| Date | Text | |
|---|---|---|
30 Nov 1985

Internet Message Access Protocol |
Internet Message Access Protocol (computer science) Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) is visualized by Mark Crispin. |
|
30 Nov 1985

3D printing |
3D printing (computer science) 3D printing is developed by Charles Hull. |
|
30 Nov 1985

Kenneth Alan Ribet |
Kenneth Alan Ribet (mathematics) Kenneth Alan Ribet demonstrates proof of the ε-conjecture, subsequently known as Ribet's theorem confirming Gerhard Frey's suggestion that the Taniyama–Shimura conjecture implies Fermat's Last Theorem. |
|
30 Nov 1985

Lee Sallows |
Lee Sallows (mathematics) Lee Sallows introduces the alphamagic square. |
|
30 Nov 1985

Food and Drug Administration |
Food and Drug Administration (medicine) Food and Drug Administration approval of the first monoclonal antibody drug, Muronomab-CD3 (also known as Orthoclone OKT3), for treatment of transplant rejection. |
|
30 Nov 1985

Crafoord Prize in Geosciences |
Crafoord Prize in Geosciences (awards) Crafoord Prize in Geosciences: Gerald Wasserburg and Claude Jean Allègre |
|
30 Nov 1985

Fields Prize in Mathematics |
Fields Prize in Mathematics (awards) Fields Prize in Mathematics: Simon Donaldson, Gerd Faltings and Michael Freedman |
|
30 Nov 1985

Turing Award |
Turing Award (awards) Turing Award – John Hopcroft, Robert Tarjan |
|
30 Nov 1985

Wollaston Medal for Geology |
Wollaston Medal for Geology (awards) Wollaston Medal for Geology – Claude Jean Allègre |
|
07 Jan 1986

Rex Wailes |
death Rex Wailes Rex Wailes (b. 1901), English engineer and historian of technology. |
|
19 Jan 1986
MS-DOS |
MS-DOS (computer science) The first MS-DOS-based personal computer virus, Brain, starts to spread. |
|
24 Jan 1986

Uranus |
Uranus In 1986, the Voyager II space probe made closest approach to Uranus. The spacecraft came within 81,500-km (50,600 miles) of Uranus's cloudtops. The probe radioed thousands of images and great amounts of other scientific data on the planet, its moons, rings, atmosphere, interior and the magnetic environment surrounding Uranus. Its images of the five largest moons around Uranus revealed complex surfaces indicative of varying geologic pasts. The cameras also detected 10 previously unseen moons. It also studied the fine detail of the ring system and newly discovered two more rings. Launched on 20 Aug 1977, Voyager II earlier visited Jupiter and Saturn. After Uranus, it travelled on to Neptune and eventually interstellar space. |
|
24 Jan 1986

Voyager 2 |
Voyager 2 (astronomy and space ) Voyager 2 space probe makes first encounter with Uranus. |
|
28 Jan 1986

Space Shuttle Challenger |
Space Shuttle Challenger (astronomy and space ) Space Shuttle Challenger explodes on launch, killing all seven astronauts aboard. Their bodies are located by United States Navy divers on March 9. |
|
19 Feb 1986

Soviet Union |
Soviet Union (astronomy and space ) The Soviet Union launches the Mir space station. |
|
08 Mar 1986

Suisei |
Suisei (astronomy and space ) Japanese spacecraft Suisei flies by Halley's Comet, studying its UV hydrogen corona and solar wind. |
|
03 Apr 1986

IBM |
IBM (computer science) IBM unveils the PC Convertible, the first laptop computer. |
|
22 Apr 1986

Honor Fell |
death Honor Fell Dame Honor Fell (b. 1900), English biologist. |
|
01 May 1986
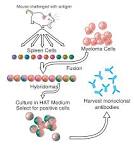
monoclonal antibody |
monoclonal antibody (biology) First reported methods for constructing a monoclonal antibody containing parts from mouse and human antibodies, a required first step toward the development of humanized antibodies used later as medical therapeutics (such as Infliximab). |
|
23 Jun 1986
LISTSERV |
LISTSERV (computer science) Eric Thomas develops LISTSERV, the first email list management software. |
|
18 Jul 1986

Titanic explored |
Titanic explored In 1986, videotapes, taken by the deep-sea Alvin submersible, showing Titanic's remains were released. Looking like huge stalagmites rusticles ("rust icicles"), are a byproduct of the bacteria slowly converting the iron in the hull. The colony of iron-eating bacteria flourish in the anaerobic (without oxygen) environment inside the hollow multi-layered rusticles while on the outside, porous layers support oxygen-dependent bacteria. In this eerie way, there is still life on the Titanic as the ship lies deep on the ocean floor. |
|
21 Jul 1986

Zhang Yuzhe |
death Zhang Yuzhe Zhang Yuzhe (b. 1902), Chinese astronomer. |
|
22 Oct 1986

Albert Szent-Györgyi |
death Albert Szent-Györgyi Albert Szent-Györgyi (b. 1893), Hungarian physiologist, winner of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. |
|
23 Oct 1986

Edward Adelbert Doisy |
death Edward Adelbert Doisy Edward Adelbert Doisy (b. 1893), American biochemist, winner of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. |
|
25 Nov 1986

Ivan Magill |
death Ivan Magill Sir Ivan Magill (b. 1888), British anesthesiologist. |
|
08 Dec 1986

Harrison Brown |
death Harrison Brown Died 8 Dec 1986 at age 69 (born 26 Sep 1917). Harrison (Scott) Brown was an American geochemist known for his role in isolating plutonium for its use in the first atomic bombs and for his studies regarding meteorites and the Earth's origin. He was one of 67 concerned Manhattan Project scientists at Oak Ridge to sign a July 1945 petition to the President, which said, in part, "...Therefore we recommend that before this weapon be used without restriction in the present conflict, its powers should be adequately described and demonstrated, and the Japanese nation should be given the opportunity to consider the consequences of further refusal to surrender." His later studies included mass spectroscopy, thermal diffusion, fluorine and plutonium chemistry, geochemistry and planetary structure. |