul 1987

Transatlantic hot-air balloon crossing |
Transatlantic hot-air balloon crossing In 1987, British millionaire Richard Branson and Per Lindstrand became the first to cross the Atlantic by hot-air balloon, named Virgin Atlantic Flyer. They jumped into the sea as their craft went down off the Scottish coast. They travelled a distance of 2,900 miles from from Sugarloaf Mountain, Maine, in 33 hours to set a new record for hot air ballooning. At the time, the balloon was the largest ever flown having 2.3 million cubic feet of capacity. Three years later, they crossed the Pacific in another balloon from Japan to Arctic Canada, a distance of 6,700 miles, breaking all existing records with speeds of up to 245 miles per hour. |
|
31 Aug 1987
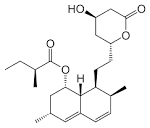
statin |
statin (medicine) The FDA for the first time approves a statin, lovastatin. |
|
13 Oct 1987

Walter H. Brattain |
death Walter H. Brattain Died 13 Oct 1987 at age 85 (born 10 Feb 1902). Walter Houser Brattain was an American physicist who shared (with John Bardeen and William B. Shockley) the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1956 for investigating semiconductors (materials of which transistors are made) and for the development of the transistor. At college, he said, he majored in physics and math because they were the only subjects he was good at. He became a solid physicist with a good understanding of theory, but his strength was in physically constructing experiments. Working with the ideas of Shockley and Bardeen, Brattain's hands built the first transistor. Shortly, the transistor replaced the bulkier vacuum tube for many uses and was the forerunner of microminiature electronic parts. |
|
13 Oct 1987

Walter Houser Brattain |
death Walter Houser Brattain Walter Houser Brattain (b. 1902), American physicist. |
|
20 Oct 1987

Andrey Kolmogorov |
death Andrey Kolmogorov Andrey Kolmogorov (b. 1903), Russian mathematician. |
|
06 Nov 1987

rapist |
rapist (genetics) Florida rapist Tommy Lee Andrews is the first person to be convicted as a result of DNA fingerprinting. |
|
01 Dec 1987
Channel Tunnel |
Channel Tunnel (technology) Channel Tunnel digging commences. |
|
02 Dec 1987

Yakov Borisovich Zel'dovich |
death Yakov Borisovich Zel'dovich Yakov Borisovich Zel'dovich (b. 1914), Belarusian astrophysicist. |
|
07 Dec 1987

Helen Porter |
death Helen Porter Helen Porter (b. 1899), English plant physiologist. |
|
22 Dec 1987

Genetics |
Genetics In 1987, U.S. scientists say a single gene may decide the sex of a baby. |
|
29 Dec 1987

Record stay in space |
Record stay in space In 1987, cosmonaut Yuri Romanenko return to Earth, ending his record 326-day space flight orbiting Earth in the Mir space station. The Soyuz spacecraft landed at a snow-covered site in Kazakhstan. His stay in space broke the previous Soviet record of 237 days. For comparison, the U.S. space endurance record is 87 days. Romanenko rocketed into orbit 6 Feb 1987 with flight engineer Alexander Laveikin who suffered heart problems five months later and was replaced with Alexander Alexandrov. They conducted 1,000 experiments in biology, medicine, materials processing and geology. Romanenko and Alexandrov used the giant Kvant (Quantum) astrophysics laboratory attached to the Mir to collect data from remote parts of the solar system. In a total of 3 space missions he accumulated 430.76 days in space. |